
先进材料疑固实验室 Application:Zone melting Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Process of zone melting: Start with a solid alloy bar with uniform cross-section. Place the bar horizontally. Only melt the bar within a short zone with a small heater. Move the heater along the bar from one end to the other end. Repeat the process for many times. y o vancedl Matera 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Application: Zone melting Process of zone melting: • Start with a solid alloy bar with uniform cross-section. • Place the bar horizontally. • Only melt the bar within a short zone with a small heater. • Move the heater along the bar from one end to the other end. • Repeat the process for many times
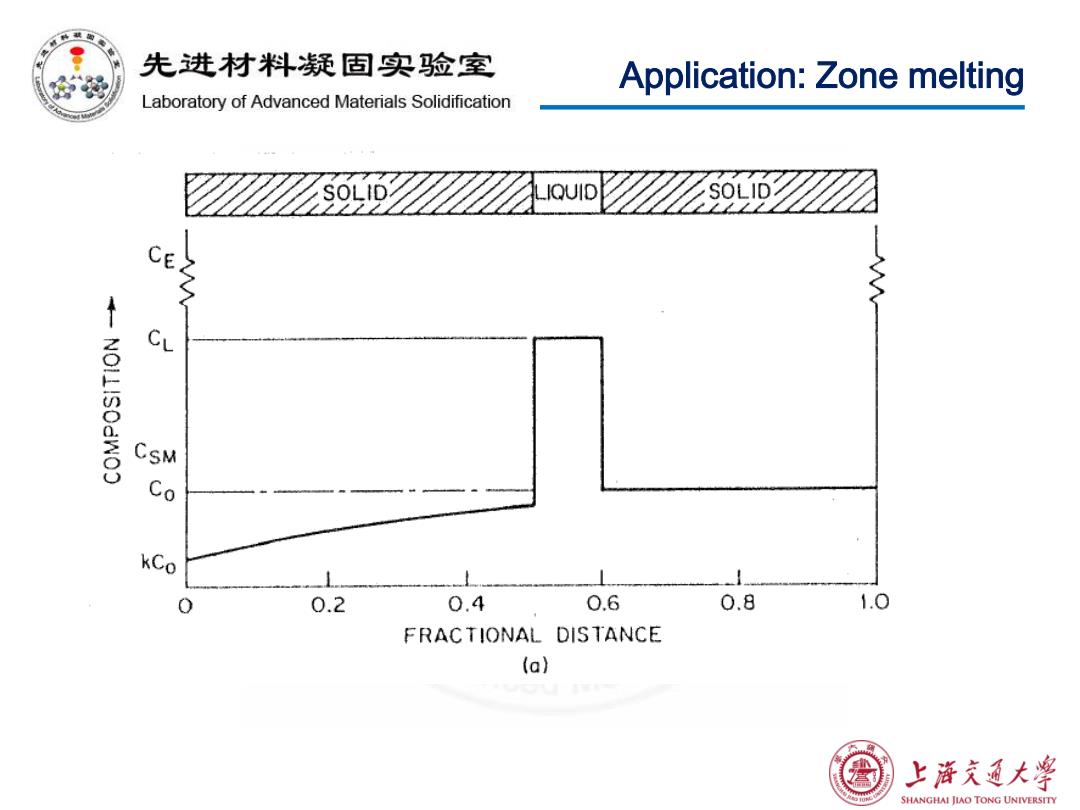
先进材料疑固实验室 Application:Zone melting Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification IQUID CE CL CSM kCo 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0 FRACTIONAL DISTANCE (a) 上游文通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Application: Zone melting

先进材料疑固实验室 Application:Zone melting Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification Zone melting is a widely used technique for purifying metals. We can derive the equation used to calculate the solute concentration distribution in the solid after the first pass. ©Assumptions: No solute diffusion in the solid Complete solute diffusion and mixing in the liquid zone. 上浒充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Application: Zone melting Zone melting is a widely used technique for purifying metals. We can derive the equation used to calculate the solute concentration distribution in the solid after the first pass. Assumptions: • No solute diffusion in the solid • Complete solute diffusion and mixing in the liquid zone

先进材料疑固实验室 Application:Zone melting Laboratory of Advanced Materials Solidification From the mass balance,we have: (CL*-Cs*)Adx+(Co-CL*)Adx ALdCL* (1) L is the length of the liquid zone,A is the cross-section area of the bar. Equation(1)can be simplified to get: (Co-Cs*)dx LdCL* (2) We know Cs*=kCL*,so we can change equation(2)into: k(Co-Cs*)dx LdCs* anced M (3) 上海充通大¥ SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY
Application: Zone melting From the mass balance, we have: (CL* - CS*)Adx + (C0 – CL*) Adx = ALdCL * (1) L is the length of the liquid zone, A is the cross-section area of the bar. Equation (1) can be simplified to get: (C0 – CS*) dx = LdCL * (2) We know CS*=kCL*, so we can change equation (2) into: k(C0 – CS*) dx = LdCS * (3)