
Chapter 12,part A The Eukaryotes:Fungi,Algae,Protozoa, and Helminths
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin Cummings B.E Pruitt & Jane J. Stein Chapter 12, part A The Eukaryotes: Fungi, Algae, Protozoa, and Helminths

The Fungi 。Eukaryotic Aerobic or facultatively anaerobic ·Chemoheterotrophic ·Most are decomposers Mycology is the study of fungi
The Fungi • Eukaryotic • Aerobic or facultatively anaerobic • Chemoheterotrophic • Most are decomposers • Mycology is the study of fungi
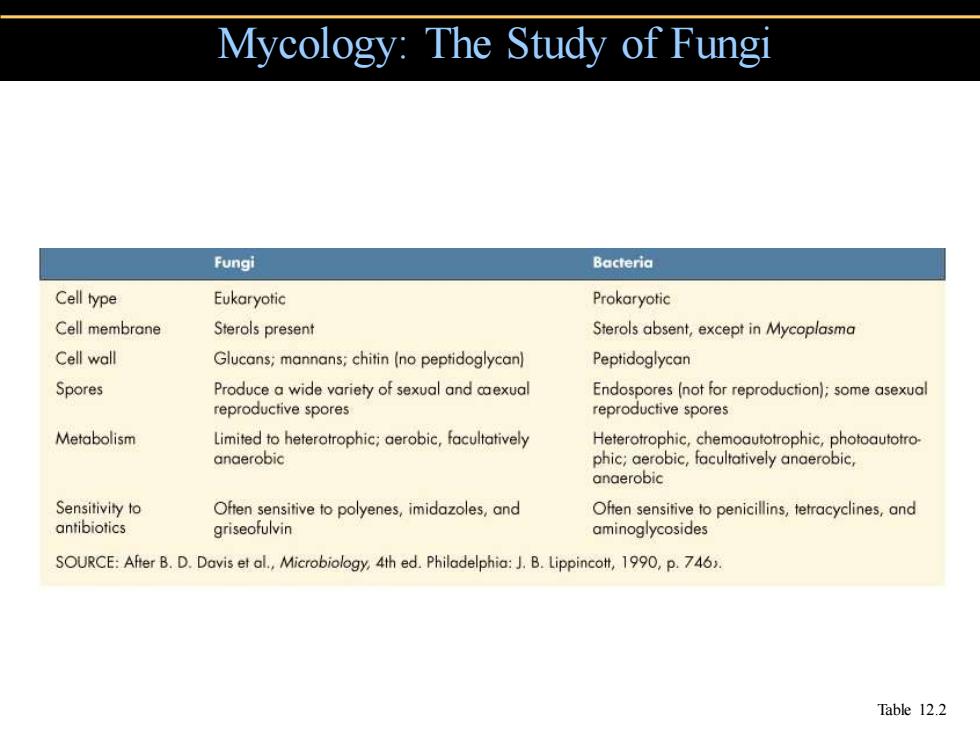
Mycology:The Study of Fungi Fungi Bacteria Cell type Eukaryotic Prokaryotic Cell membrane Sterols present Sterols absent,except in Mycoplasma Cell wall Glucans;mannans;chitin(no peptidoglycan) Peptidoglycan Spores Produce a wide variety of sexual and caexual Endospores (not for reproduction);some asexual reproductive spores reproductive spores Metabolism Limited to heterotrophic;aerobic,facultatively Heterotrophic,chemoautotrophic,photoautotro- anaerobic phic;aerobic,facultatively anaerobic, anaerobic Sensitivity to Often sensitive to polyenes,imidazoles,and Often sensitive to penicillins,tetracyclines,and antibiotics griseofulvin aminoglycosides SOURCE:After B.D.Davis et al.,Microbiology,4th ed.Philadelphia:J.B.Lippincolt,1990,p.7463. Table 12.2
