
Addition Addition involves introducing information into the drawing that is either non-visual or non-architectur- al.It may be information about function or use,or tell us something about the underlying geometrical system,such as axes and zones.Generally speaking such information is added once the drawing has been stripped of as much superfluous and distract- ing data as possible (i.e.has been reduced). Demontage Drawing the object for analysis as though it had been taken apart can bring out the relationship between components or aspects of the design. Juxtaposing or superimposing drawings,giving complementary information,can be helpful when examining the relationship between different systems in the design,whether these be several stories or several layers in a plan.It is also possible to draw the object as though it had been blown apart.Graphically termed an exploded view,this type of drawing helps to provide insight into the relationship between many elements. Giambattista Nolli,map of Rome,1748.re- markable in that it makes a distinction between public and private space.Nolli shows not only the street as public space but freely accessible interior space as well Material protegido por derechos de autor
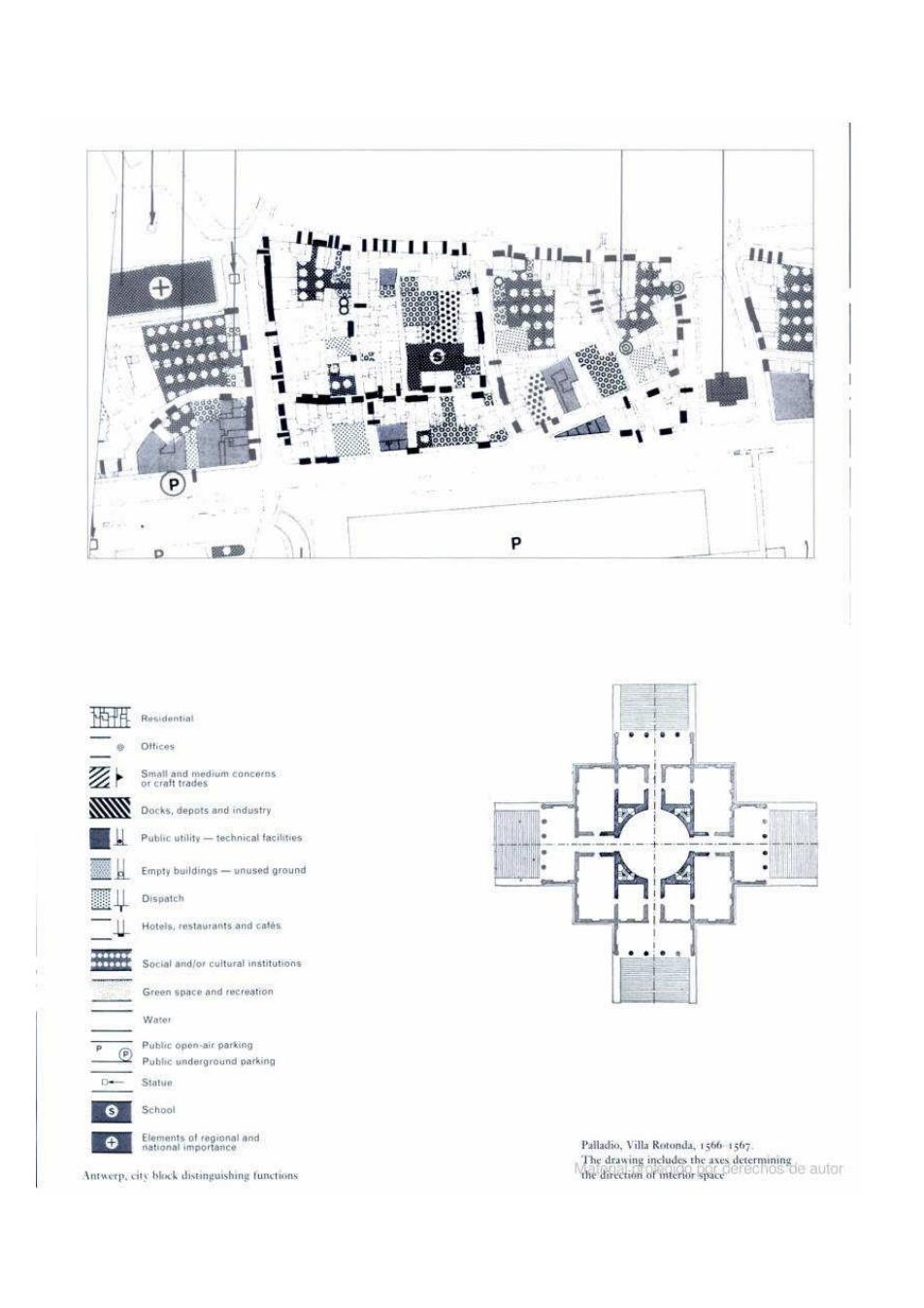
IIM111-I 8 P 班 Oftice等 哑 Docks,depots and industry 圆以 Public utility-technical facitities e h Empty buildings-unused ground 蟹↓ Dispatch 二 Hotels,restaurants and cates Social and/or cultural institutions Green space and recreation 三 Water Public open-air parking Public underground parking 0- Statue School Palladio,Villa Rotonda.1566 1567 The drawing inude the dee Antwerp.city block distinguishing functions the direction of interior space
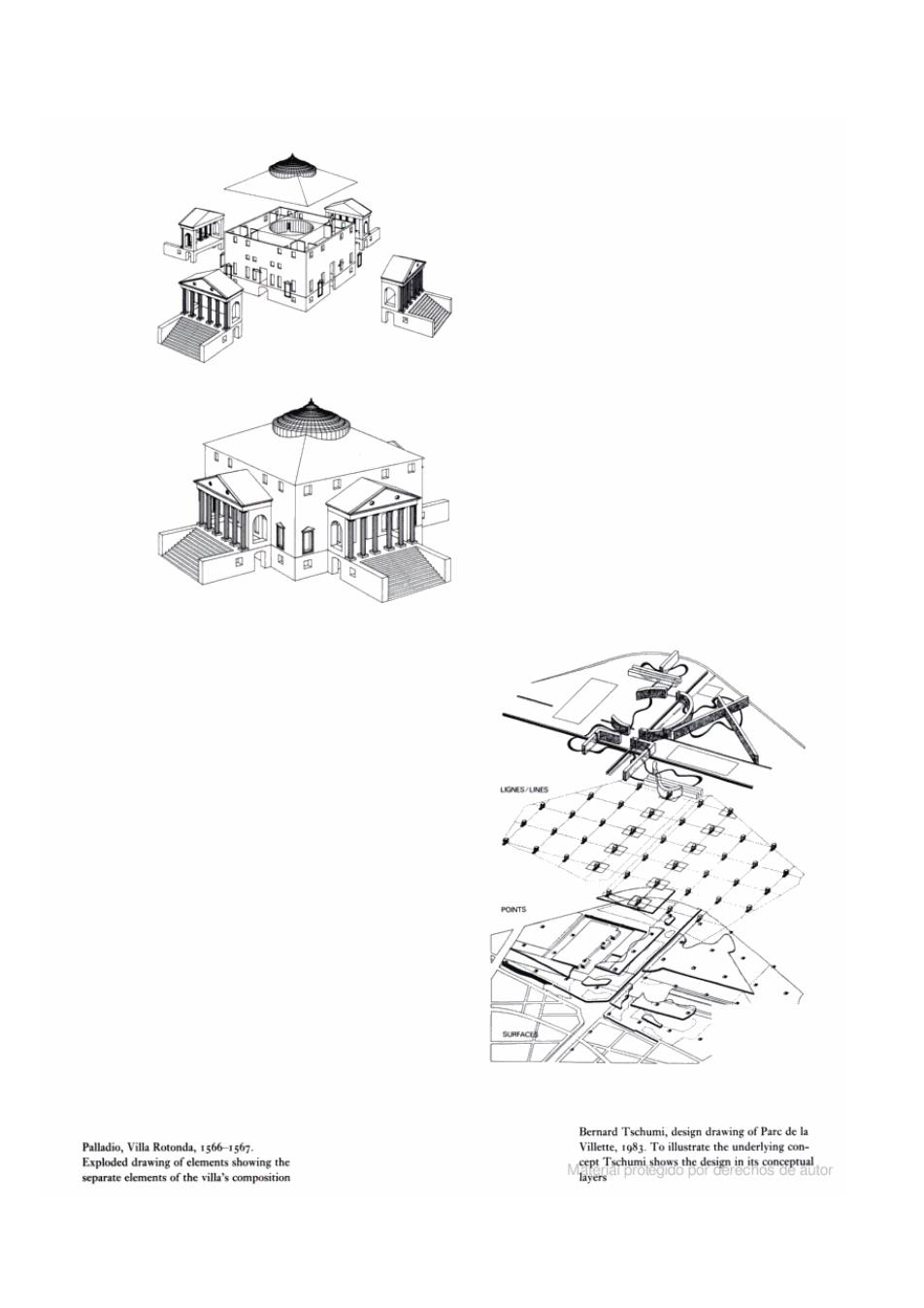
9® Bernard Tschumi,design drawing of Parc de la Palladio,Villa Rotonda,1566-1567. Villette,1983.To illustrate the underlying con- Exploded drawing of elements showing the separate elements of the villa's composition layers

