
Copyright The McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 17 The mechanism of translation I:initiation
Chapter 17 The mechanism of translation I: initiation
Initiation Translation了 Elongation Termination mRNA →Protein(peptide) Ribosome (factories) tRNA (adaptors)
Translation mRNA Protein (peptide) Ribosome (factories) tRNA (adaptors) Initiation Elongation Termination

Bacteria (recall operons)can dive into an initiation site in the middle of an mRNA; Eukaryotic ribosomes usually only need to find the single 5'initiation site
Bacteria (recall operons) can dive into an initiation site in the middle of an mRNA; Eukaryotic ribosomes usually only need to find the single 5’ initiation site

17.1 Initiation of prokaryotes -Before translation initiation -tRNA charging -Dissociation of ribosome -Formation of the 30s initiation complex -The first codon and the first aminoacyl tRNA -Binding mRNA to the 30s Ribosomeal subunit -Binding fMet-tRNAfMet to the 30s initiation complex -Formation of the 70s initiation complex
17.1 Initiation of prokaryotes -Before translation initiation -tRNA charging -Dissociation of ribosome -Formation of the 30S initiation complex -The first codon and the first aminoacyl tRNA -Binding mRNA to the 30S Ribosomeal subunit -Binding fMet-tRNAfMet to the 30S initiation complex -Formation of the 70S initiation complex
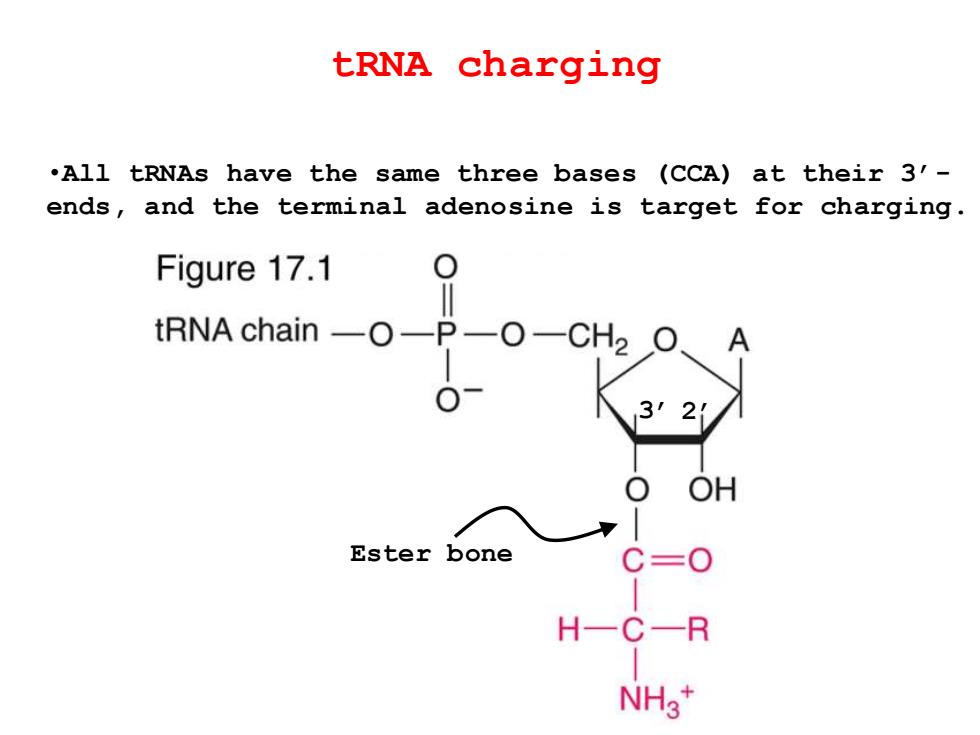
tRNA charging .All tRNAs have the same three bases (CCA)at their 3'- ends,and the terminal adenosine is target for charging. Figure 17.1 tRNA chain -O-P-C OH Ester bone H-C-R H3*
tRNA charging •All tRNAs have the same three bases (CCA) at their 3’- ends, and the terminal adenosine is target for charging. 3’ 2’ Ester bone