Basic Circuit Concepts Standard Convention -2-Terminal Devices Assign and-designations to terminals Arbitrary,but may have reasons to assign polarities in a particular way Device Positive current enters terminal Under Test Positive current leaves -terminal For 2-terminal devices, IIN must equal IoUT At the end,might find that V or I (or both)are negative That's OK-Just means that actual current or voltage is opposite of what was assumed Nomenclature ·Upper case:DC Variables→Vo ·Lower case:AC variables→v(t) Basic Electronics-Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 11 Gary Drake,Argonne National Lab-Session 1
Basic Electronics – Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 11 Gary Drake, Argonne National Lab – Session 1 Basic Circuit Concepts Standard Convention – 2-Terminal Devices • Assign + and – designations to terminals Arbitrary, but may have reasons to assign polarities in a particular way • Positive current enters + terminal • Positive current leaves – terminal • For 2-terminal devices, IIN must equal IOUT • At the end, might find that V or I (or both) are negative That’s OK – Just means that actual current or voltage is opposite of what was assumed Nomenclature • Upper case: DC Variables VO • Lower case: AC variables vo(t) Device Under Test I + V I
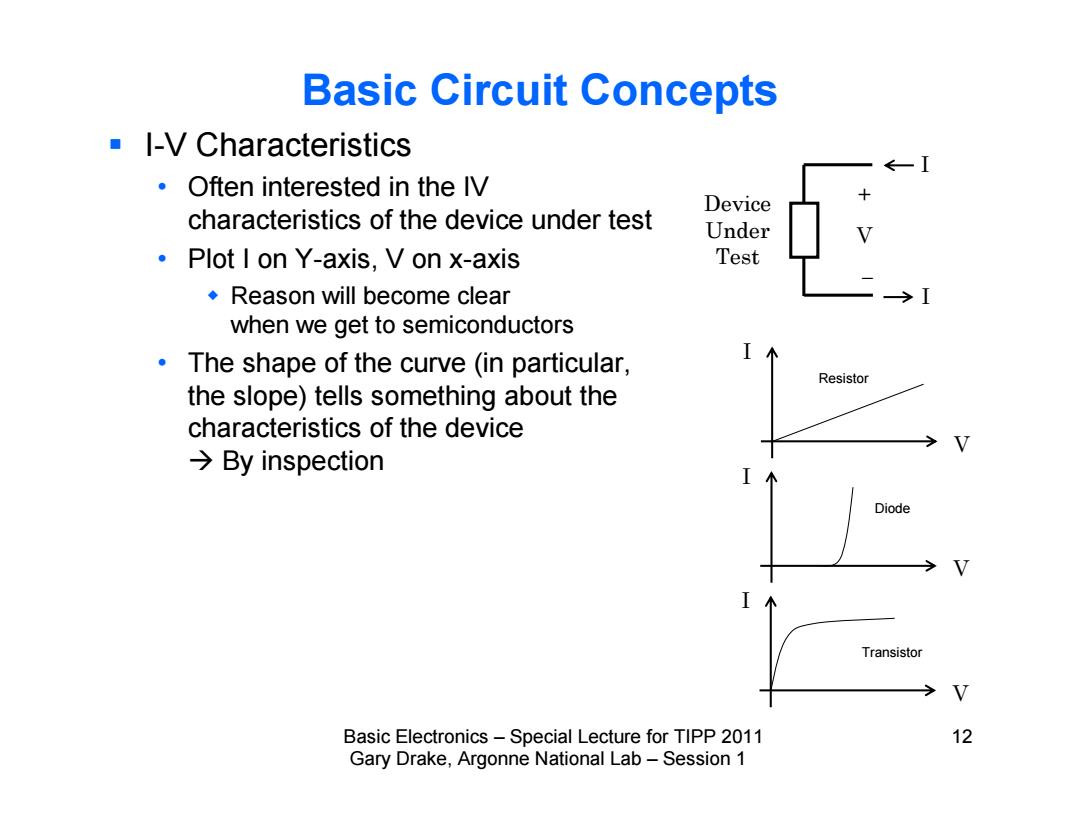
Basic Circuit Concepts ■l-V Characteristics ←一 Often interested in the IV Device characteristics of the device under test Under Plot I on Y-axis,V on x-axis Test Reason will become clear when we get to semiconductors The shape of the curve (in particular, Resistor the slope)tells something about the characteristics of the device →By inspection Diode Transistor Basic Electronics-Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 12 Gary Drake,Argonne National Lab-Session 1