2 Order and composition Material protegido por derechos de autor

DESIGN AND ANALYSIS 2.I Introduction 24 A points grid of i20 x t2o meters with a folly at every point,a grid also there to relate to the sur- In (hapter I we examined the broad lines of the rounding urban fabric.Then there is a system of design process.We saw how aspects such as form, lines,a covered axial intersection as main access.. type and context affect the ordering of a design,a and a fanciful promenade architecturale along the process deseribed as the"black box."Chapter 2 theme gardens.Third,there is a system of planes takes a look inside this black box. larger spaces meant for open-air activities,bounded by taut rows of trees.' Material and space Both descriptions use technical terms.On the Whether designing a house,part of a city,a garden. one hand,they draw on concepts that refer to the a park or a landscape,the design is predicated upon elements of which the design is constructed-follies, a composition of spaces and material.In a house circular domed chamber and porticoes.On the other, these are the rooms as against the exterior and they include terms that describe how these interior walls,in a park the open spaces.paths and components are treated and arranged into a whole, lawns as against the trees,and in a city the open such as points grid of 120 x 120 meters and fanciful spaces of streets and squares as against buildings promenade architecturale in Le Parc de la Villette and and trees alike. axial line in the Villa Rotonda. Activities take place in the spaces;this is where the prugram is situated.Broadly speaking.form, Elements place and the nature of the material dictate the Every design,then,can be broken down into spatial qualities of that space.Thus the quality of a square and material elements.Spatial elements include is governed by the form,place,nature and function cupboards,rooms and urban squares,whereas door of buildings around it,and