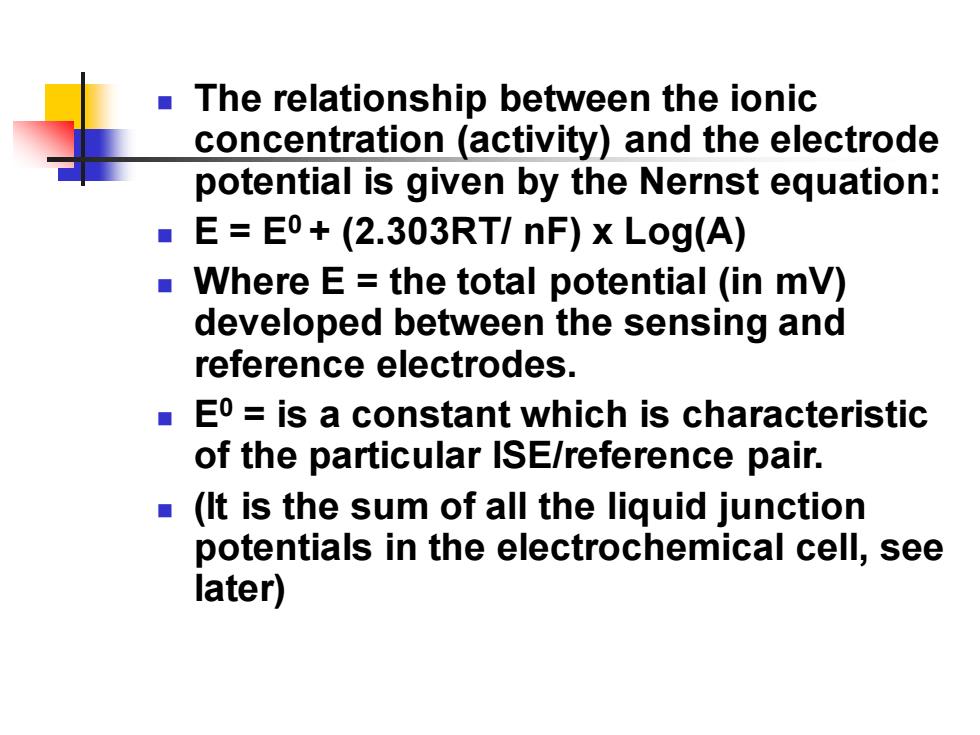
The relationship between the ionic concentration (activity)and the electrode potential is given by the Nernst equation: E=E0+(2.303RT/nF)x Log(A) Where E=the total potential (in mV) developed between the sensing and reference electrodes. ■ Eo=is a constant which is characteristic of the particular ISE/reference pair. (It is the sum of all the liquid junction potentials in the electrochemical cell,see later)
◼ The relationship between the ionic concentration (activity) and the electrode potential is given by the Nernst equation: ◼ E = E0 + (2.303RT/ nF) x Log(A) ◼ Where E = the total potential (in mV) developed between the sensing and reference electrodes. ◼ E0 = is a constant which is characteristic of the particular ISE/reference pair. ◼ (It is the sum of all the liquid junction potentials in the electrochemical cell, see later)
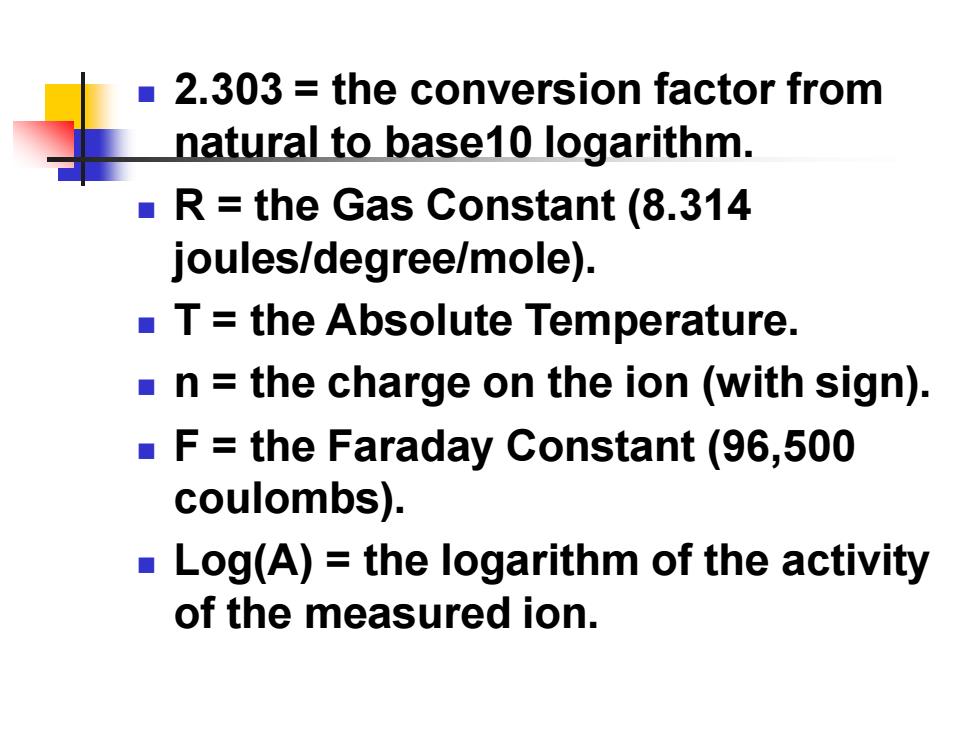
2.303 the conversion factor from natural to base10 logarithm. R=the Gas Constant (8.314 joules/degree/mole). T=the Absolute Temperature. n the charge on the ion (with sign). F=the Faraday Constant (96,500 coulombs). Log(A)=the logarithm of the activity of the measured ion
