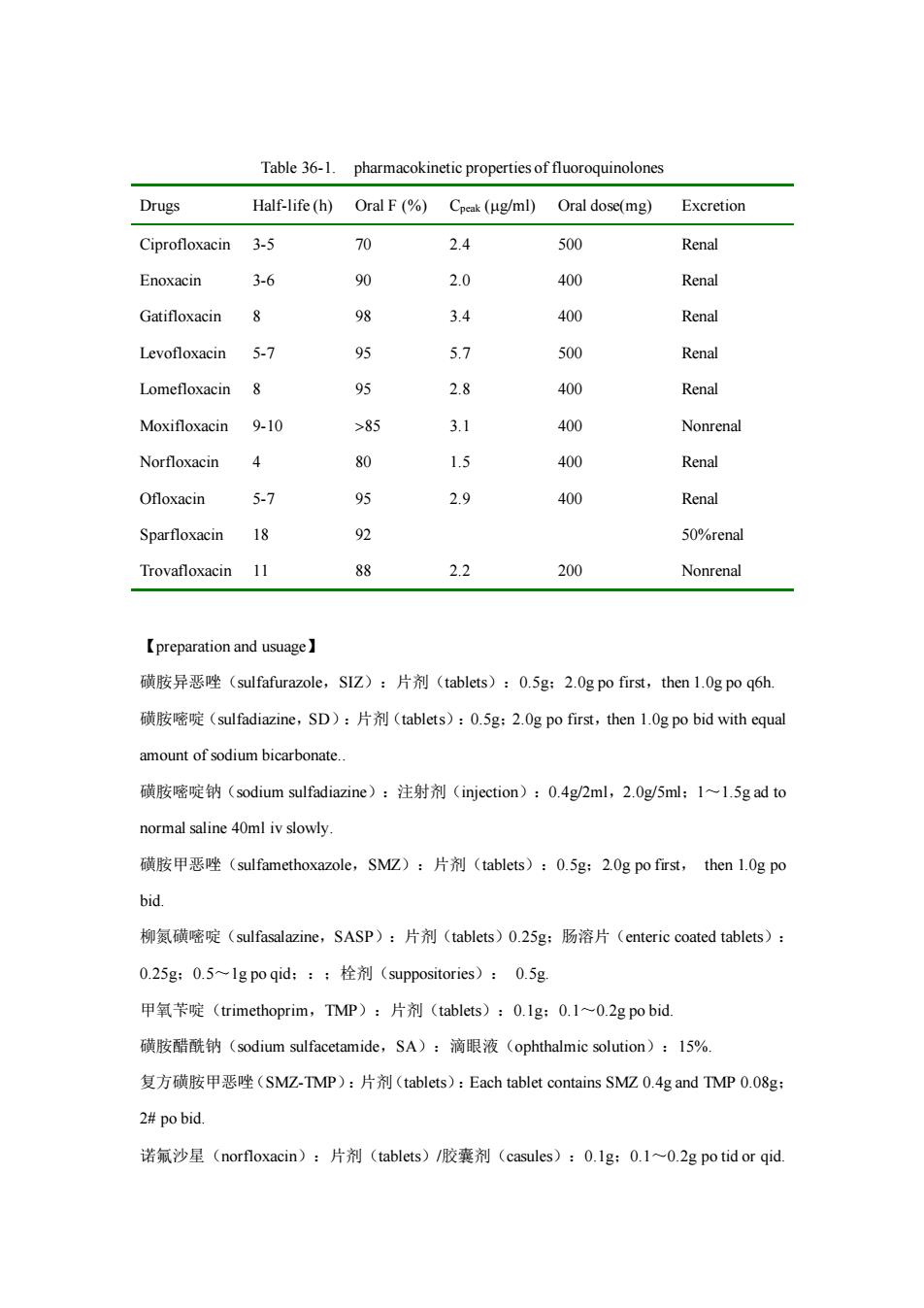
Table 36-1.pharmacokinetic properties of fluoroquinolones Drugs Half-life(h)Oral F(%)Cpeak(ug/ml)Oral dose(mg)Excretion Ciprofloxacin 3-5 70 2.4 500 Renal Enoxacin 3-6 90 2.0 400 Renal Gatifloxacin 8 98 3.4 400 Renal Levofloxacin 5-7 95 5.7 500 Renal Lomefloxacin 8 95 2.8 400 Renal Moxifloxacin 9-10 >85 3.1 400 Nonrenal Norfloxacin 80 1.5 400 Renal Ofloxacin 5-7 95 2.9 400 Renal Sparfloxacin 18 92 50%renal Trovafloxacin 11 88 2.2 200 Nonrenal 【preparation and usuage】 磺胺异恶唑(sulfafurazole,SZ):片剂(tablets):0.5g:2.0 gpofirst,then 1.0gpoq6h 磺胺密啶(sulfadiazine,SD):片剂(tablets):0.5g:2.0 g po first,then 1.0 gpo bid with equal amount of sodium bicarbonate. 磺胺密啶钠(sodium sulfadiazine):注射剂(injection):0.4g/2ml,2.0g/5ml:1~1.5 g ad to normal saline 40ml ivslowly. 磺胺甲恶唑(sulfamethoxazole,SM亿):片剂(tablets):0.5g:20 g po first,then1.0gpo bid. 柳氨磺嘧啶(sulfasalazine,SASP):片剂(tablets)0.2Sg:肠溶片(enteric coaed tabes): 0.25g:0.5~lg poqid:::栓剂(suppositories):0.5g 甲氧苄啶(trimethoprim,TMP):片剂(tablets):0.1g:0.1~0.2 g po bid. 磺胺醋酰钠(msulfacetamide,SA):滴眼液(ophthalmic):l5%. 复方磺胺甲恶唑(SM亿-TMP):片剂(tablets):Each tablet contains SMZ0.4 gand TMP0.08g 2#po bid. 诺氟沙星(norfloxacin):片剂(tablets)/胶囊剂(casules):0.1g:0.1~0.2 g potid or qid
Table 36-1. pharmacokinetic properties of fluoroquinolones Drugs Half-life (h) Oral F (%) Cpeak (g/ml) Oral dose(mg) Excretion Ciprofloxacin Enoxacin Gatifloxacin Levofloxacin Lomefloxacin Moxifloxacin Norfloxacin Ofloxacin Sparfloxacin Trovafloxacin 3-5 3-6 8 5-7 8 9-10 4 5-7 18 11 70 90 98 95 95 85 80 95 92 88 2.4 2.0 3.4 5.7 2.8 3.1 1.5 2.9 2.2 500 400 400 500 400 400 400 400 200 Renal Renal Renal Renal Renal Nonrenal Renal Renal 50%renal Nonrenal 【preparation and usuage】 磺胺异恶唑(sulfafurazole,SIZ):片剂(tablets):0.5g;2.0g po first,then 1.0g po q6h. 磺胺嘧啶(sulfadiazine,SD):片剂(tablets):0.5g;2.0g po first,then 1.0g po bid with equal amount of sodium bicarbonate. 磺胺嘧啶钠(sodium sulfadiazine):注射剂(injection):0.4g/2ml,2.0g/5ml;1~1.5g ad to normal saline 40ml iv slowly. 磺胺甲恶唑(sulfamethoxazole,SMZ):片剂(tablets):0.5g;2.0g po first, then 1.0g po bid. 柳氮磺嘧啶(sulfasalazine,SASP):片剂(tablets)0.25g;肠溶片(enteric coated tablets): 0.25g;0.5~1g po qid;:;栓剂(suppositories): 0.5g. 甲氧苄啶(trimethoprim,TMP):片剂(tablets):0.1g;0.1~0.2g po bid. 磺胺醋酰钠(sodium sulfacetamide,SA):滴眼液(ophthalmic solution):15%. 复方磺胺甲恶唑(SMZ-TMP):片剂(tablets):Each tablet contains SMZ 0.4g and TMP 0.08g; 2# po bid. 诺氟沙星(norfloxacin):片剂(tablets)/胶囊剂(casules):0.1g;0.1~0.2g po tid or qid

