
Digital Image Processing Chapter 8: Image Compression-2
Digital Image Processing Chapter 8: Image Compression-2

Outline 1 Fundamentals 2 Some basic compression method ·Huffman coding ·Arithmetic coding ·LZW coding Block Transform coding ·Predictive coding
Outline 1 Fundamentals 2 Some basic compression method • Huffman coding • Arithmetic coding • LZW coding • Block Transform coding • Predictive coding • …
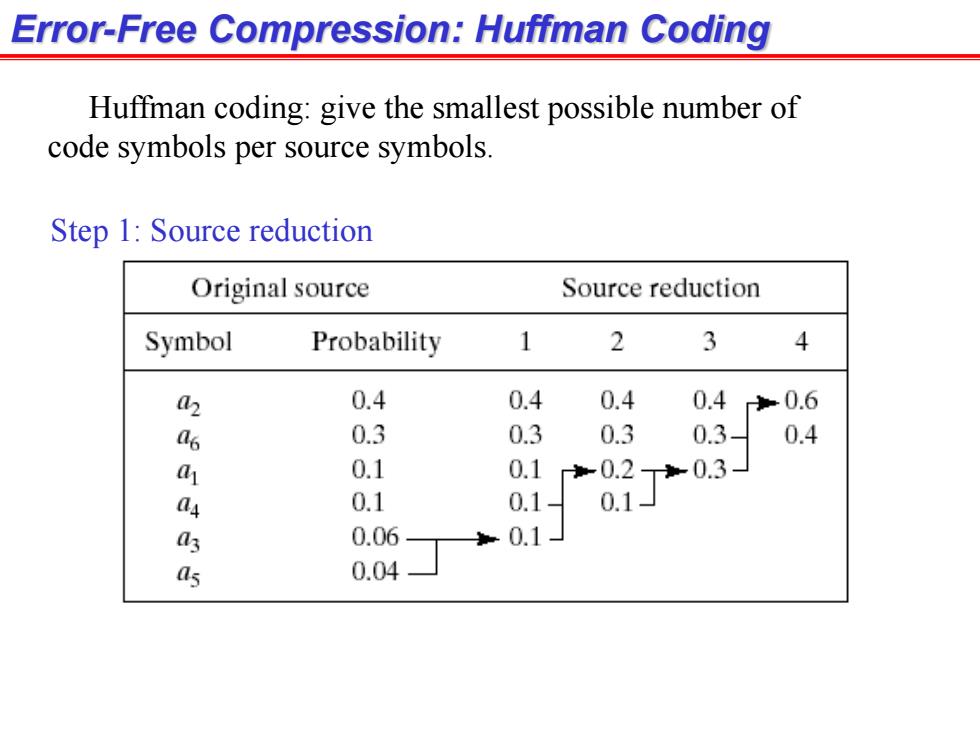
Error-Free Compression:Huffman Coding Huffman coding:give the smallest possible number of code symbols per source symbols. Step 1:Source reduction Original source Source reduction Symbol Probability 1 2 3 4 a 0.4 0.4 0.4 0.40.6 as 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.3 0.4 a 0.1 0.10.2 T0.3 4 0.1 0.1 0.1 as 0.06 0.1 as 0.04
Error-Free Compression: Huffman Coding Step 1: Source reduction Huffman coding: give the smallest possible number of code symbols per source symbols
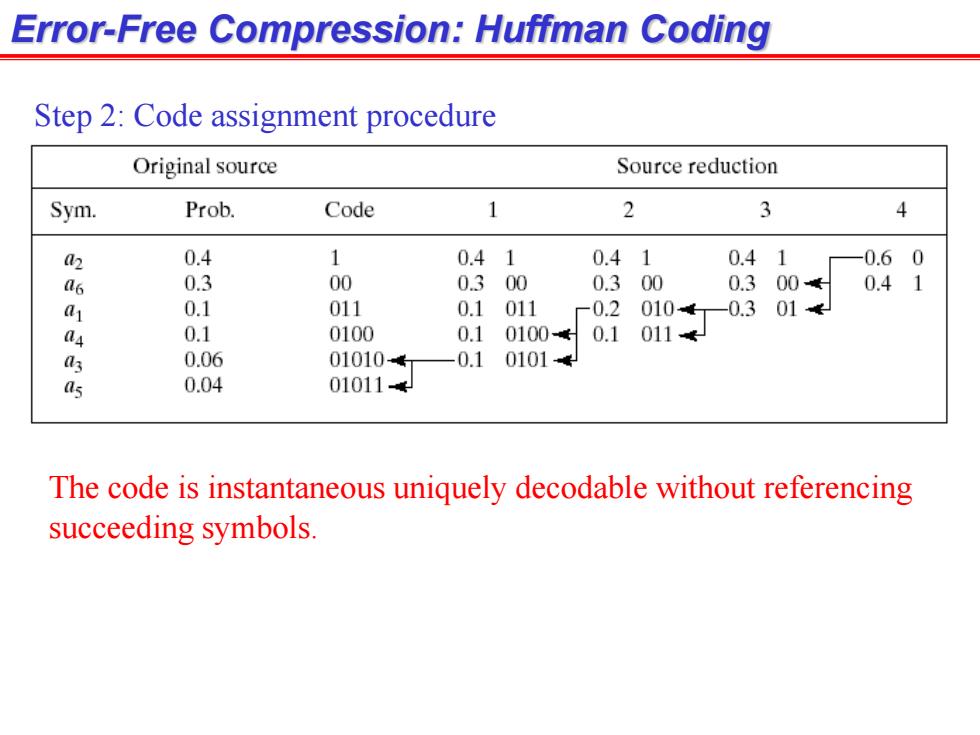
