
Splicing Signals(剪接信号) Splicing signals in nuclear mRNA precursors are remarkably uniform -First 2 bases of introns are GU Last 2 are AG -Exon/GU-intron-AG/exon 5'-and 3'-splice sites have consensus sequences extending beyond GU and AG motifs 一 5'-AG/GUAAGU-intron-YNCURAC-YnNAG/exon Y:pyrimidine;Yn:about 9 pyrimidine;R:purine; Whole consensus sequences are important to proper splicing Abnormal splicing can occur when the consensus sequences are mutated 14-6
14-6 Splicing Signals (剪接信号) ✓ Splicing signals in nuclear mRNA precursors are remarkably uniform – First 2 bases of introns are GU – Last 2 are AG – Exon/ GU-intron- AG/ exon ✓ 5’- and 3’-splice sites have consensus sequences extending beyond GU and AG motifs – 5’- AG/ GUAAGU-intron- YNCURAC-YnNAG/ exon Y: pyrimidine; Yn: about 9 pyrimidine; R: purine; ✓ Whole consensus sequences are important to proper splicing ✓ Abnormal splicing can occur when the consensus sequences are mutated
14.2 Mechanism of Splicing of Nuclear mRNA Precursors Intermediate in nuclear mRNA precursor splicing is branched-looks like a lariat(套索) √2-step model -2'-OH group of adenosine nucleotide in middle of intron attacks phosphodiester bond between 1st exon and G beginning of intron Forms loop of the lariat Separates first exon from intron -3'-OH left at end of 1st exon attacks phosphodiester bond linking intron to 2nd exon Forms the exon-exon phosphodiester bond Releases intron in lariat form at same time 14-7
14-7 14.2 Mechanism of Splicing of Nuclear mRNA Precursors ✓ Intermediate in nuclear mRNA precursor splicing is branched – looks like a lariat (套索) ✓ 2-step model – 2’-OH group of adenosine nucleotide in middle of intron attacks phosphodiester bond between 1 st exon and G beginning of intron • Forms loop of the lariat • Separates first exon from intron – 3’-OH left at end of 1st exon attacks phosphodiester bond linking intron to 2nd exon • Forms the exon-exon phosphodiester bond • Releases intron in lariat form at same time
