25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins Coated vesicles are vesicles whose membrane has on its surface a layer of a protein such as clathrin,cop-I or COP-II. Endocytosis is process by which proteins at the surface of the cell are internalized,being transported into the cell within membranous vesicles. Exocytosis is the process of secreting proteins from a cell into the medium,by transport in membranous vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum,through the Golgi,to storage vesicles,and finally (upon a regulatory signal)through the plasma membrane. Retrograde transport describes movement of proteins in the reverse direction in the reticuloendothelial system,typically from Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum. 清菜大学
Coated vesicles are vesicles whose membrane has on its surface a layer of a protein such as clathrin, cop-I or COP-II. Endocytosis is process by which proteins at the surface of the cell are internalized, being transported into the cell within membranous vesicles. Exocytosis is the process of secreting proteins from a cell into the medium, by transport in membranous vesicles from the endoplasmic reticulum, through the Golgi, to storage vesicles, and finally (upon a regulatory signal) through the plasma membrane. Retrograde transport describes movement of proteins in the reverse direction in the reticuloendothelial system, typically from Golgi to endoplasmic reticulum. 25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins
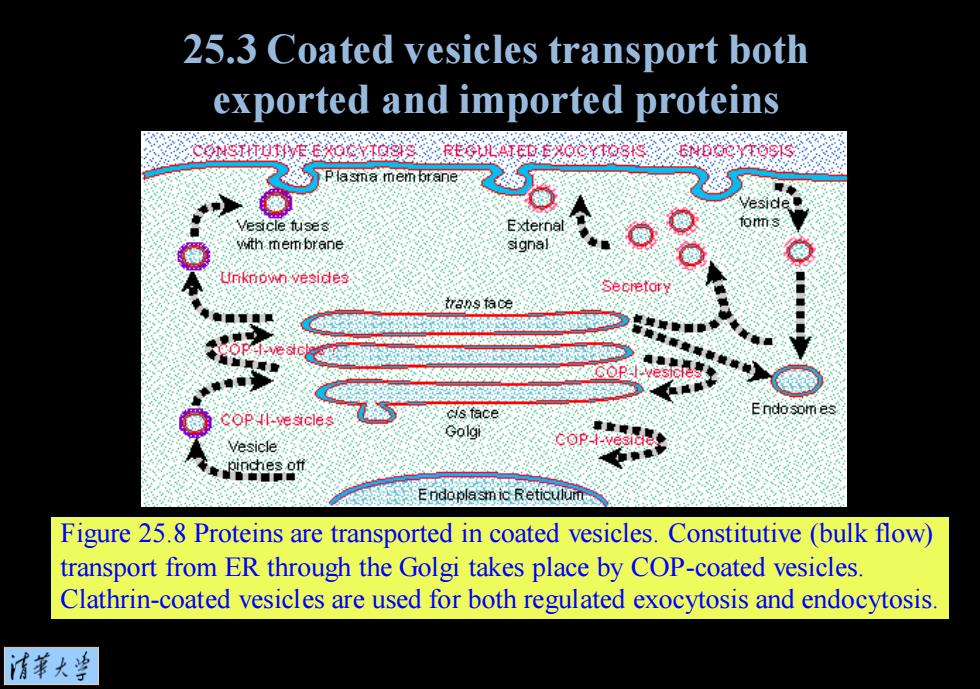
25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins P lasma mem brane wth mem brane koeide COP II-vescles cis tace Golgi Vesicle 6o2 Endopiamic Reticulum Figure 25.8 Proteins are transported in coated vesicles.Constitutive (bulk flow) transport from ER through the Golgi takes place by COP-coated vesicles Clathrin-coated vesicles are used for both regulated exocytosis and endocytosis. 清菜大当
Figure 25.8 Proteins are transported in coated vesicles. Constitutive (bulk flow) transport from ER through the Golgi takes place by COP-coated vesicles. Clathrin-coated vesicles are used for both regulated exocytosis and endocytosis. 25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins
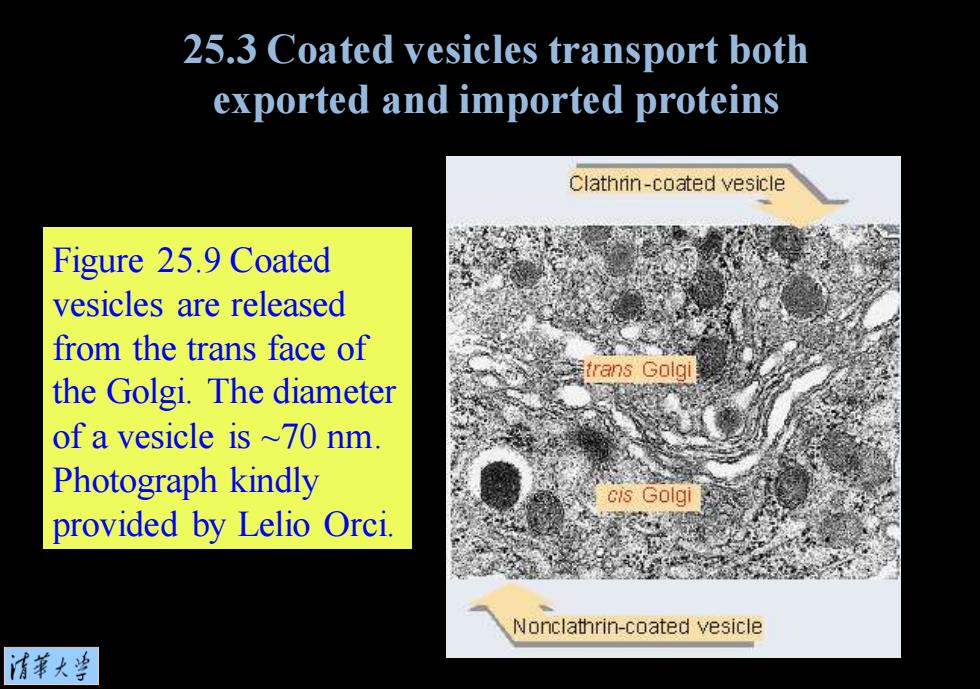
25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins Clathrin-coated vesicle Figure 25.9 Coated vesicles are released from the trans face of trans Golgi the Golgi.The diameter of a vesicle is ~70 nm. Photograph kindly cis Golgi provided by Leli ri Nonclathrin-coated vesicle 情華大当
Figure 25.9 Coated vesicles are released from the trans face of the Golgi. The diameter of a vesicle is ~70 nm. Photograph kindly provided by Lelio Orci. 25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins
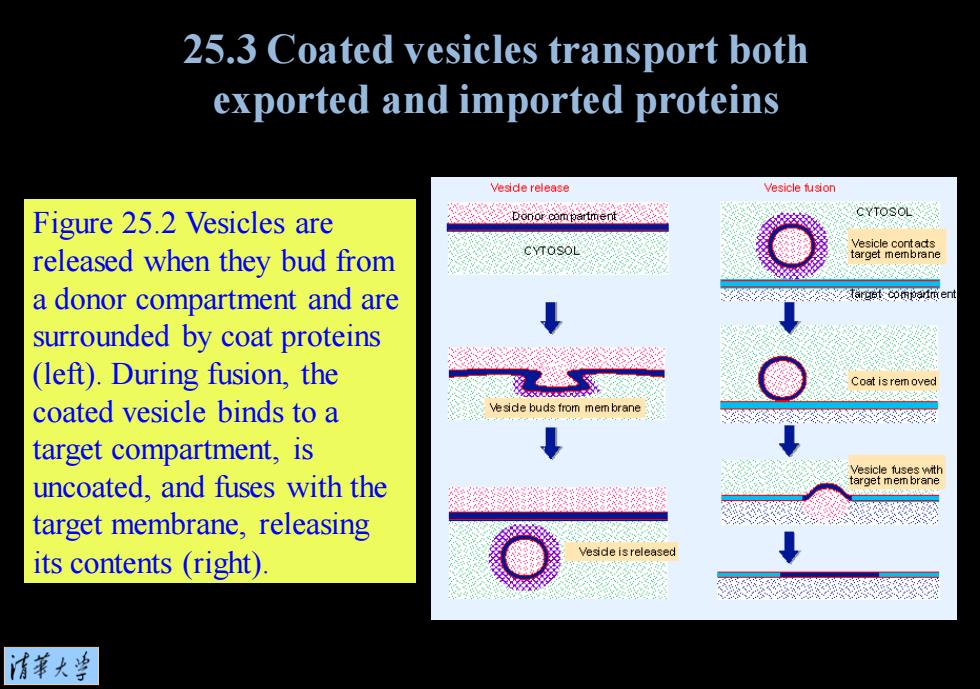
