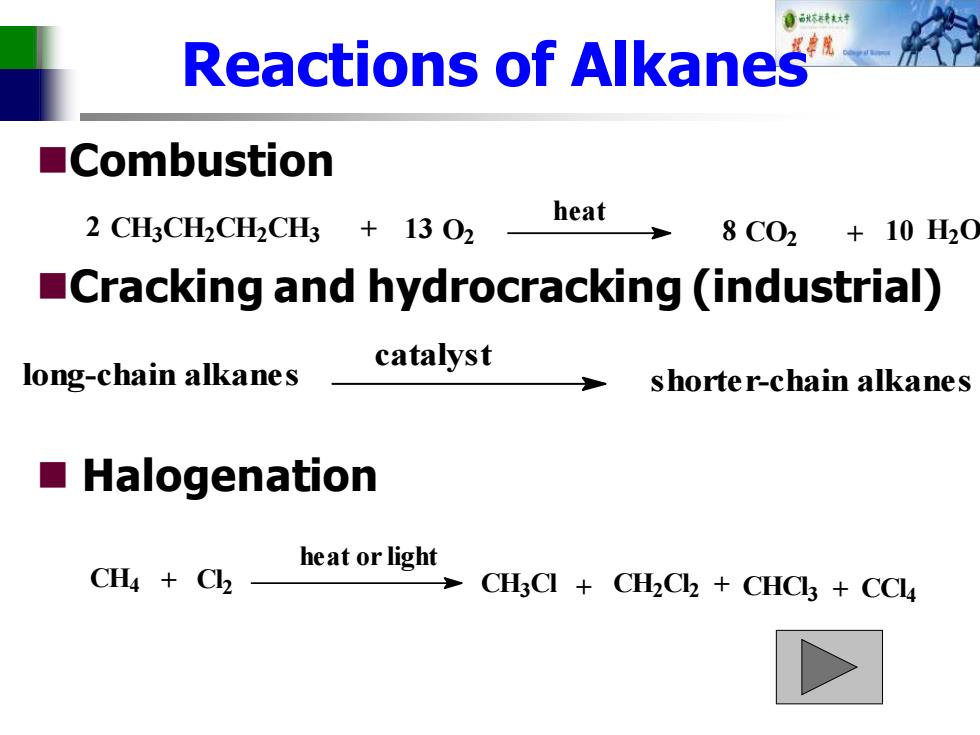
自秋标转对 Reactions of Alkanes ■Combustion 2 CH3CH2CH2CH3 13 O2 heat 8C02+10H20 Cracking and hydrocracking (industrial) catalyst long-chain alkanes shorter-chain alkanes Halogenation heat or light CH4 Cl CHCI+CHC2+CHC+CC4
Reactions of Alkanes ◼Combustion ◼Cracking and hydrocracking (industrial) ◼ Halogenation CH3CH2CH2CH3 + O2 CO2 + H2O heat 2 13 8 10 long-chain alkanes catalyst shorter-chain alkanes CH4 + Cl 2 CH3Cl + CH2Cl 2 CHCl 3 CCl 4 + + heat or light

自秋转对 #忧 Petroleum Refining ■Cracking >converts high molecular weight hydrocarbons to more useful,low molecular weight ones ■Reforming >increases branching of hydrocarbon chains >branched hydrocarbons have better burning characteristics for automobile engines
Petroleum Refining ◼Cracking ➢converts high molecular weight hydrocarbons to more useful, low molecular weight ones ◼Reforming ➢increases branching of hydrocarbon chains ➢branched hydrocarbons have better burning characteristics for automobile engines
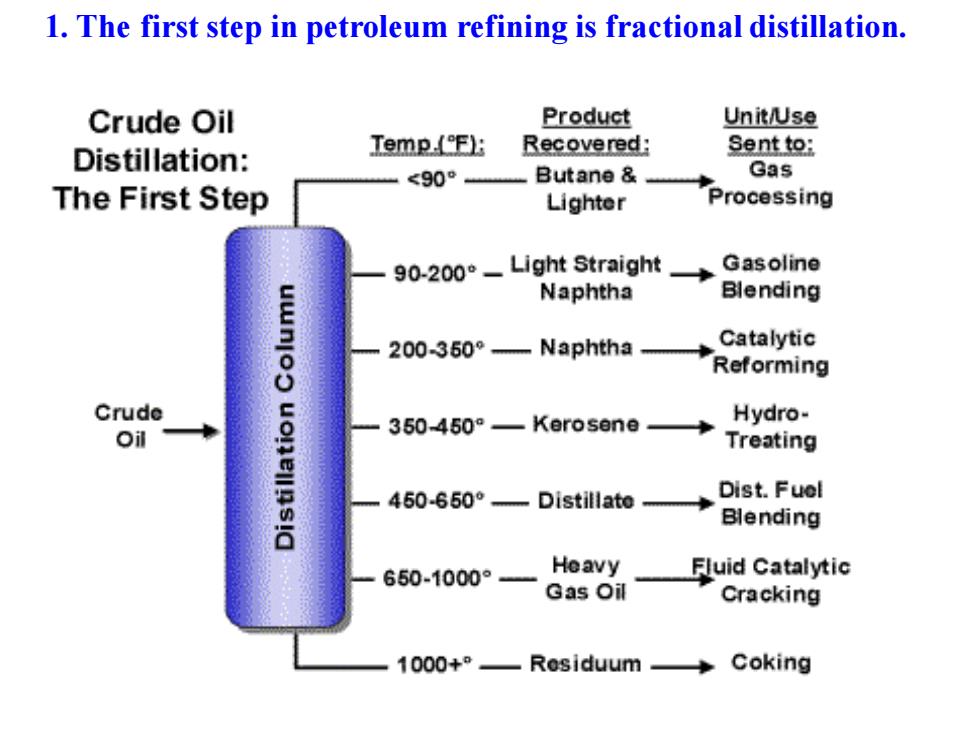
1.The first step in petroleum refining is fractional distillation. Crude Oil Product Unit/Use Distillation: Temp(F): Recovered: Sentto: <90° Butane Gas The First Step Lighter Processing 90-200°- Light Straight Gasoline Naphtha Blending 200360°-Naphtha Catalytic Reforming Crude Oil 350-450°-Kerosene Hydro- Treating 450-650°-Distillate Dist.Fuel Blending 650-1000° Heavy Fluid Catalytic Gas Oil Cracking 1000+0- Residuum Coking
1. The first step in petroleum refining is fractional distillation
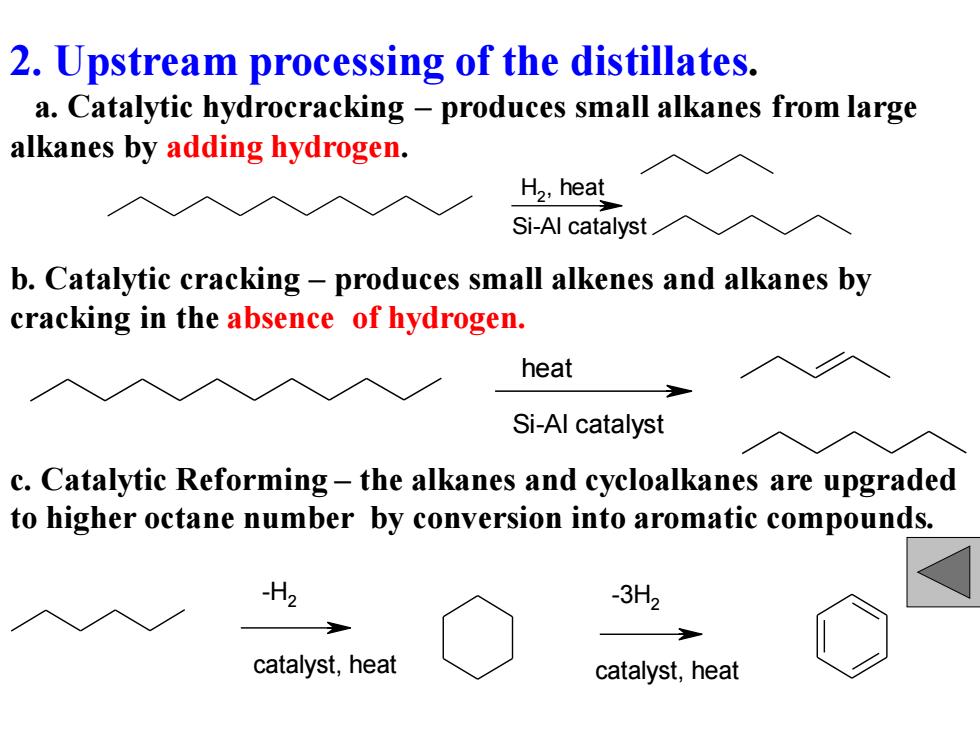