◼ 2.303 = the conversion factor from natural to base10 logarithm. ◼ R = the Gas Constant (8.314 joules/degree/mole). ◼ T = the Absolute Temperature. ◼ n = the charge on the ion (with sign). ◼ F = the Faraday Constant (96,500 coulombs). ◼ Log(A) = the logarithm of the activity of the measured ion

For practical use in measuring pH,it is not normally necessary for the operator to construct a calibration graph and interpolate the results for unknown samples.Most pH electrodes are connected directly to a special pH meter which performs the calibration automatically.This determines the slope mathematically and calculates the unknown pH value for immediate display on the meter
◼ For practical use in measuring pH, it is not normally necessary for the operator to construct a calibration graph and interpolate the results for unknown samples. Most pH electrodes are connected directly to a special pH meter which performs the calibration automatically. This determines the slope mathematically and calculates the unknown pH value for immediate display on the meter

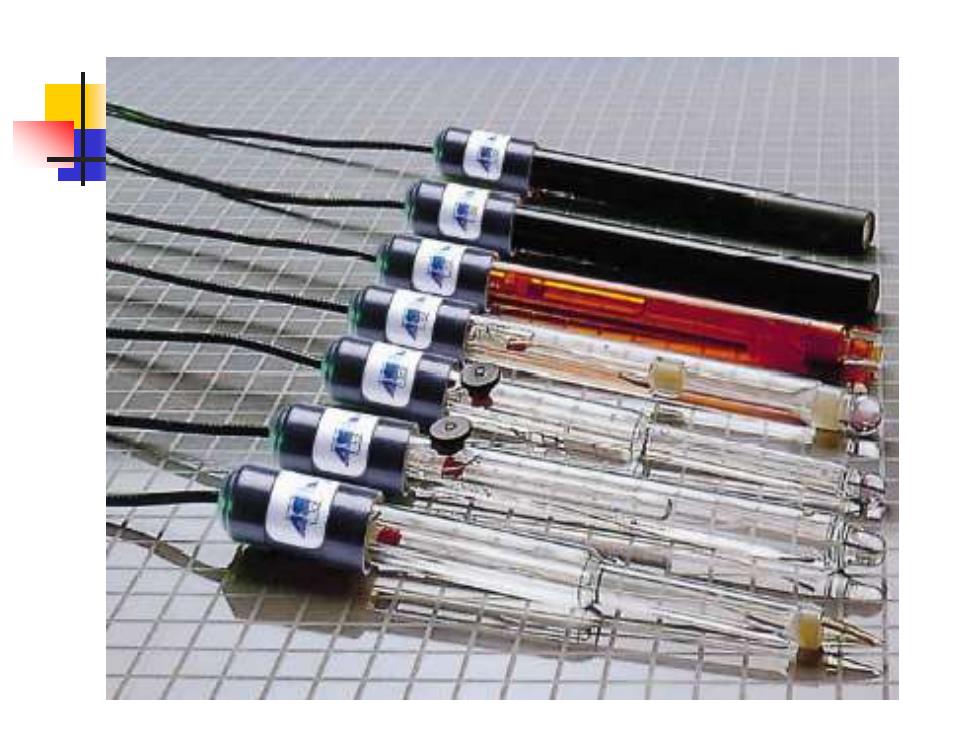
离子选择性电极类型 ◆ pH电极 阳离子玻璃电极 晶体电极 氟电极 ■硫、卤素电极 ■流动载体电极 气敏电极 酶电极 离子敏感场效应晶体管电极
离子选择性电极类型 ◼ pH电极 ◼ 阳离子玻璃电极 ◼ 晶体电极 ◼ 氟电极 ◼ 硫、卤素电极 ◼ 流动载体电极 ◼ 气敏电极 ◼ 酶电极 ◼ 离子敏感场效应晶体管电极