
Chapter 6 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes
Chapter 6 The mechanism of transcription in prokaryotes
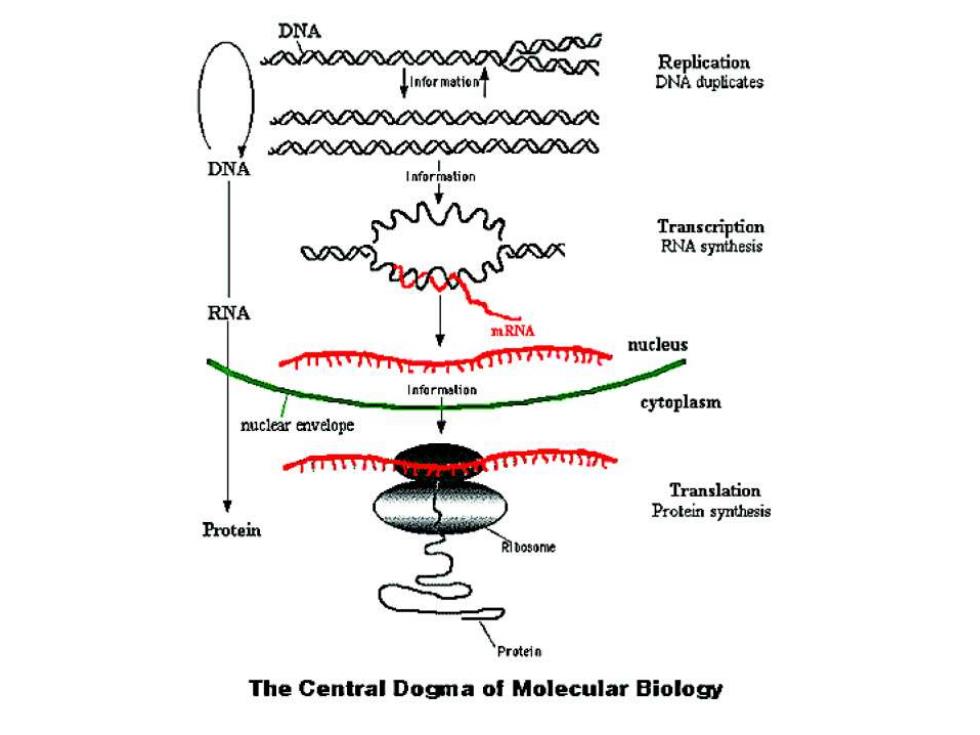
DNA aooogo Replication 叶 DNA duplicates NNV八X000a0 N八V八aa八NN DNA Transcription RNA synthesis RNA MRNA nucleus cytoplasm nuclear envelope T Translation Protein synthesis Protein Protein The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology
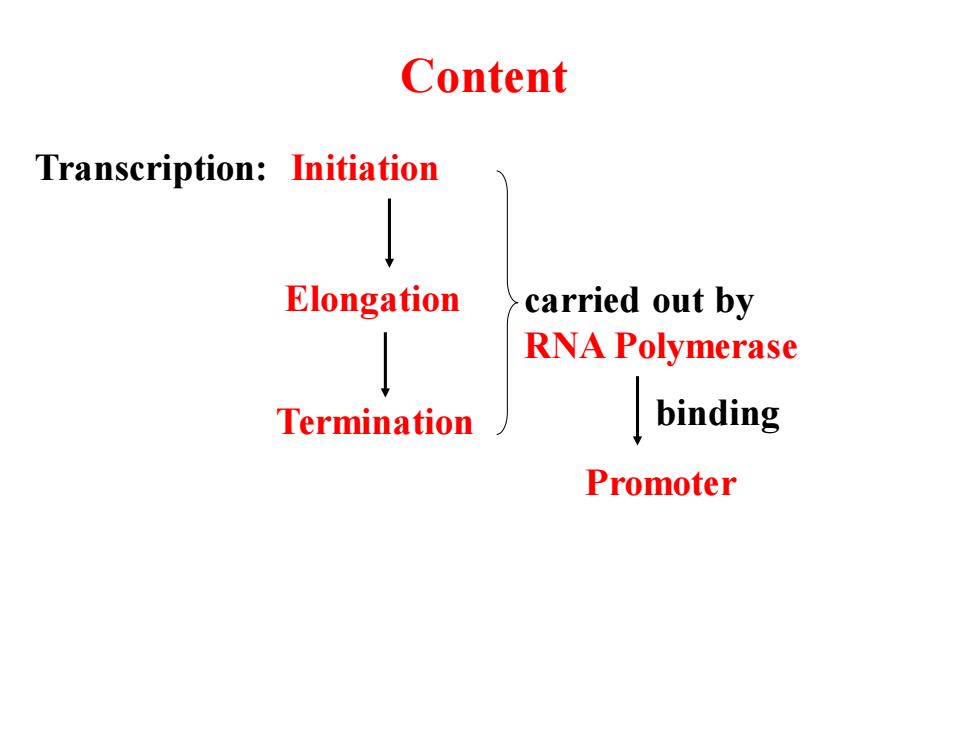
Content Transcription:Initiation Elongation carried out by RNA Polymerase Termination binding Promoter
Transcription: Initiation Elongation Termination binding carried out by RNA Polymerase Promoter Content
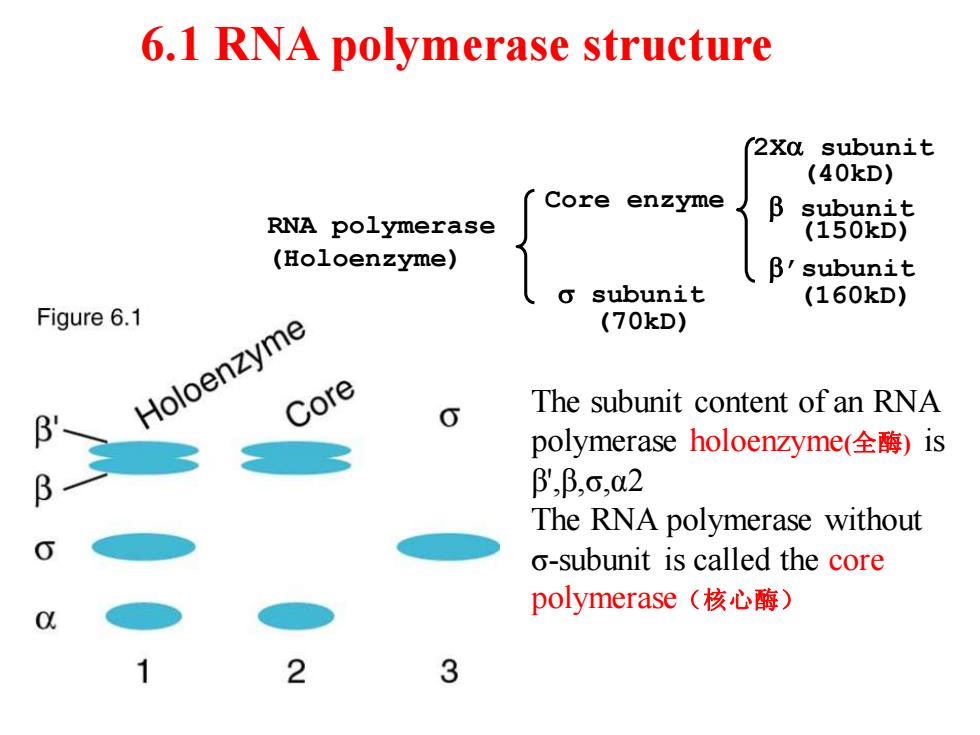
6.1 RNA polymerase structure 2Xa subunit (40kD) Core enzyme 】 B subunit RNA polymerase (150kD) (Holoenzyme) B'subunit subunit (160kD) Figure 6.1 (70kD) Holoenzyme Core The subunit content of an RNA polymerase holoenzyme(全酶)is β,β,o,02 The RNA polymerase without o-subunit is called the core polymerase(核心酶) 2 3
