
Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry's Organic Chemistry,6th edition,Chapter 3
Organic Compounds: Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Based on McMurry’s Organic Chemistry, 6th edition, Chapter 3
Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features The common structural feature that makes it possible to classify compounds by reactivity are called functional groups Functional group-collection of atoms at a site within a molecule with a common bonding pattern The group reacts in a typical way,generally independent of the rest of the molecule For example,the double bonds in simple and complex alkenes react with bromine in the same way
Families of Organic Compounds Organic compounds can be grouped into families by their common structural features The common structural feature that makes it possible to classify compounds by reactivity are called functional groups Functional group - collection of atoms at a site within a molecule with a common bonding pattern The group reacts in a typical way, generally independent of the rest of the molecule For example, the double bonds in simple and complex alkenes react with bromine in the same way
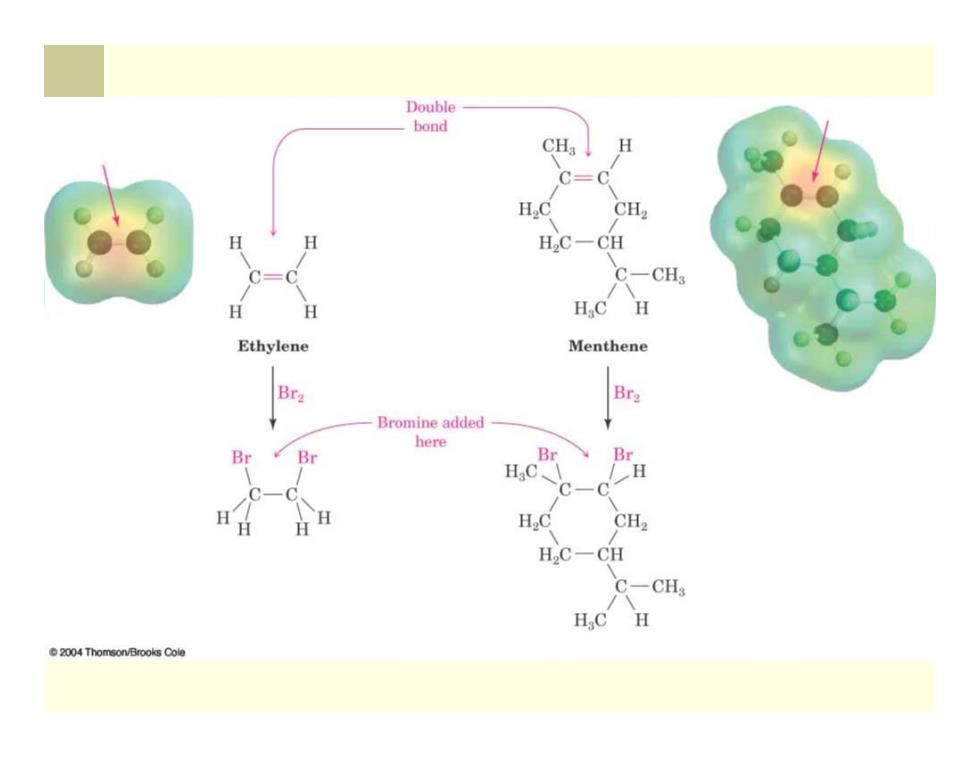
Double bond CH C=C CH2 H2C一CH C-CH3 H H HC H Ethylene Menthene Br2 Br2 Bromine added here Br Br -H C-C H.C CH2 HC一CH C-CH HC 日 2004 Thomson/Brooks Cole
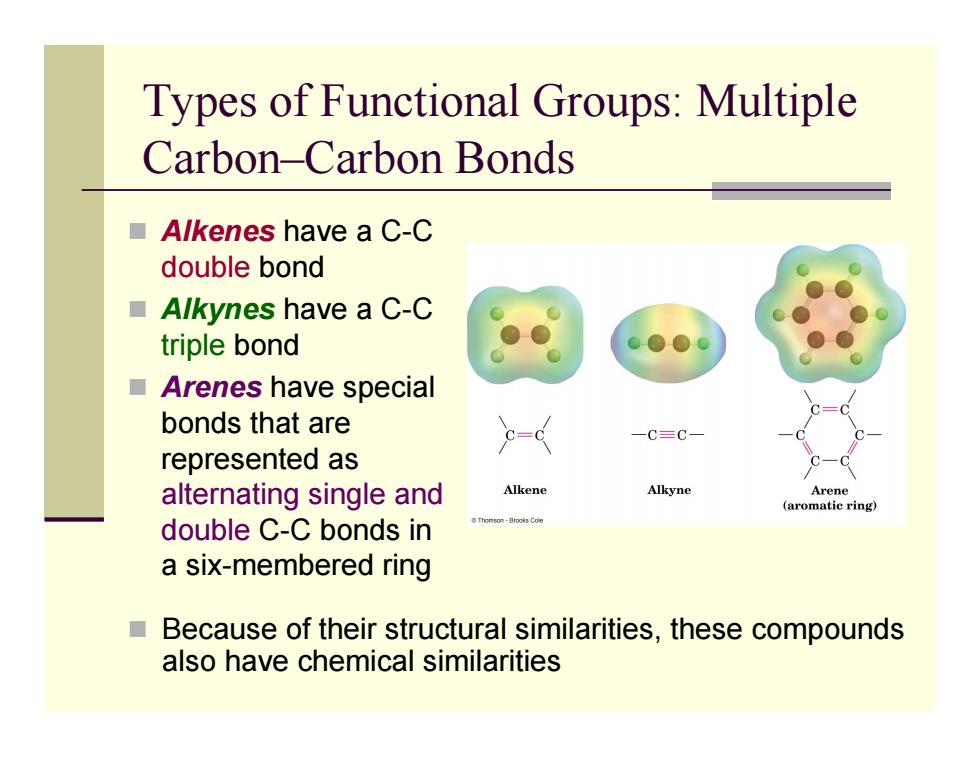
Types of Functional Groups:Multiple Carbon-Carbon Bonds ■Alkenes have a C-C double bond ■Alkynes have a C-C triple bond ■Arenes have special bonds that are 一C三C represented as alternating single and Alkene Alkyne Arene (aromatic ring) double C-C bonds in a six-membered ring Because of their structural similarities,these compounds also have chemical similarities
Types of Functional Groups: Multiple Carbon–Carbon Bonds Alkenes have a C-C double bond Alkynes have a C-C triple bond Arenes have special bonds that are represented as alternating single and double C-C bonds in a six-membered ring Because of their structural similarities, these compounds also have chemical similarities

Functional Groups with Carbon Singly Bonded to an Electronegative Atom Alkyl halide:C bonded to halogen (C-X) Alcohol:C bonded O of a hydroxyl group(C-OH) Ether:Two C's bonded to the same O(C-O-C) Amine:C bonded to N(C-N) ■ Thiol:C bonded to SH group(C-SH) ■ Sulfide:Two C's bonded to same S(C-S-C) Bonds are polar,with partial positive charge on C (+)and partial negative charge(⑧-)on electronegative atom
Functional Groups with Carbon Singly Bonded to an Electronegative Atom Alkyl halide: C bonded to halogen (C-X ) Alcohol: C bonded O of a hydroxyl group ( C OH ) Ether: Two C’s bonded to the same O ( C O C ) Amine : C bonded to N ( C N ) Thiol : C bonded to SH group ( C SH ) Sulfide: Two C’s bonded to same S ( C S C ) Bonds are polar, with partial positive charge on C ( δ+) and partial negative charge (δ−) on electronegative atom