氧氟沙星(ofloxacin):片剂(tablets):0.lg:0.1~0.3 g po bid.注射剂(injection):0.4g10ml: 0.4g iv gtt q12h after diluted. 培氟沙星(perfloxacin):片剂(tablets):0.2g:0.4 gpo bid.注射剂((injection):0.4g/5ml: 0.4g iv gtt q2hafter diluted with5%GS 250ml. 依诺沙星(enoxacin):片剂(tablets)/胶囊剂(casules):0.1g:0.2~0.3 gpobid. 环丙沙星(ciprofloxacin):片剂(tablets)/胶囊剂(casules):0.1g:0.25g,0.5g,0.75g: 0.25~0.5g po bid (injection):0.1g/100ml,0.2g/200ml:0.1~0.2giv gut after diluted with normal salineor%GS 左氧氟沙星(1 evofloxacin):片剂(tablets):0.1g:0.1~0.2 g po bid.注射剂(injection): .g/100ml,0.3g/100ml:0.2g ivgtt q2hafter diluted. 洛美沙星(lomefloxacin):簿膜衣片((flm tablets):0.4g:0.4 g poqd.注射剂(injection): .g/100ml.g/50ml:0.givgtr4givgqd after diluted. 司氟沙星(sparfloxacin):胶囊剂(capsules):0.lg:0.1~0.3gqd 加替沙星(gatifloxacin):片剂(Ktablets):0.1g,0.2g,0.4g:0.2~0.4 g po qd.注射剂(): 0.Ig/100ml,0.2g/100ml:.~.4giv gtt qd after diluted. (Q-X-Zhou)
氧氟沙星(ofloxacin):片剂(tablets):0.1g;0.1~0.3g po bid. 注射剂(injection):0.4g/10ml; 0.4g iv gtt q12h after diluted. 培氟沙星(perfloxacin):片剂(tablets):0.2g;0.4g po bid. 注射剂(injection):0.4g/5ml; 0.4g iv gtt q12h after diluted with 5% GS 250ml. 依诺沙星(enoxacin):片剂(tablets)/胶囊剂(casules):0.1g;0.2~0.3g po bid. 环丙沙星(ciprofloxacin):片剂(tablets)/胶囊剂(casules):0.1g;0.25g,0.5g,0.75g; 0.25~0.5g po bid. 注射剂(injection):0.1g/100ml,0.2g/200ml;0.1~0.2g iv gtt after diluted with normal saline or 5% GS. 左氧氟沙星(levofloxacin):片剂(tablets):0.1g;0.1~0.2g po bid. 注射剂(injection): 0.2g/100ml,0.3g/100ml;0.2g iv gtt q12h after diluted. 洛美沙星(lomefloxacin):薄膜衣片(film tablets):0.4g;0.4g po qd. 注射剂(injection): 0.2g/100ml,0.4g/250ml;0.2g iv gtt q12h or 0.4g iv gtt qd after diluted. 司氟沙星(sparfloxacin):胶囊剂(capsules):0.1g;0.1~0.3g qd. 加替沙星(gatifloxacin):片剂(tablets):0.1g,0.2g,0.4g;0.2~0.4g po qd. 注射剂(injection): 0.1g/100ml,0.2g/100ml;0.2~0.4g iv gtt qd after diluted. (Q-X-Zhou)

Chapter 37 Antifungal drugs Human fungal have inereased dramaticaly in recent years,due to surgery,cancer treatment,and critical care with the use of broad-spectrum antimicrobials as well as the HIV epidemic. Fungal infections traditionally are divided into two distinct classes:systemic and superficial. Conseqently.the mjor antifungal agents describd in this chapter fall into systemic drugs and topical drugs. Amphotericin B Amphotericin B was discovered in 956 by Gold and co-workers who were studying a strain of Srreplomyces nod an aerobic actinomycete.obtained from the Orinoco River Valley of Venezuela Asa polyen macrolide antibiotic,amphotericin B is unstable at room temperature. 【Antifungal Activity and Mechanism】
Chapter 37 Antifungal drugs Human fungal infections have increased dramatically in recent years, due to surgery, cancer treatment, and critical care with the use of broad-spectrum antimicrobials as well as the HIV epidemic. Fungal infections traditionally are divided into two distinct classes:systemic and superficial. Conseqently, the major antifungal agents described in this chapter fall into systemic drugs and topical drugs. Amphotericin B Amphotericin B was discovered in 1956 by Gold and co-workers who were studying a strain of Streptomyces nodosus, an aerobic actinomycete, obtained from the Orinoco River Valley of Venezuela. As a polyen macrolide antibiotic, amphotericin B is unstable at room temperature. 【Antifungal Activity and Mechanism】

Amphotericin B has the broadest spectrum of antifungi activity,including Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neofimans that cause endemic mycoses(Blastomyces dermatitidis.Histoplasma capsulatm.Coccidioides immitis).and the pathogenic molds,such as Aspergillus fumigats and mcor.Some fungal organisms such as Candida lusitaniae and Pseudallescheria boydii display intrinsic amphotericin B resistance. Antifungal activity of amphotericin B depends at least partly on its binding to a sterol moiety. primarily ergosterol existing in the membrane of sensitive fungi.By virtue of the interaction with the sterols of cell membranes,amphotericin B makes membrane form pores or channels which allowing leakage ofa variety of small molecules.At last,the fungi are dead. 【Clinical Use】 Amphotericin B is the drug of choice for treating systemic mycoses in spite of its toxic potential.It is sometimes used in combination with flucytosine so that lower levels of amphotericin B are possible in order to relieve the toxicity.amphotericin B is given by intravenous infusion. 【Adverse Effects】 Amphotericin B has a low therapeutic index.A total daily dose should not exceed 1.5 mg/kg Small test dose is usually administered to assess the degree of a patient's negative response After infusion,it can cause high fever,chills,muscle spasms,vomiting headache,and hypotension,which could be ameliorated by slowing infusion rate and decreasing daily dose,or premedication with glucocorticosteroids or antipyretics.Renal damage is the most significant after it is used time.Renal impairment curs in nearly all patients reated with clinically significant doses of amphotericin Aminoglycosides,cyclosporine,and pentamidine exacerbate the renal damage. Azoles Azoles include imdazoles and triazoles.The imidazoles consist of ketoconazole, miconazole,and clotrimazole.These three drugs are used mainly in topical therapy.The triazoles include itraconazole and fluconazole both of which are in common use for systemic treatment of fungal disease
Amphotericin B has the broadest spectrum of antifungi activity, including Candida albicans and Cryptococcus neoftmans that cause endemic mycoses (Blastomyces dermatitidis, Histoplasma capsulatum, Coccidioides immitis), and the pathogenic molds, such as Aspergillus fumigatus and mucor. Some fungal organisms such as Candida lusitaniae and Pseudallescheria boydii display intrinsic amphotericin B resistance. Antifungal activity of amphotericin B depends at least partly on its binding to a sterol moiety, primarily ergosterol existing in the membrane of sensitive fungi. By virtue of the interaction with the sterols of cell membranes, amphotericin B makes membrane form pores or channels, which allowing leakage of a variety of small molecules. At last, the fungi are dead. 【Clinical Use】 Amphotericin B is the drug of choice for treating systemic mycoses in spite of its toxic potential. It is sometimes used in combination with flucytosine so that lower levels of amphotericin B are possible in order to relieve the toxicity. amphotericin B is given by intravenous infusion. 【Adverse Effects】 Amphotericin B has a low therapeutic index. A total daily dose should not exceed 1.5 mg/kg. Small test dose is usually administered to assess the degree of a patient’s negative response. After infusion, it can cause high fever, chills, muscle spasms, vomiting, headache, and hypotension, which could be ameliorated by slowing infusion rate and decreasing daily dose, or premedication with glucocorticosteroids or antipyretics. Renal damage is the most significant toxic reaction after it is used for long time. Renal impairment occurs in nearly all patients treated with clinically significant doses of amphotericin. Aminoglycosides, cyclosporine, and pentamidine exacerbate the renal damage. Azoles Azoles include imdazoles and triazoles. The imidazoles consist of ketoconazole, miconazole, and clotrimazole. These three drugs are used mainly in topical therapy. The triazoles include itraconazole and fluconazole, both of which are in common use for systemic treatment of fungal disease

Ketoconazole Ketoconazole is used in the treatment of many kinds of mucocutaneous candidiasis.Topical and shampoo forms of ketoconazole are also available and useful in the treatment of seborheic dermatitis and pityriasis versicolor.It is easy to be absorbed at a low gastric PH.Because of liver toxicity,it is limited for systemic treatment.Ketoconazole may cause gastrointestinal upset,abnormity of liver function,and synthetic disorders of androgen and adrenal steroids. etraconazole is available in an oral formulation and its absorption is increased by food and by low gastric PH.Itraconazole isa drag of choice in the treatment of dermatopyoses and onchomcos and is the only agent with significant activity against aspergillus secies. isrelatively lowtoxic.The is upset. Fluconazole The drug is available in oral and intravenous formulations.Renal excretion accounts for over%of elimination,and the elimination half-life is25 to30 hours.It is used for treating candidiasis.cryplococcosis and AIDS patients with cryptococcal meningitis.The and dizziness may be seen. Clotrimazole and miconazole Clotrimazole and miconazole are often used for vulvovaginal candidiasis.In cream form,both agents are useful for dermatophytic infections.Absorption is neglible,and adverse effects are rare. Griseofulvin Its only use is in the systemic treatment of dermatophytosis.It is available in an oral formulation and absorption is improved when it is given with fatty foods.Its action is to prevent new infection of skin structures It must be administered for at least -6weeks for skin and hair infections to allow the replacement of infected keratin by the resistant