Mycology: The Study of Fungi Table 12.2
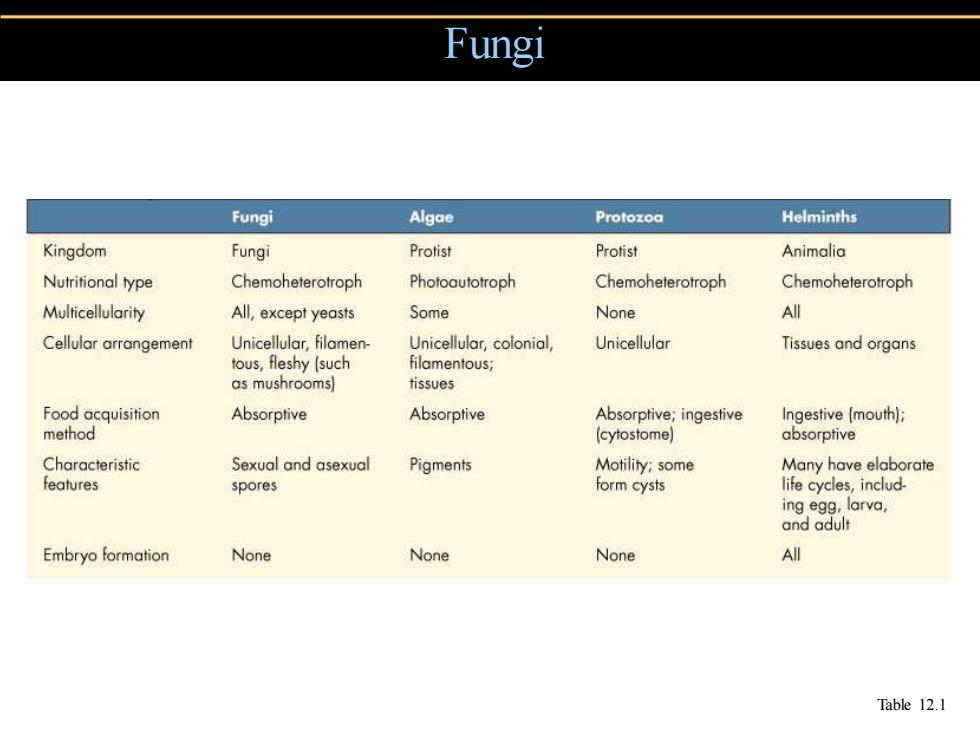
Fungi Fungi Algae Protozoa Helminths Kingdom Fungi Protist Protist Animalia Nutritional type Chemoheterotroph Photoautotroph Chemoheterotroph Chemoheterotroph Multicellularity All,except yeasts Some None All Cellular arrangement Unicellular,filamen- Unicellular,colonial, Unicellular Tissues and organs tous,fleshy (such filamentous; as mushrooms) tissues Food acquisition Absorptive Absorptive Absorptive;ingestive Ingestive (mouth); method (cytostome) absorptive Characteristic Sexual and asexual Pigments Motility;some Many have elaborate features spores form cysts life cycles,includ- ing egg,larva, and adult Embryo formation None None None All Table 12.1
Fungi Table 12.1
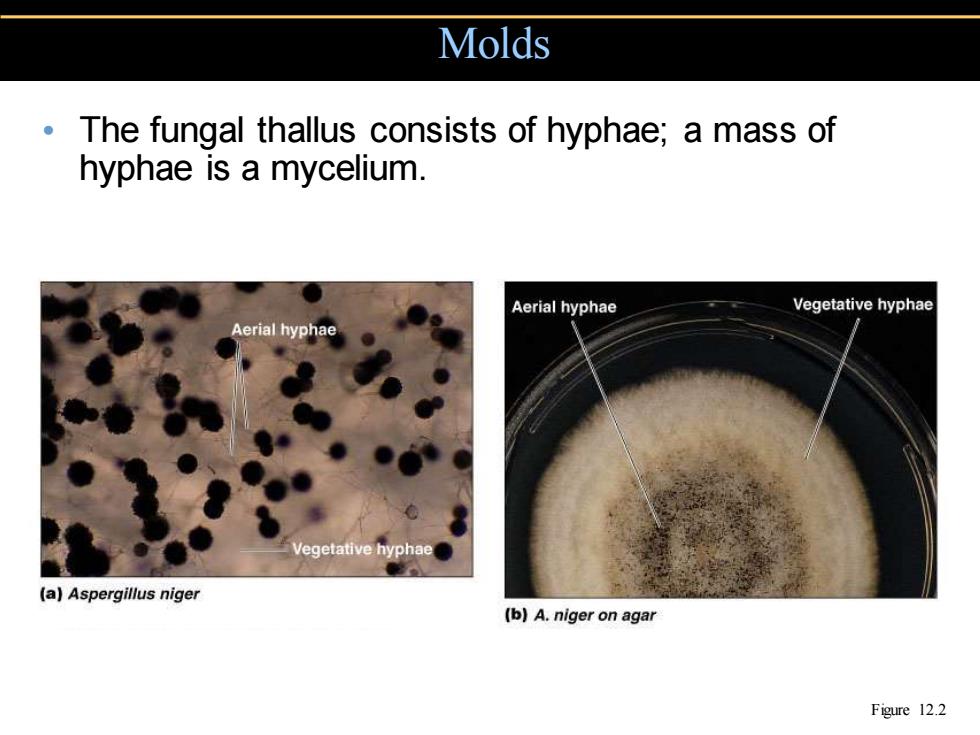
Molds The fungal thallus consists of hyphae;a mass of hyphae is a mycelium. Aerial hyphae Vegetative hyphae Aerial hyphae Vegetative hyphae (a)Aspergillus niger (b)A.niger on agar Figure 12.2
• The fungal thallus consists of hyphae; a mass of hyphae is a mycelium. Molds Figure 12.2