25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins Veside release Vesicle fusion Figure 25.2 Vesicles are released when they bud from CYTOSOL Vesicle contacts arget membrane a donor compartment and are surrounded by coat proteins (left).During fusion,the Coat is rem oved coated vesicle binds to a eside buds from target compartment,is Vesicle fuses with uncoated,and fuses with the arget mem brane target membrane,releasing its contents (right). eside is released 清苇大当
Figure 25.2 Vesicles are released when they bud from a donor compartment and are surrounded by coat proteins (left). During fusion, the coated vesicle binds to a target compartment, is uncoated, and fuses with the target membrane, releasing its contents (right). 25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins
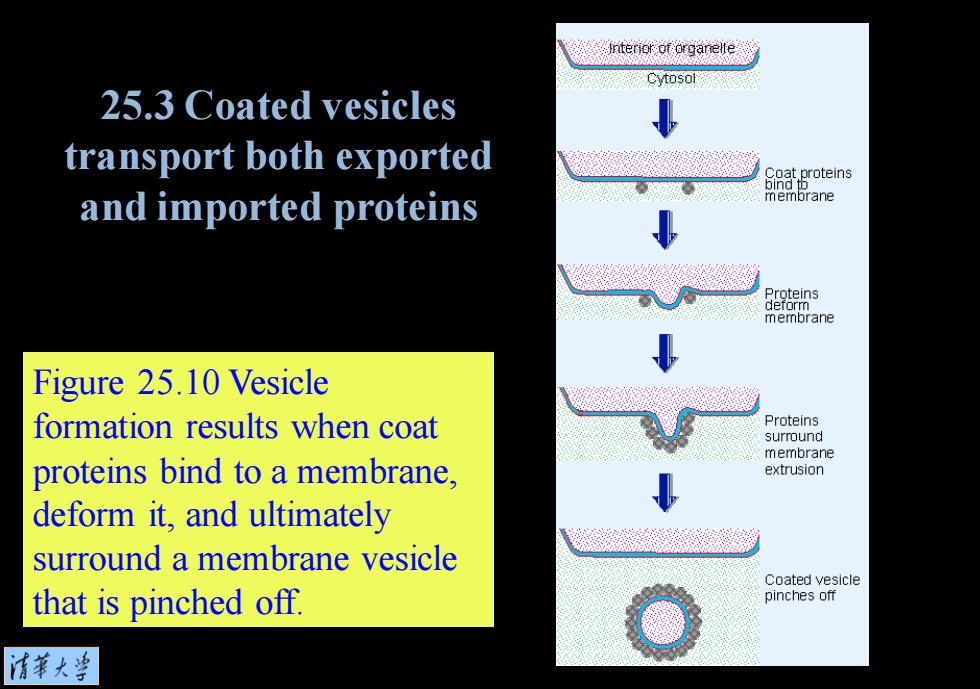
Cytosol 25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported roteins and imported proteins membrane deorms membrane Figure 25.10 Vesicle formation results when coat Proteins surround membrane proteins bind to a membrane, extrusion deform it,and ultimately surround a membrane vesicle Coated vesicle that is pinched off. pinches off 情華大当
Figure 25.10 Vesicle formation results when coat proteins bind to a membrane, deform it, and ultimately surround a membrane vesicle that is pinched off. 25.3 Coated vesicles transport both exported and imported proteins