6.1 RNA polymerase structure RNA polymerase (Holoenzyme) Core enzyme 2Xa subunit b subunit b’subunit s subunit (150kD) (160kD) (40kD) (70kD) The subunit content of an RNA polymerase holoenzyme(全酶) is β',β,σ,α2 The RNA polymerase without σ-subunit is called the core polymerase(核心酶)
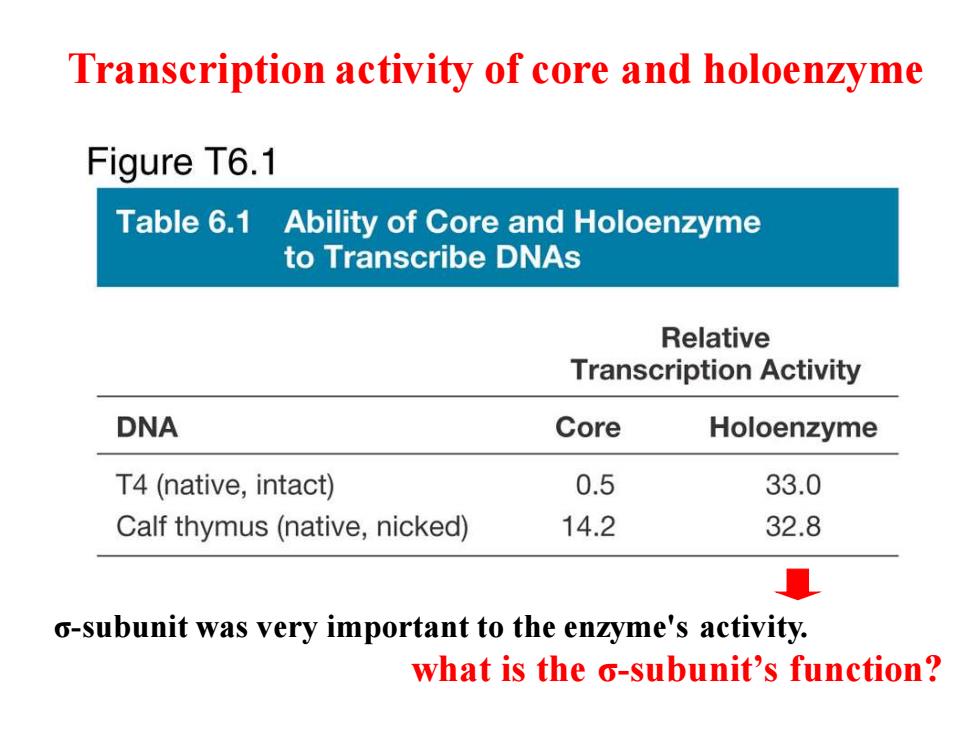
Transcription activity of core and holoenzyme Figure T6.1 Table 6.1 Ability of Core and Holoenzyme to Transcribe DNAs Relative Transcription Activity DNA Core Holoenzyme T4(native,intact) 0.5 33.0 Calf thymus(native,nicked) 14.2 32.8 o-subunit was very important to the enzyme's activity. what is the o-subunit's function?
Transcription activity of core and holoenzyme σ-subunit was very important to the enzyme's activity. what is the σ-subunit’s function?