
Organic Chemistry,6th Edition L.G.Wade,Jr. Chapter 23 Condensation and Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds
Chapter 23 Condensation and Alpha Substitution of Carbonyl Compounds Organic Chemistry, 6th Edition L. G. Wade, Jr
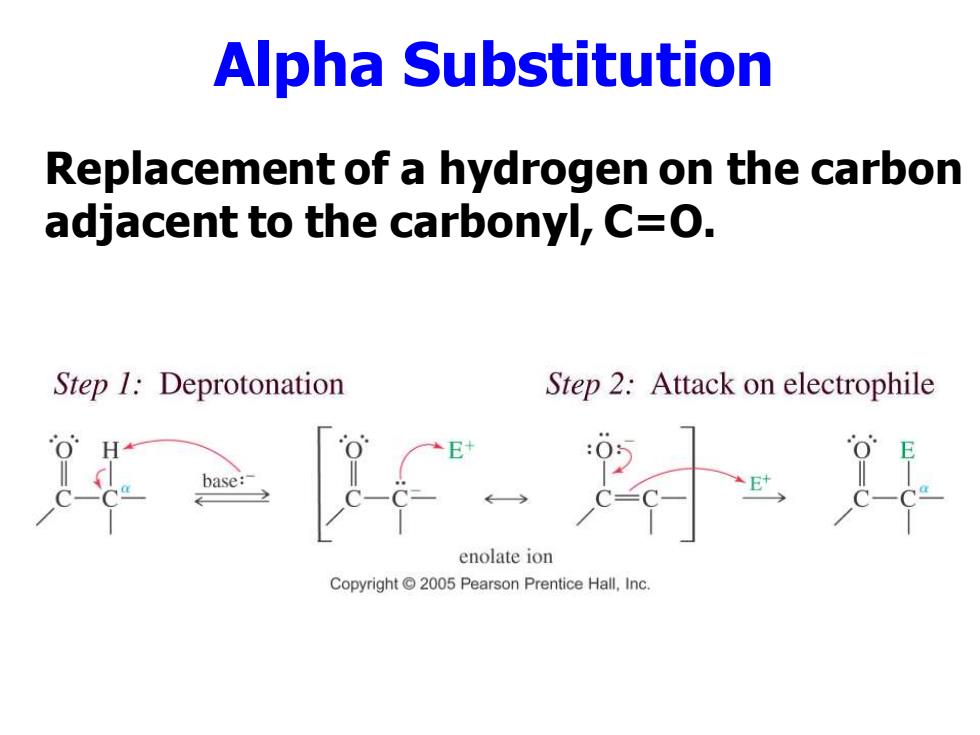
Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl,C=O. Step 1:Deprotonation Step 2:Attack on electrophile base: enolate ion Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Alpha Substitution Replacement of a hydrogen on the carbon adjacent to the carbonyl, C=O
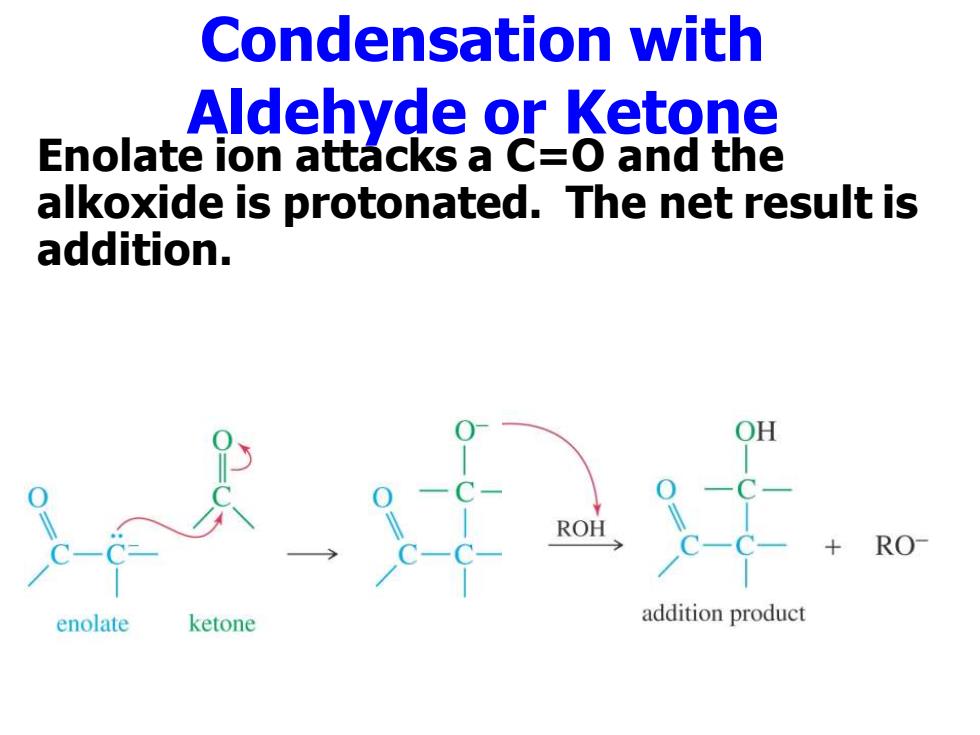
Condensation with Aldehyde or Ketone Enolate ion attacks a C=O and the alkoxide is protonated.The net result is addition. RO enolate ketone addition product
Condensation with Aldehyde or Ketone Enolate ion attacks a C=O and the alkoxide is protonated. The net result is addition