Error-Free Compression:Huffman Coding Step 2:Code assignment procedure Original source Source reduction Sym. Prob. Code 1 2 3 4 2 0.4 1 0.41 0.41 0.41 -0.60 as 0.3 00 0.300 0.300 0.300 0.41 a 0.1 011 0.1011 -0.2010-0.301← a4 0.1 0100 0.10100 0.1011 a3 0.06 010104 -0.101014 as 0.04 010114 The code is instantaneous uniquely decodable without referencing succeeding symbols
Error-Free Compression: Huffman Coding Step 2: Code assignment procedure The code is instantaneous uniquely decodable without referencing succeeding symbols
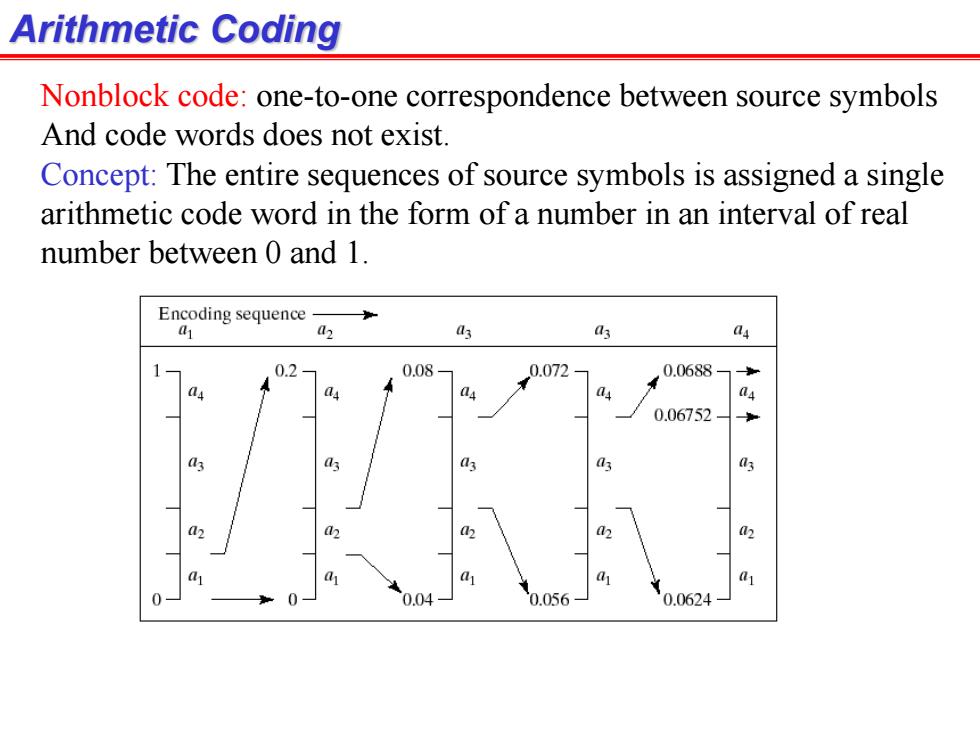
Arithmetic Coding Nonblock code:one-to-one correspondence between source symbols And code words does not exist. Concept:The entire sequences of source symbols is assigned a single arithmetic code word in the form of a number in an interval of real number between 0 and 1. Encoding sequence 41 9 0.2 0.08 0.072 0.0688 a4 0.06752 3 a 3 02 h 2 子 a a a 0.04 0.056 0.0624
Arithmetic Coding Nonblock code: one-to-one correspondence between source symbols And code words does not exist. Concept: The entire sequences of source symbols is assigned a single arithmetic code word in the form of a number in an interval of real number between 0 and 1