
Groups with a Carbon-Oxygen Double Bond (Carbonyl Groups) Aldehyde:one hydrogen bonded to C=O Ketone:two C's bonded to the C=O Carboxylic acid:-OH bonded to the C=O Ester:C-O bonded to the C=O Amide:C-N bonded to the C=O Acid chloride:CI bonded to the C=O ■Carbonyl C has partial positive charge(δ+) Carbonyl O has partial negative charge(5-)
Groups with a Carbon–Oxygen Double Bond (Carbonyl Groups) Aldehyde: one hydrogen bonded to C=O Ketone: two C’s bonded to the C=O Carboxylic acid: ⎯OH bonded to the C=O Ester: C-O bonded to the C=O Amide: C-N bonded to the C=O Acid chloride: Cl bonded to the C=O Carbonyl C has partial positive charge ( δ+) Carbonyl O has partial negative charge ( δ-)

Alkanes and Alkane Isomers Alkanes:Compounds with C-C single bonds and C-H bonds only(no functional groups) ■ Connecting carbons can lead to large or small molecules The formula for an alkane with no rings in it must be C H2n+2 where the number of C's is n ■ Alkanes are saturated with hydrogen(no more can be added They are also called aliphatic compounds HH HHH HHHH H一C-H H-C-C-H H-C-C-C-H H-C-C-C-C-H ...and so on H HH HHH H丑HH Methaneosca Ethane Propane Butane
Alkanes and Alkane Isomers Alkanes: Compounds with C-C single bonds and C-H bonds only (no functional groups) Connecting carbons can lead to large or small molecules The formula for an alkane with no rings in it must be C n H2n+2 where the number of C’s is n Alkanes are saturated with hydrogen (no more can be added They are also called aliphatic compounds
Alkane Isomers ■ CH4=methane,C2H6=ethane,C3H8=propane The molecular formula of an alkane with more than three carbons can give more than one structure Ca(butane)=butane and isobutane Cs(pentane)=pentane,2-methylbutane,and 2,2- dimethylpropane Alkanes with C's connected to no more than 2 other C's are straight-chain or normal alkanes Alkanes with one or more C's connected to 3 or 4 C's are branched-chain alkanes
Alkane Isomers CH 4 = methane, C 2 H 6 = ethane, C 3 H 8= propane The molecular formula of an alkane with more than three carbons can give more than one structure C4 (butane) = butane and isobutane C5 (pentane) = pentane, 2-methylbutane, and 2,2- dimethylpropane Alkanes with C’s connected to no more than 2 other C’s are straight-chain or normal alkanes Alkanes with one or more C’s connected to 3 or 4 C’s are branched-chain alkanes
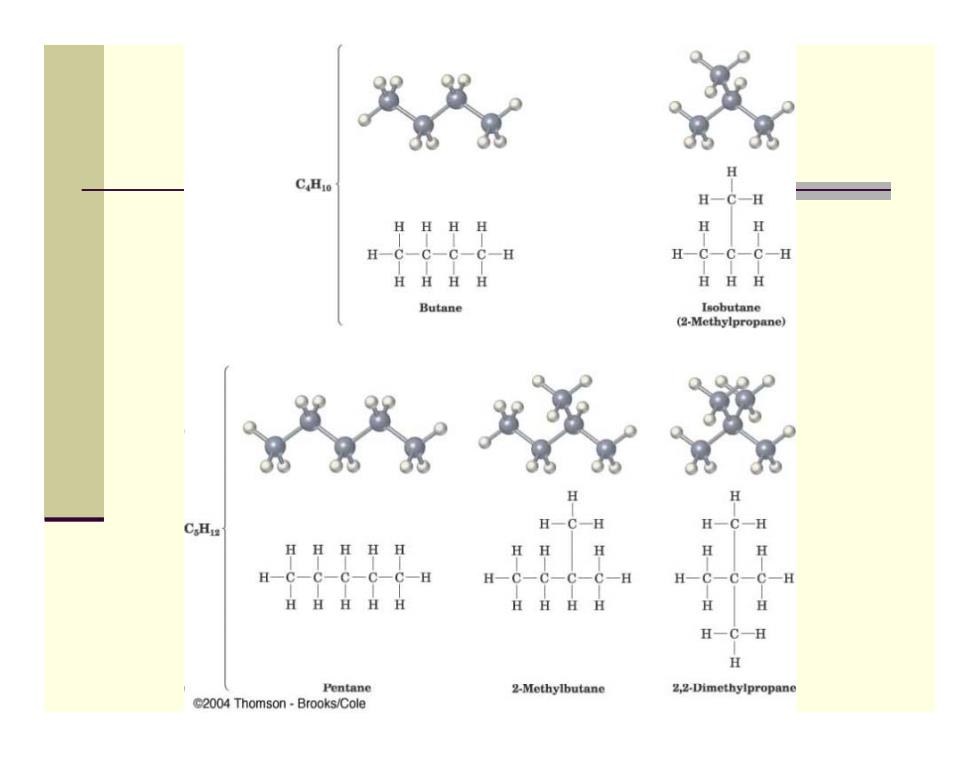
H-C一C-C一H HHH Butane Isobutane (2-Methylpropane) C.Hiz H H H H一C H Pentane 2-Methylbutane 2,2-Dimethylpropane 2004 Thomson Brooks/Cole