the form,nature and knobs,walls,building blocks and clumps of trees quality of the enfolding materials determine the come under objects or material elements. quality of a room in a house. The components or elements that constitute a When designers or crities must describe how a design are designated in part with terms referring to design is composed without the aid of drawings, existing components most probably used on more they resort to technical terms.The Danish architect than one occasion,such as the porticoes of the Villa Steen Rasmussen,for example,describes Palladio's Rotonda and Tschumi's follies.We can then speak Villa Rotonda thus:"Most famous of all the villas of types (see Chapter 5). was the so-called Villa Rotunda,an almost square Some elements are described in terms of their block with a large,colonnaded portico on all four basic geometric form,such as the circular domed sides.Ascending the broad flight of stairs to one of chamber,or a triangular space. the porticoes you are aware of the same composition The fanciful promenade confronts us with an of rooms as in the School of.ithens (a fresco of 1508 clement lacking a geometrically defined form. by the Italian renaissance painter Raphael which Evidently the designer shaped this element along shows a building with a like spatial composition intuitive lines. ed.).From the broad,open portico you enter the barrel-vaulted hall,which leads you into the circular domed chamber in the center.From there the axial line continues through a new barrel-vaulted hall out to the portico on the other side." The design by the Swiss architect Bernard Tschumi for the competition for Le Parc de la Villette in Paris has been described as follows: "The plan is characterized by the regularly disposed follies,all on the same principle but each with its own program of activities.In composition the scheme is a 'plan libre'based on three autonomous systems. Material protegido por derechos de autor