2.Upstream processing of the distillates. a.Catalytic hydrocracking-produces small alkanes from large alkanes by adding hydrogen. H2,heat Si-Al catalyst b.Catalytic cracking-produces small alkenes and alkanes by cracking in the absence of hydrogen. heat Si-Al catalyst c.Catalytic Reforming-the alkanes and cycloalkanes are upgraded to higher octane number by conversion into aromatic compounds. H2 3H2 catalyst,heat catalyst,heat
2. Upstream processing of the distillates. a. Catalytic hydrocracking – produces small alkanes from large alkanes by adding hydrogen. H2 , heat Si-Al catalyst b. Catalytic cracking – produces small alkenes and alkanes by cracking in the absence of hydrogen. heat Si-Al catalyst c. Catalytic Reforming – the alkanes and cycloalkanes are upgraded to higher octane number by conversion into aromatic compounds. -3H2 -H2 catalyst, heat catalyst, heat

自秋标转材 Questions Light CH4+CI-CI H-CI CH3CI CH2Cl2+CHCl3+CCl CH3CH3 CH2CICH2CI+....... Requires heat or light for initiation. The most effective wavelength is blue, which is absorbed by chlorine gas. Lots of product formed from absorption of only one photon of light (chain reaction). ■The Mechanisms? Relative Reactivities?
Questions ◼ Requires heat or light for initiation. ◼ The most effective wavelength is blue, which is absorbed by chlorine gas. ◼ Lots of product formed from absorption of only one photon of light (chain reaction). ◼The Mechanisms? ◼Relative Reactivities? + Cl - Cl Light + CH3Cl + CH2Cl 2 + CHCl 3 + CCl 4 CH3CH3 + CH2ClCH2Cl + ....... CH4 H - Cl