Basic Electronics – Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 12 Gary Drake, Argonne National Lab – Session 1 Basic Circuit Concepts I-V Characteristics • Often interested in the IV characteristics of the device under test • Plot I on Y-axis, V on x-axis Reason will become clear when we get to semiconductors • The shape of the curve (in particular, the slope) tells something about the characteristics of the device By inspection Device Under Test I + V I V Resistor I I V Diode I V Transistor
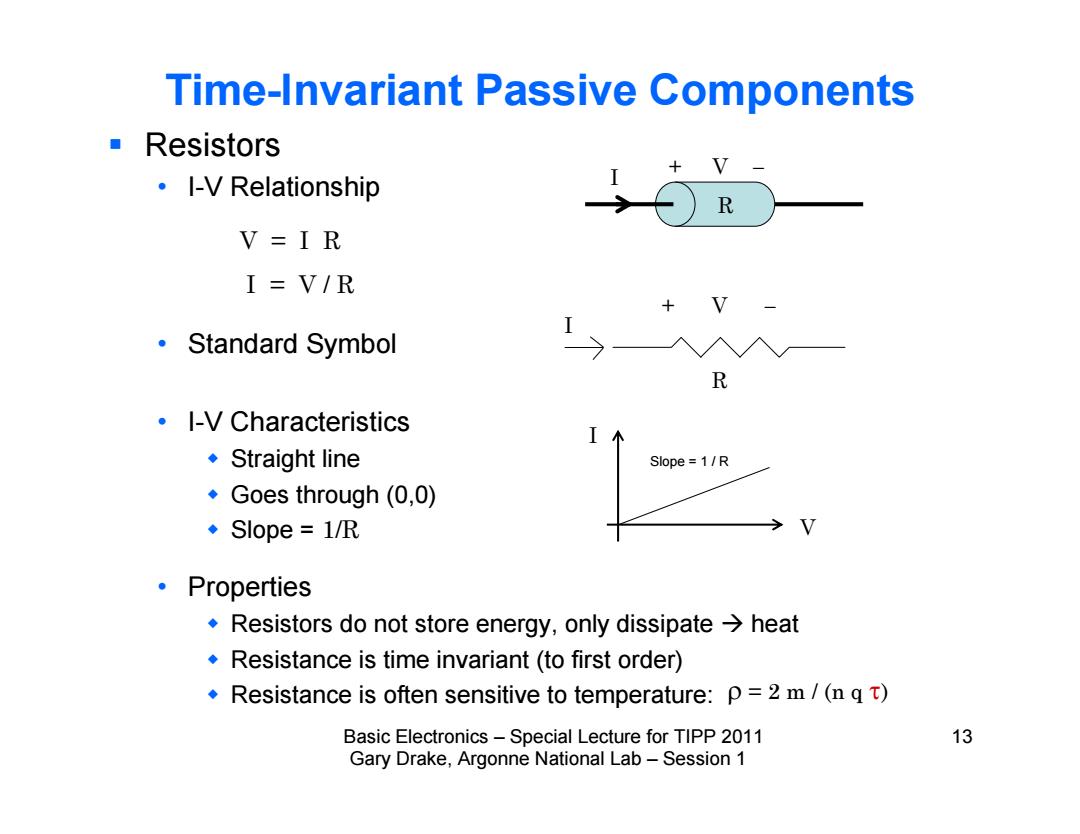
Time-Invariant Passive Components ■Resistors ·-V Relationship R V=IR I=V/R ·Standard Symbol ·-V Characteristics ◆Straight line Slope=1/R ·Goes through(0,0) ◆Slope=1/R ·Properties Resistors do not store energy,only dissipate>heat Resistance is time invariant(to first order) Resistance is often sensitive to temperature:p=2 m/(n qt) Basic Electronics-Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 13 Gary Drake,Argonne National Lab-Session 1
Basic Electronics – Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 13 Gary Drake, Argonne National Lab – Session 1 Time-Invariant Passive Components Resistors • I-V Relationship • Standard Symbol • I-V Characteristics Straight line Goes through (0,0) Slope = 1/R • Properties Resistors do not store energy, only dissipate heat Resistance is time invariant (to first order) Resistance is often sensitive to temperature: I + V R I + V R V = I R I = V / R I V Slope = 1 / R = 2 m / (n q )
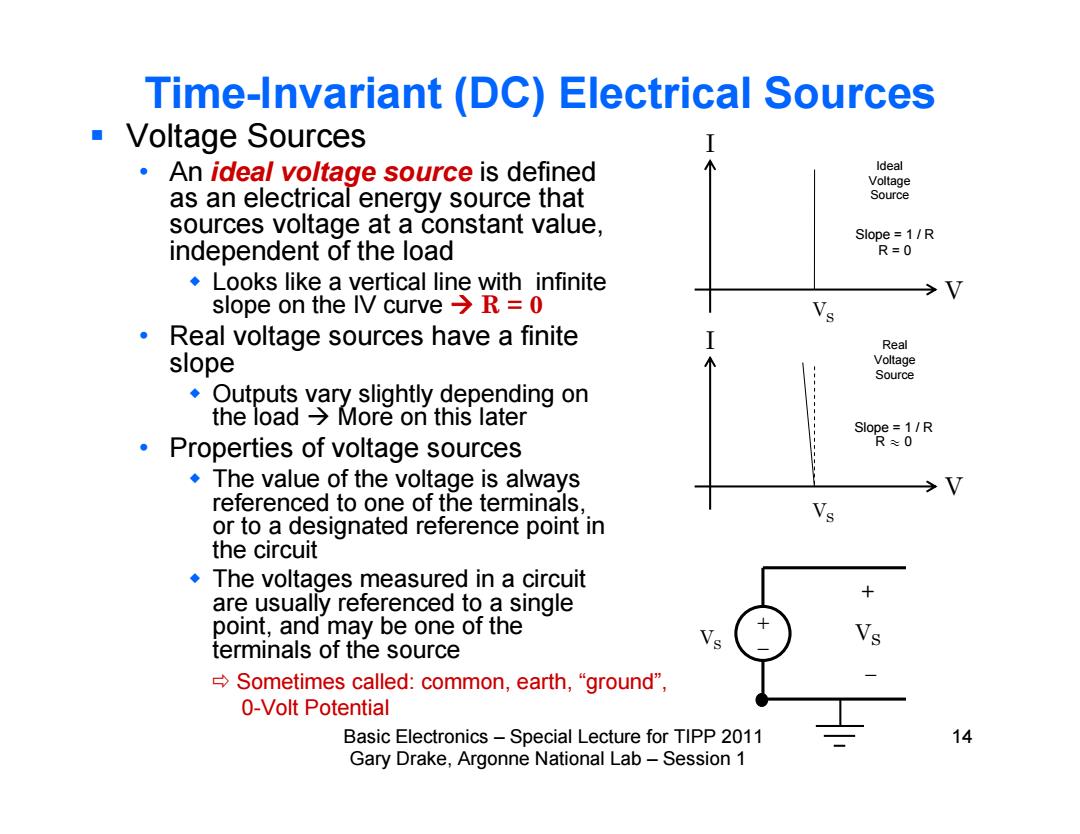
Time-Invariant (DC)Electrical Sources ■Voltage Sources An ideal voltage source is defined ldeal Voltage as an electrical energy source that Source sources voltage at a constant value, Slope =1/R independent of the load R=0 Looks like a vertical line with infinite slope on the IV curve >R=0 Real voltage sources have a finite I Real slope Voltage Source Outputs vary slightly depending on the load More on this later Slope =1/R Properties of voltage sources R≈0 The value of the voltage is always referenced to one of the terminals or to a designated reference point in the circuit The voltages measured in a circuit are usually referenced to a single point,and may be one of the terminals of the source →Sometimes called:common,earth,“ground", 0-Volt Potential Basic Electronics-Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 14 Gary Drake,Argonne National Lab-Session 1
Basic Electronics – Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 14 Gary Drake, Argonne National Lab – Session 1 Time-Invariant (DC) Electrical Sources Voltage Sources • An ideal voltage source is defined as an electrical energy source that sources voltage at a constant value, independent of the load Looks like a vertical line with infinite slope on the IV curve R = 0 • Real voltage sources have a finite slope Outputs vary slightly depending on the load More on this later • Properties of voltage sources The value of the voltage is always referenced to one of the terminals, or to a designated reference point in the circuit The voltages measured in a