structures Adverse effects include allergic syndrome,hepatitis,and drug interactions with warfarin. Griseofulvin has been largely replaced by newer antifungal medicationsschastacand terbinafine. Terbinafine It can be taken orally and used in treatment of dermatophytoses,especially onychomycosis.Like azole drugs,it interferes with ergosterol biosynthesis but rather than interacting with the P450 system.Adverse effects are rare,consisting primarily of gastrointestinal upset and headache
Ketoconazole Ketoconazole is used in the treatment of many kinds of mucocutaneous candidiasis. Topical and shampoo forms of ketoconazole are also available and useful in the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis and pityriasis versicolor. It is easy to be absorbed at a low gastric PH. Because of liver toxicity, it is limited for systemic treatment. Ketoconazole may cause gastrointestinal upset, abnormity of liver function, and synthetic disorders of androgen and adrenal steroids. Itraconazole Itraconazole is available in an oral formulation and its absorption is increased by food and by low gastric PH. Itraconazole is a drag of choice in the treatment of dermatophytoses and onychomycosis and is the only agent with significant activity against aspergillus species. Itraconazole is relatively low toxic. The most common adverse reaction is gastrointestinal upset. Fluconazole The drug is available in oral and intravenous formulations. Renal excretion accounts for over 90% of elimination, and the elimination half-life is 25 to 30 hours. It is used for treating candidiasis, cryptococcosis and AIDS patients with cryptococcal meningitis. The adverse effects of fluconazole is relatively minor in same kinds, alimentary canal upset, headache and dizziness may be seen. Clotrimazole and miconazole Clotrimazole and miconazole are often used for vulvovaginal candidiasis. In cream form, both agents are useful for dermatophytic infections. Absorption is negligible, and adverse effects are rare. Griseofulvin Its only use is in the systemic treatment of dermatophytosis. It is available in an oral formulation and absorption is improved when it is given with fatty foods. Its action is to prevent new infection of skin structures. It must be administered for at least 2-6 weeks for skin and hair infections to allow the replacement of infected keratin by the resistant structures. Adverse effects include allergic syndrome, hepatitis, and drug interactions with warfarin. Griseofulvin has been largely replaced by newer antifungal medications such as itraconazole and terbinafine. Terbinafine It can be taken orally and used in treatment of dermatophytoses, especially onychomycosis. Like azole drugs, it interferes with ergosterol biosynthesis, but rather than interacting with the P450 system. Adverse effects are rare, consisting primarily of gastrointestinal upset and headache