
Movement Across Membranes 。Osmosis Movement of water Glass tube- across a selectively Rubber permeable membrane stopper from an area of high Rubber band water concentration to Sucrose an area of lower water. molecule Cellophane 。Osmotic pressure sack Water- The pressure needed to molecule 00 stop the movement of (a)At beginning of osmotic water across the pressure experiment membrane. Figure 4.18a
• Osmosis • Movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane from an area of high water concentration to an area of lower water. • Osmotic pressure • The pressure needed to stop the movement of water across the membrane. Movement Across Membranes Figure 4.18a
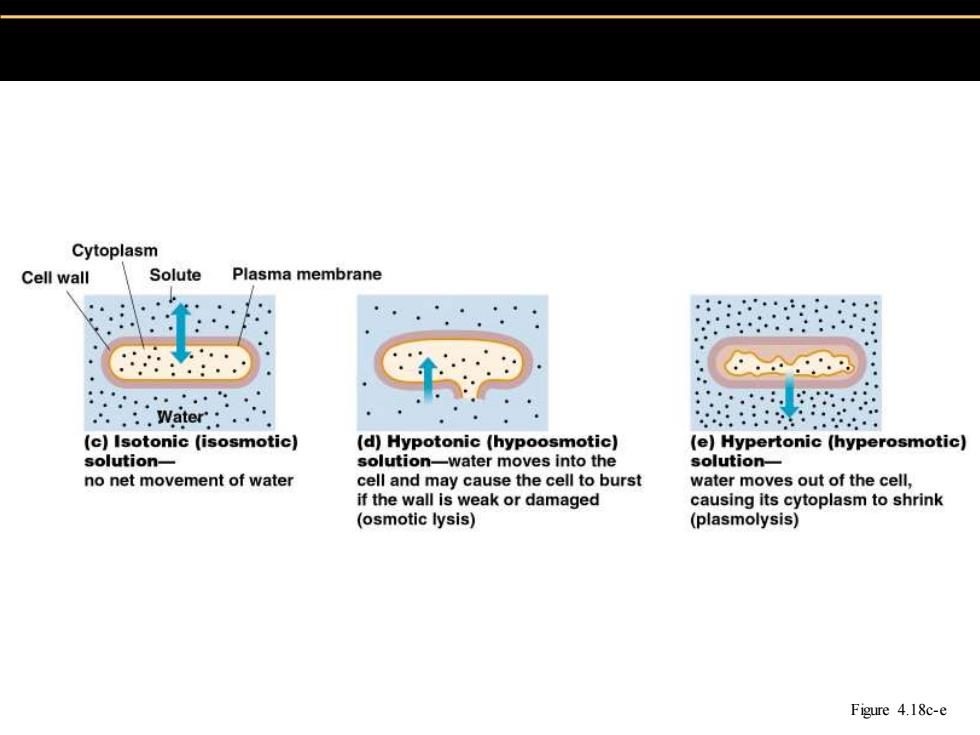
Cytoplasm Cell wall Solute Plasma membrane .'.Water. (c)Isotonic (isosmotic) (d)Hypotonic(hypoosmotic) (e)Hypertonic (hyperosmotic) solution- solution-water moves into the solution- no net movement of water cell and may cause the cell to burst water moves out of the cell, if the wall is weak or damaged causing its cytoplasm to shrink (osmotic lysis) (plasmolysis) Figure 4.18c-e
Figure 4.18c-e

Movement Across Membranes Active transport of substances requires a transporter protein and ATP Group translocation of substances requires a transporter protein and PEP
• Active transport of substances requires a transporter protein and ATP. • Group translocation of substances requires a transporter protein and PEP. Movement Across Membranes
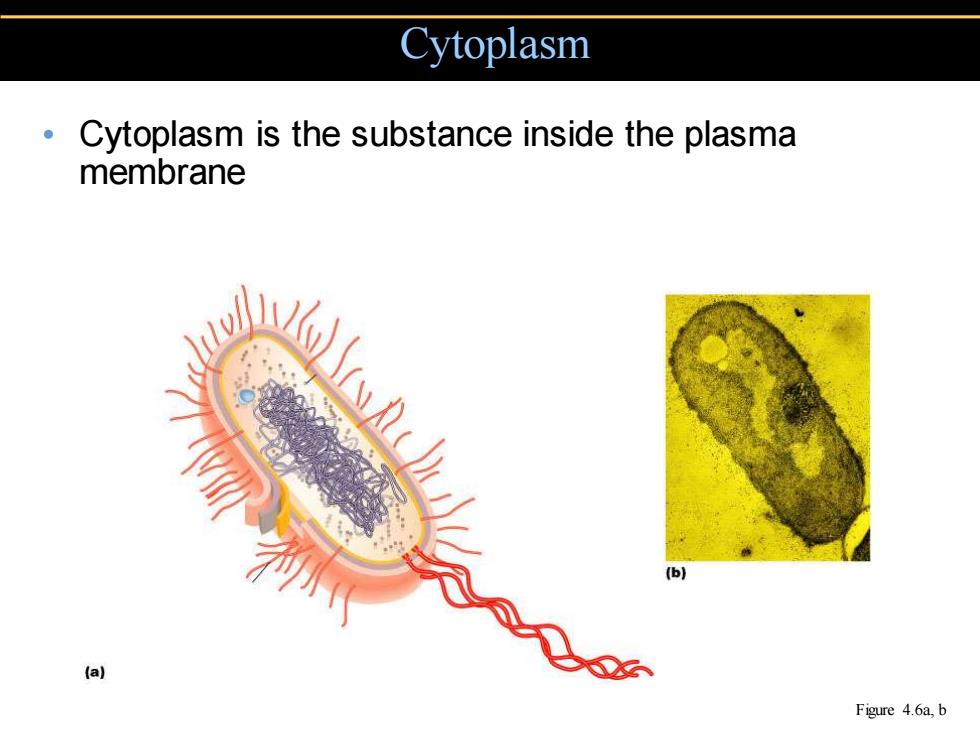
Cytoplasm Cytoplasm is the substance inside the plasma membrane (b) (a) Figure 4.6a,b
• Cytoplasm is the substance inside the plasma membrane Cytoplasm Figure 4.6a, b
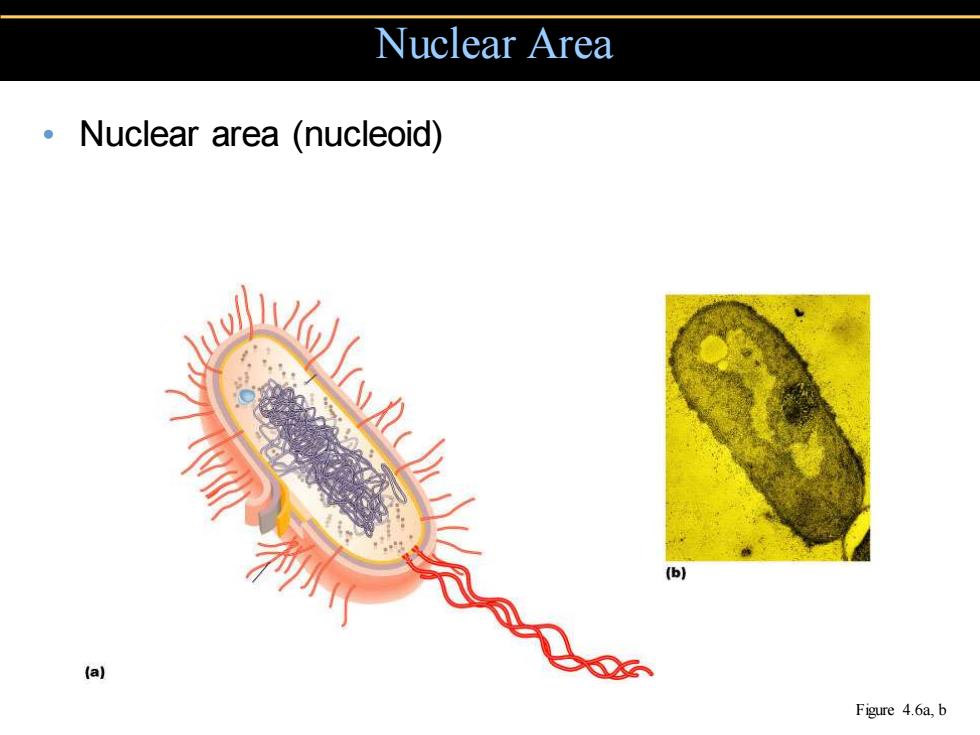
Nuclear Area Nuclear area (nucleoid) (】 (a) Figure 4.6a,b
• Nuclear area (nucleoid) Nuclear Area Figure 4.6a, b