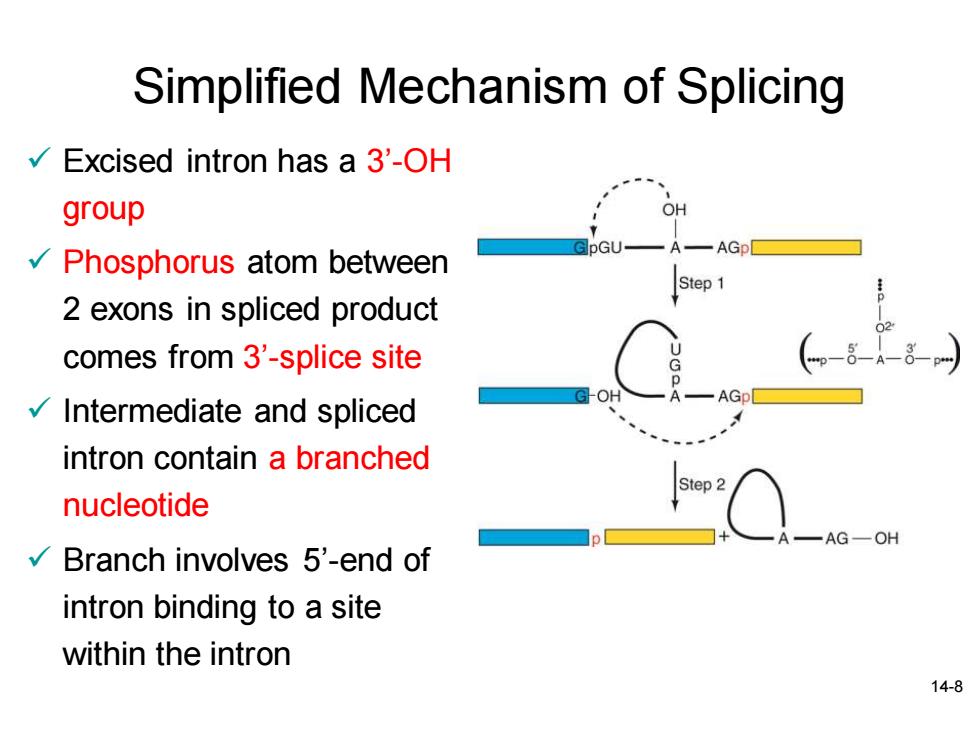
Simplified Mechanism of Splicing Excised intron has a 3'-OH group Phosphorus atom between Step 1 2 exons in spliced product comes from 3'-splice site AGD Intermediate and spliced intron contain a branched Step 2 nucleotide -AG-OH Branch involves 5'-end of intron binding to a site within the intron 14-8
14-8 Simplified Mechanism of Splicing ✓ Excised intron has a 3’-OH group ✓ Phosphorus atom between 2 exons in spliced product comes from 3’-splice site ✓ Intermediate and spliced intron contain a branched nucleotide ✓ Branch involves 5’-end of intron binding to a site within the intron
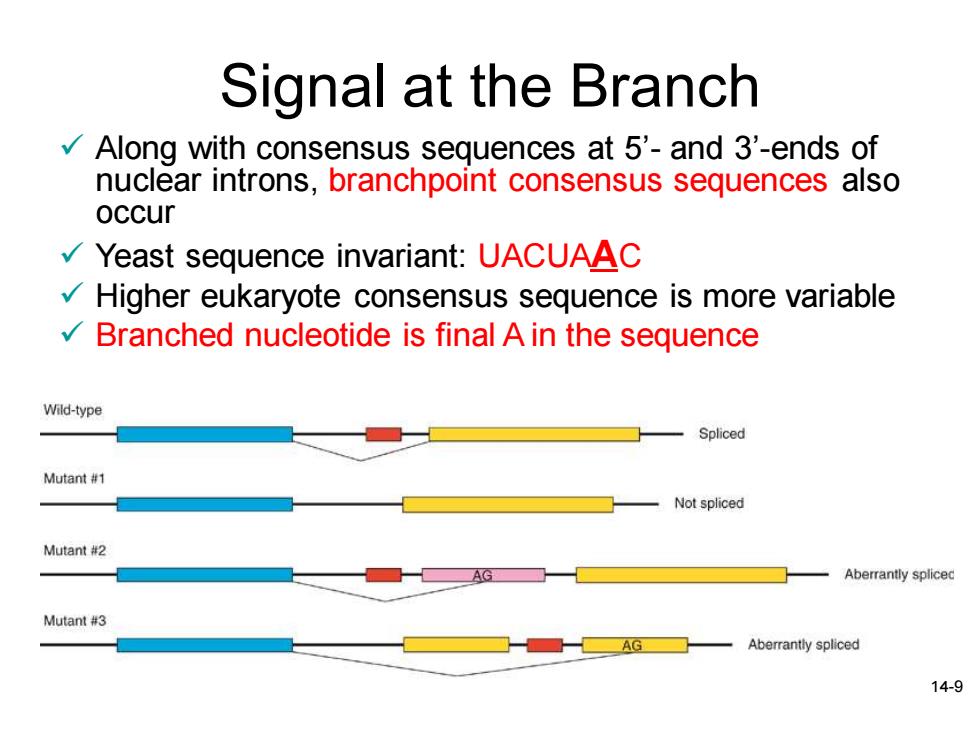
Signal at the Branch Along with consensus sequences at 5'-and 3'-ends of nuclear introns,branchpoint consensus sequences also occur Yeast sequence invariant:UACUAAC Higher eukaryote consensus sequence is more variable Branched nucleotide is final A in the sequence Wild-type Spliced Mutant #1 Not spliced Mutant#2 Aberrantly splicec Mutant #3 Aberrantly spliced 14-9
14-9 Signal at the Branch ✓ Along with consensus sequences at 5’- and 3’-ends of nuclear introns, branchpoint consensus sequences also occur ✓ Yeast sequence invariant: UACUAAC ✓ Higher eukaryote consensus sequence is more variable ✓ Branched nucleotide is final A in the sequence

Spliceosomes(剪接体) Splicing takes place on a particle called a spliceosome Spliceosomes contain the pre-mRNA -Along with snRNPs (small nuclear ribonuclearprotein,核内小核糖核蛋白体)and protein splicing factors -These recognize key splicing signals and orchestrate(组织)the splicing process 14-10
14-10 Spliceosomes (剪接体) ✓Splicing takes place on a particle called a spliceosome ✓Spliceosomes contain the pre-mRNA – Along with snRNPs (small nuclear ribonuclearprotein, 核内小核糖核蛋白体) and protein splicing factors – These recognize key splicing signals and orchestrate (组织) the splicing process