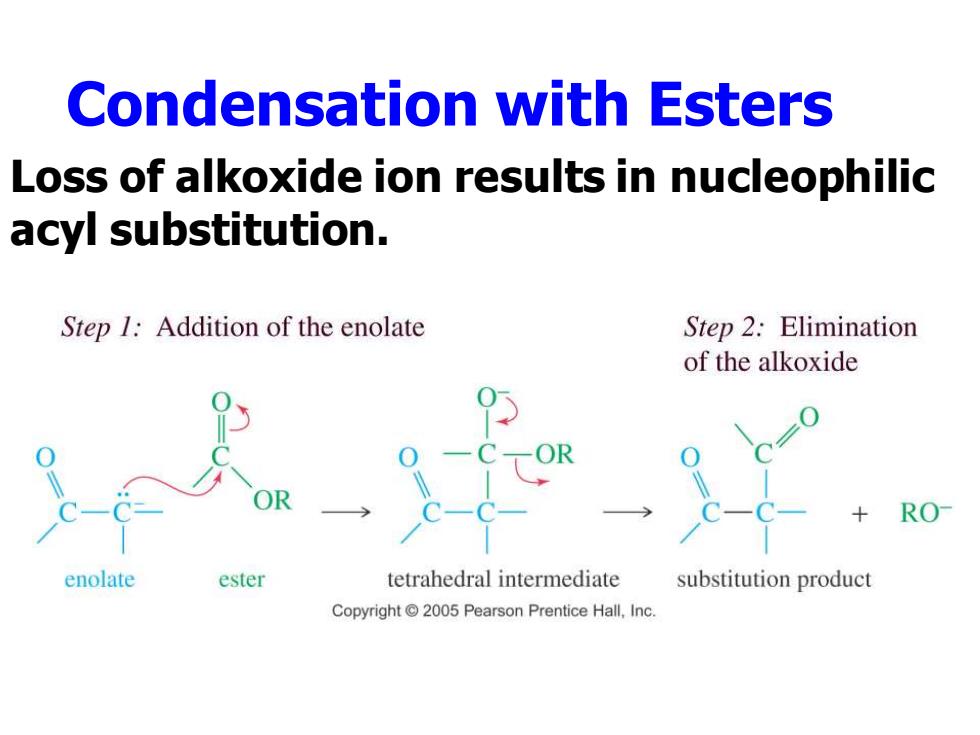
Condensation with Esters Loss of alkoxide ion results in nucleophilic acyl substitution. Step 1:Addition of the enolate Step 2:Elimination of the alkoxide RO enolate ester tetrahedral intermediate substitution product Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Condensation with Esters Loss of alkoxide ion results in nucleophilic acyl substitution
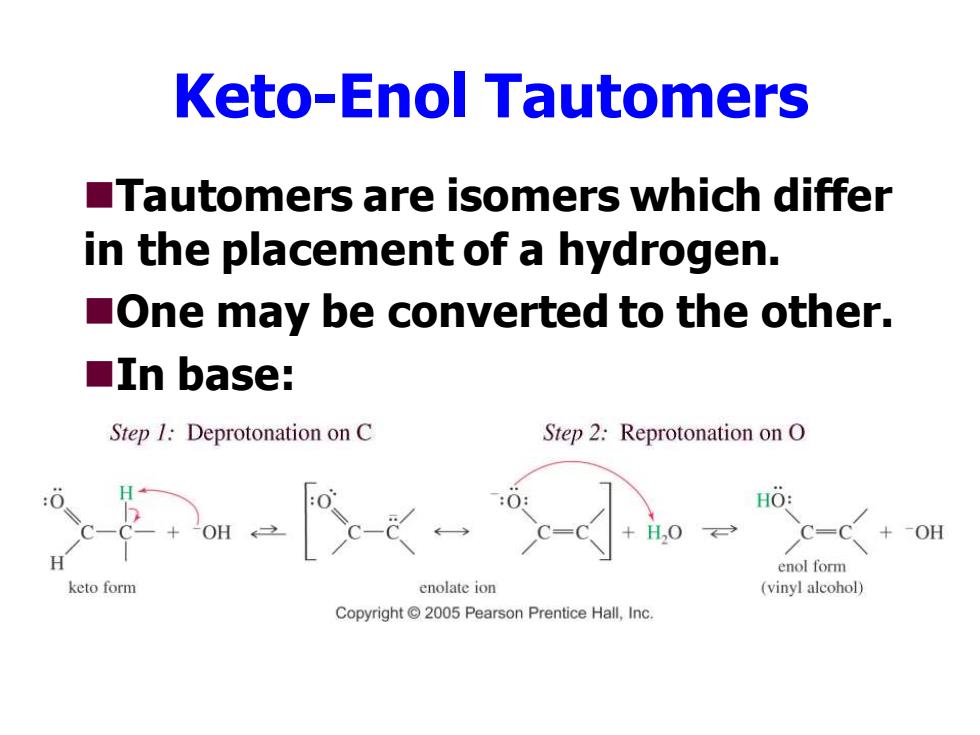
Keto-Enol Tautomers Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of a hydrogen. One may be converted to the other. ■In base: Step 1:Deprotonation on C Step 2:Reprotonation on O HO: DH +-OH enol form keto form enolate ion (vinyl alcohol) Copyright 2005 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Keto-Enol Tautomers ◼Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of a hydrogen. ◼One may be converted to the other. ◼In base: