CopyrightThe McGraw-Hill Companies,Inc.Permission required for reproduction or display. Chapter 4 Molecular Cloning Methods
Chapter 4 Molecular Cloning Methods

Why do biologists must clone genes? The molecular structure and function of the human growth hormone(hGH)gene [base sequence?promoter? Hypopituitary(垂体功能衰减的)d小warfism(侏儒症)?] You have to purify enough of the gene to study-probably about a milligram.A milligram is an overwhelming amount when you imagine purifying it from whole human DNA.And you would not know how to separate the gene from all the rest of the DNA. Gene cloning neatly solves these problems.In this chapter we will see how to clone genes in bacteria and in eukaryotes( 核细胞)
Why do biologists must clone genes? The molecular structure and function of the human growth hormone(hGH)gene [base sequence? promoter? Hypopituitary (垂体功能衰减的) dwarfism (侏儒症)?] You have to purify enough of the gene to study-probably about a milligram. A milligram is an overwhelming amount when you imagine purifying it from whole human DNA.And you would not know how to separate the gene from all the rest of the DNA. Gene cloning neatly solves these problems. In this chapter we will see how to clone genes in bacteria and in eukaryotes(真 核细胞).
4.1 Gene Cloning(Molecular Cloning) Clone:a group of identical cells or organisms/molecular Gene cloning:The process of inserting a piece of DNA molecular (foreign gene into a DNA carrier (vector)and making multiple copies of the DNA of interest in a host cell,such as bacteria Purposes of molecular cloning 1.Isolation of a gene from a pool of genetic materials 2.Amplification of a gene 3.Manipulation of a piece of DNA for further experiments Vector(DNA carrier):Plasmids(质粒)/Bateriophage(噬菌体 YAC(yeast artificial chromosome,人工酵母染色体)/BAC(Bacteria artificial chromosome,人工细菌染色体)/Cosmids(粘粒)Virus Restriction Endonucleases,ligase
4.1 Gene Cloning(Molecular Cloning) Clone:a group of identical cells or organisms/molecular Gene cloning: The process of inserting a piece of DNA molecular (foreign gene ) into a DNA carrier (vector) and making multiple copies of the DNA of interest in a host cell, such as bacteria Purposes of molecular cloning 1. Isolation of a gene from a pool of genetic materials 2. Amplification of a gene 3. Manipulation of a piece of DNA for further experiments Vector (DNA carrier): Plasmids(质粒)/Bateriophage(噬菌体 /YAC(yeast artificial chromosome, 人工酵母染色体)/ BAC(Bacteria artificial chromosome, 人工细菌染色体)/ Cosmids(粘粒)/Virus Restriction Endonucleases, ligase
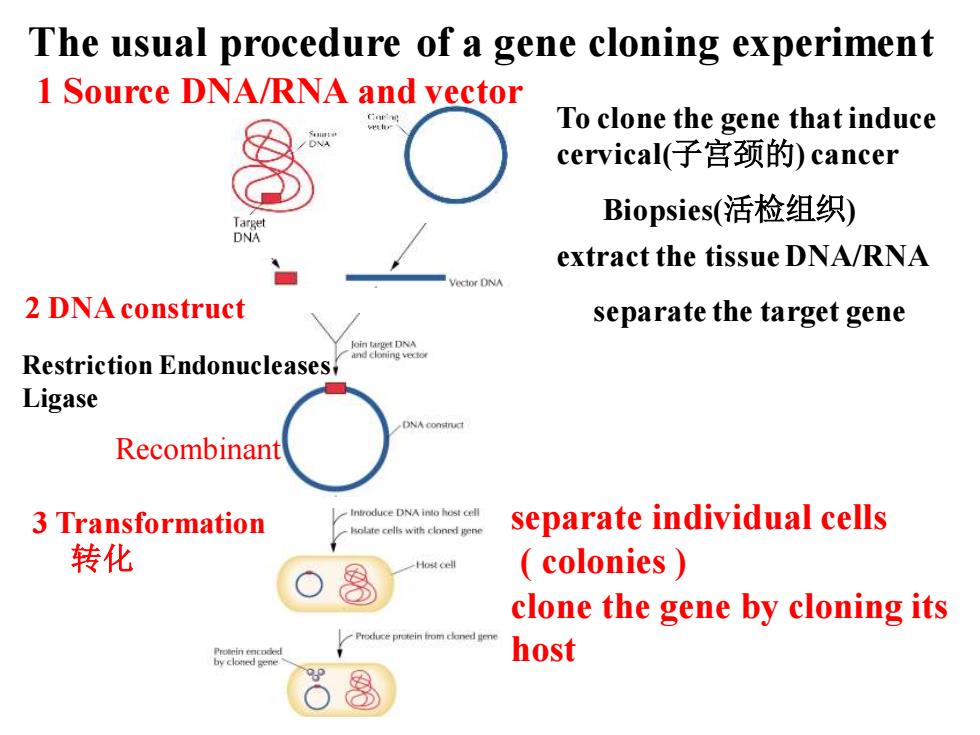
The usual procedure of a gene cloning experiment 1 Source DNA/RNA and vector To clone the gene that induce cervical(子宫颈的)cancer Biopsies(活检组织) DNA extract the tissue DNA/RNA ector DNA 2 DNA construct separate the target gene Restriction Endonucleases Ligase DNA comstruct Recombinant 3 Transformation Introduce DNA into host cell lsolate cells with cloned gene separate individual cells 转化 ho以cel colonies clone the gene by cloning its host
The usual procedure of a gene cloning experiment To clone the gene that induce cervical(子宫颈的) cancer Biopsies(活检组织) extract the tissue DNA/RNA 1 Source DNA/RNA and vector 2 DNA construct separate the target gene 3 Transformation 转化 Recombinant separate individual cells ( colonies ) clone the gene by cloning its host Restriction Endonucleases Ligase
Restriction Endonucleases(限制性核酸内切酶) -The Molecular Scissors The enzymes would cut DNA at specific sites->molecular knives ,or Molecular Scissors. Host enzymes that prevent the invasion of foreign DNAs such as viral DNA,by cutting them up. Restriction These enzymes cut within the foreign DNAs,rather than chewing them away from the ends. Endonucleases
Restriction Endonucleases(限制性核酸内切酶) -The Molecular Scissors Host enzymes that prevent the invasion of foreign DNAs such as viral DNA, by cutting them up. These enzymes cut within the foreign DNAs, rather than chewing them away from the ends. Restriction Endonucleases The enzymes would cut DNA at specific sites→molecular knives ,or Molecular Scissors