circuit are usually referenced to a single point, and may be one of the terminals of the source I V I V V S V S V S Ideal Voltage Source Real Voltage Source + V S Slope = 1 / R R = 0 Slope = 1 / R R y 0 Sometimes called: common, earth, “ground”, 0-Volt Potential
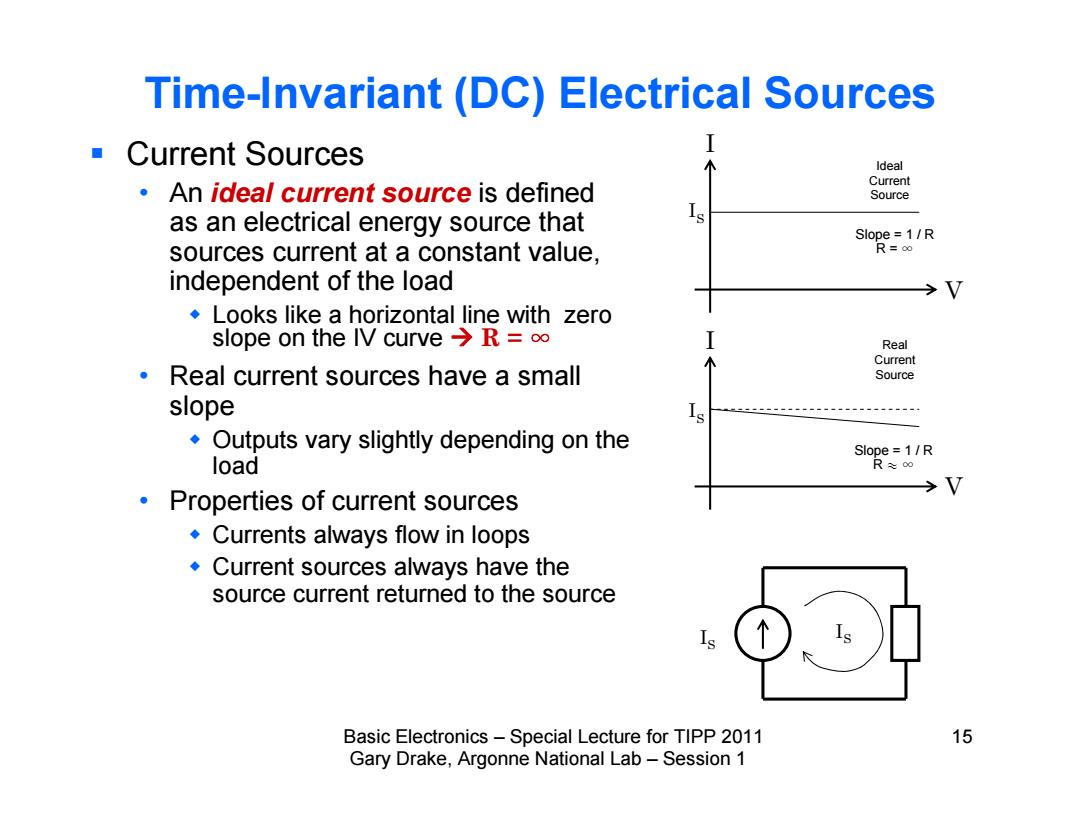
Time-Invariant (DC)Electrical Sources ■Current Sources Ideal Current An ideal current source is defined Source as an electrical energy source that 人 Slope=1/R sources current at a constant value, R=∞ independent of the load Looks like a horizontal line with zero slope on the IV curveR= Real Current Real current sources have a small Source slope Outputs vary slightly depending on the Slope=1/R load R00 →V Properties of current sources Currents always flow in loops Current sources always have the source current returned to the source Basic Electronics-Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 15 Gary Drake,Argonne National Lab-Session 1
Basic Electronics – Special Lecture for TIPP 2011 15 Gary Drake, Argonne National Lab – Session 1 Time-Invariant (DC) Electrical Sources Current Sources • An ideal current source is defined as an electrical energy source that sources current at a constant value, independent of the load Looks like a horizontal line with zero slope on the IV curve R = h • Real current sources have a small slope Outputs vary slightly depending on the load • Properties of current sources Currents always flow in loops Current sources always have the source current returned to the source I V I V IS IS IS Ideal Current Source Real Current Source IS Slope = 1 / R R = h Slope = 1 / R R y h