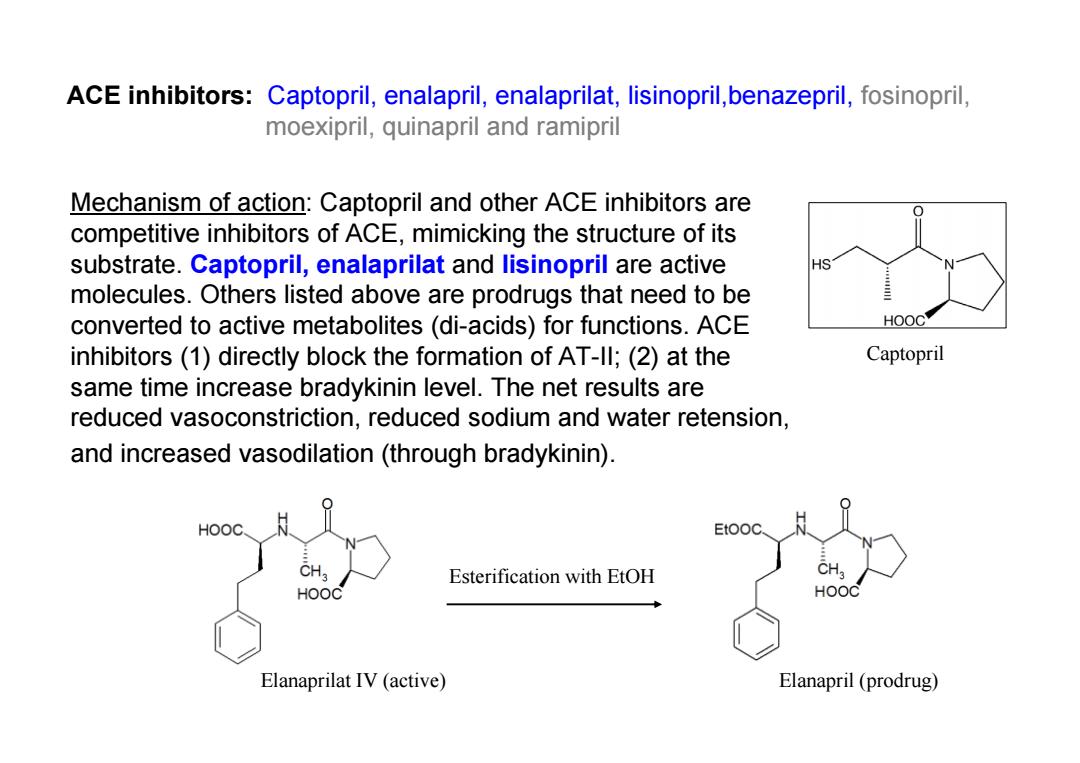
ACE inhibitors:Captopril,enalapril,enalaprilat,lisinopril,benazepril,fosinopril, moexipril,quinapril and ramipril Mechanism of action:Captopril and other ACE inhibitors are competitive inhibitors of ACE,mimicking the structure of its substrate.Captopril,enalaprilat and lisinopril are active molecules.Others listed above are prodrugs that need to be converted to active metabolites(di-acids)for functions.ACE inhibitors(1)directly block the formation of AT-Il;(2)at the Captopril same time increase bradykinin level.The net results are reduced vasoconstriction,reduced sodium and water retension, and increased vasodilation(through bradykinin). HOOC Etooc Esterification with EtOH HOOC HOOC Elanaprilat IV (active) Elanapril(prodrug)
ACE inhibitors: Captopril, enalapril, enalaprilat, lisinopril,benazepril, fosinopril, moexipril, quinapril and ramipril Mechanism of action: Captopril and other ACE inhibitors are competitive inhibitors of ACE, mimicking the structure of its substrate. Captopril, enalaprilat and lisinopril are active molecules. Others listed above are prodrugs that need to be converted to active metabolites (di-acids) for functions. ACE inhibitors (1) directly block the formation of AT-II; (2) at the same time increase bradykinin level. The net results are reduced vasoconstriction, reduced sodium and water retension, and increased vasodilation (through bradykinin). Captopril Esterification with EtOH Elanaprilat IV (active) Elanapril (prodrug)
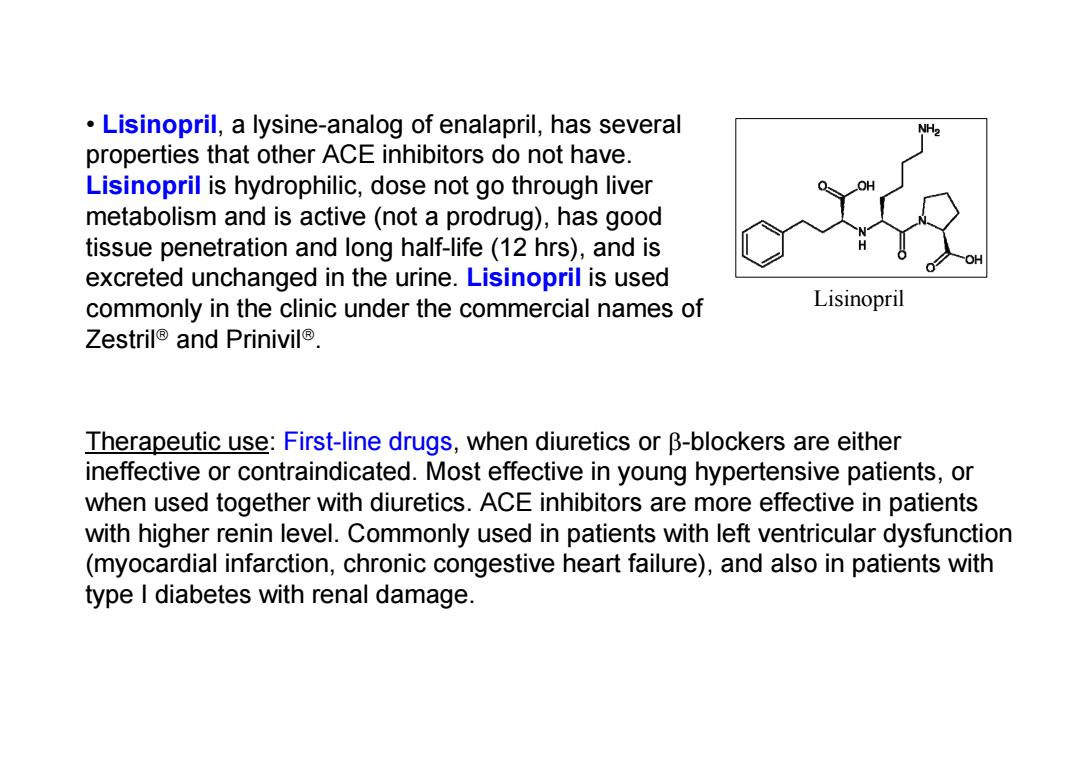
Lisinopril,a lysine-analog of enalapril,has several properties that other ACE inhibitors do not have. Lisinopril is hydrophilic,dose not go through liver metabolism and is active(not a prodrug),has good tissue penetration and long half-life(12 hrs),and is excreted unchanged in the urine.Lisinopril is used commonly in the clinic under the commercial names of Lisinopril Zestril and Prinivil. Therapeutic use:First-line drugs,when diuretics or B-blockers are either ineffective or contraindicated.Most effective in young hypertensive patients,or when used together with diuretics.ACE inhibitors are more effective in patients with higher renin level.Commonly used in patients with left ventricular dysfunction (myocardial infarction,chronic congestive heart failure),and also in patients with type I diabetes with renal damage
• Lisinopril, a lysine-analog of enalapril, has several properties that other ACE inhibitors do not have. Lisinopril is hydrophilic, dose not go through liver metabolism and is active (not a prodrug), has good tissue penetration and long half-life (12 hrs), and is excreted unchanged in the urine. Lisinopril is used commonly in the clinic under the commercial names of Zestril and Prinivil. Lisinopril Therapeutic use: First-line drugs, when diuretics or -blockers are either ineffective or contraindicated. Most effective in young hypertensive patients, or when used together with diuretics. ACE inhibitors are more effective in patients with higher renin level. Commonly used in patients with left ventricular dysfunction (myocardial infarction, chronic congestive heart failure), and also in patients with type I diabetes with renal damage

