
原子核的稳定性 1.原子核稳定性-一核力 特点一大、短、与电荷无关、饱和 2.原子核不稳定的原因:核子数、P/N比例 3.原子核不稳定的常见形式:衰变、核反应
原子核的稳定性 1.原子核稳定性-核力 特点-大、短、与电荷无关、饱和 2.原子核不稳定的原因:核子数、P/N比例 3.原子核不稳定的常见形式:衰变、核反应
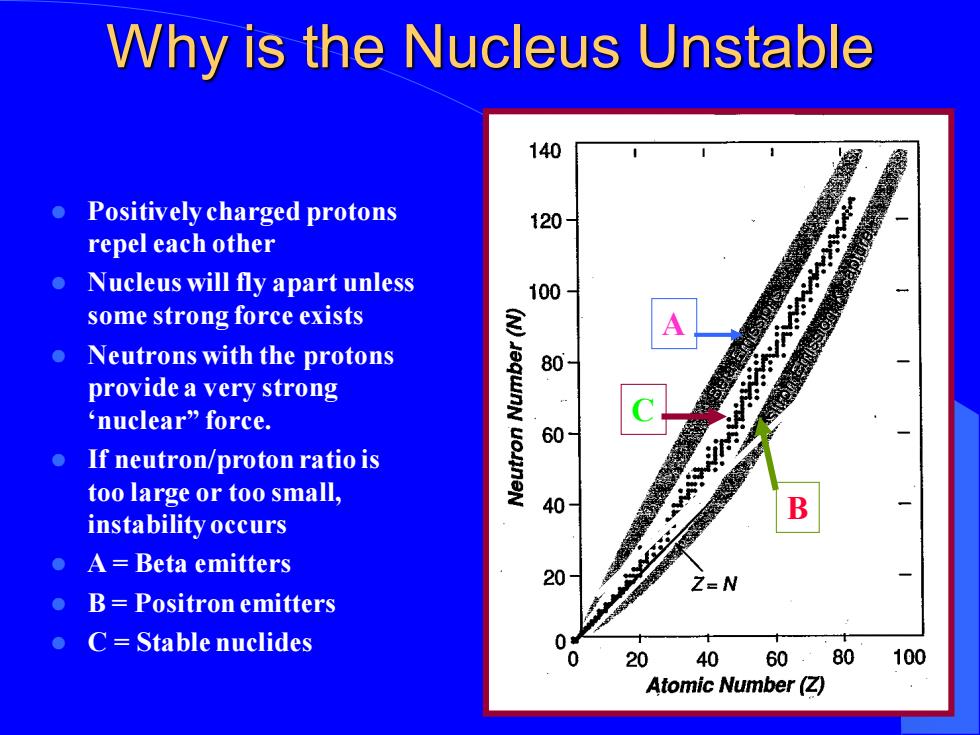
Why is the Nucleus Unstable 140 ● Positively charged protons 120 repel each other ● Nucleus will fly apart unless 100 some strong force exists Neutrons with the protons 80 provide a very strong 'nuclear”force. 60 If neutron/proton ratio is too large or too small, 40 B instability occurs A=Beta emitters 20 Z=N B=Positron emitters C=Stable nuclides 0 20 40 60.80100 Atomic Number(Z)
Why is the Nucleus Unstable ⚫ Positively charged protons repel each other ⚫ Nucleus will fly apart unless some strong force exists ⚫ Neutrons with the protons provide a very strong ‘nuclear” force. ⚫ If neutron/proton ratio is too large or too small, instability occurs ⚫ A = Beta emitters ⚫ B = Positron emitters ⚫ C = Stable nuclides A B C
原子核 核衰变(核子数、p/n比例与核稳定性的关系) 的转变 放射现象、放射线、核衰变
原子核 的转变 核衰变(核子数、p/n比例与核稳定性的关系) 放射现象、放射线、核衰变

一、核衰变 。1.类型(1898年Madame Curie的试 *从衰变的类型、例子、射线性质、应用举例论述
一、核 衰 变 ⚫ 1. 类型(1898年Madame Curie的试验) α β γ *从衰变的类型、例子、射线性质、应用举例论述
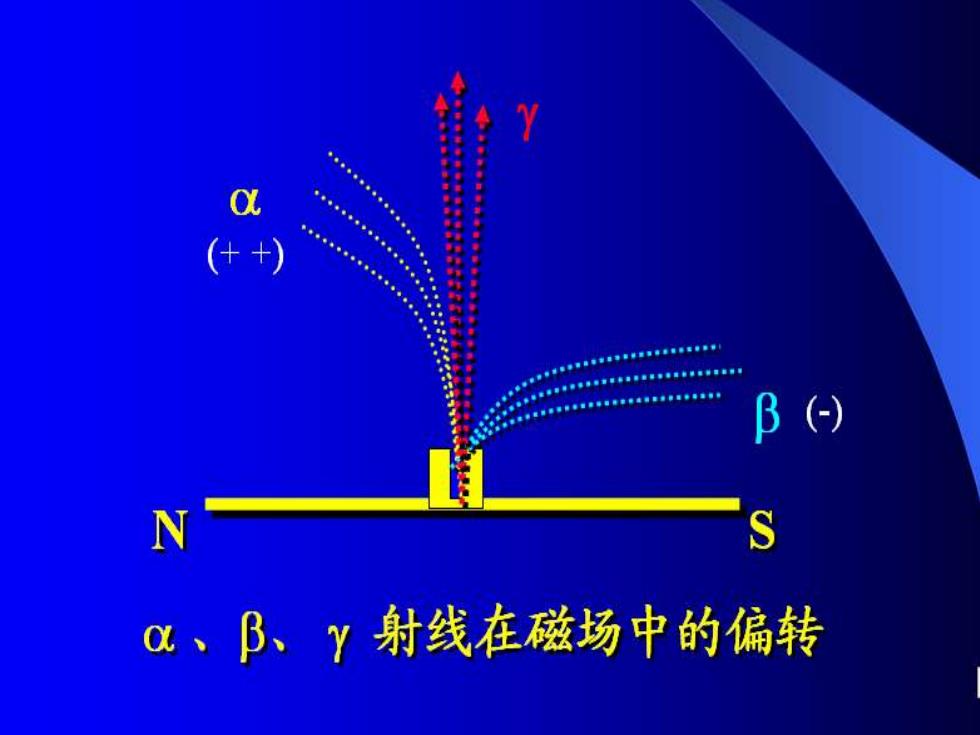
B N a、B、Y射线在磁场中的偏转