Adverse effects and toxicity:In hypovolemic patients,severe hypotension may occur after initial doses.Fetotoxic and should not be used in pregnant women. Other adverse effects:Angioedema,dry cough,rashes,altered taste,and proteinuria,and hyperkalemia(especially when used with K+-sparing diuretics)
Adverse effects and toxicity: In hypovolemic patients, severe hypotension may occur after initial doses. Fetotoxic and should not be used in pregnant women. Other adverse effects: Angioedema, dry cough, rashes, altered taste, and proteinuria, and hyperkalemia (especially when used with K+-sparing diuretics)

Angiotensin-ll receptor antagonists. Losartan(FDA approval in 1995)and valsartan are non-peptide antagonists of AT-lI receptor.Other non-peptide antagonists of this class include candesartan,irbesartan,telmisartan(Micardis), eprosartan,zolasartan and valsartan(Diovan). These are products of rational drug design.Some of these are in various stages of clinical development.Saralasin is a peptide analog and competitive inhibitor of AT-ll receptor,but is orally ineffective and requires continuous intravenous infusion.Saralasin also has partial agonist activity,and is not currently used for hypertension treatment. Mechanism of action:Competitive inhibition of AT-ll receptor(Type 1),thereby (1)inhibiting the vasoconstrictor effect of AT-ll;(2)prevent the release of aldosterone.Effect is more specific on AT-ll action,and less or none on bradykinin production or metabolism
Angiotensin-II receptor antagonists. Losartan (FDA approval in 1995) and valsartan are non-peptide antagonists of AT-II receptor. Other non-peptide antagonists of this class include candesartan, irbesartan, telmisartan (Micardis ®), eprosartan, zolasartan and valsartan (Diovan ®). These are products of rational drug design. Some of these are in various stages of clinical development. Saralasin is a peptide analog and competitive inhibitor of AT-II receptor, but is orally ineffective and requires continuous intravenous infusion. Saralasin also has partial agonist activity, and is not currently used for hypertension treatment. Mechanism of action: Competitive inhibition of AT-II receptor (Type 1), thereby (1) inhibiting the vasoconstrictor effect of AT-II; (2) prevent the release of aldosterone. Effect is more specific on AT-II action, and less or none on bradykinin production or metabolism

Therapeutic use:Clinical use is similar to ACE inhibitors.Losartan has the advantage of not causing dry cough and angioedema,which are side effects of ACE inhibitors through their bradykinin-increasing action. Adverse effects and toxicity:Similar to those of ACE inhibitors.AT-lI antagonists are also fetotoxic and should not be used for treating hypertension in pregnant women
Therapeutic use: Clinical use is similar to ACE inhibitors. Losartan has the advantage of not causing dry cough and angioedema, which are side effects of ACE inhibitors through their bradykinin-increasing action. Adverse effects and toxicity: Similar to those of ACE inhibitors. AT-II antagonists are also fetotoxic and should not be used for treating hypertension in pregnant women