
Digital Image Processing Chapter 8: Image Compression-1
Digital Image Processing Chapter 8: Image Compression-1

Outline 1 Fundamentals 2 Some basic compression method ·Huffman coding ·Arithmetic coding ·LZW coding Block Transform coding ·Predictive coding
Outline 1 Fundamentals 2 Some basic compression method • Huffman coding • Arithmetic coding • LZW coding • Block Transform coding • Predictive coding • …

Image Compression Reducing the amount of data required to represent a digital image while keeping information as much as possible
Reducing the amount of data required to represent a digital image while keeping information as much as possible Image Compression
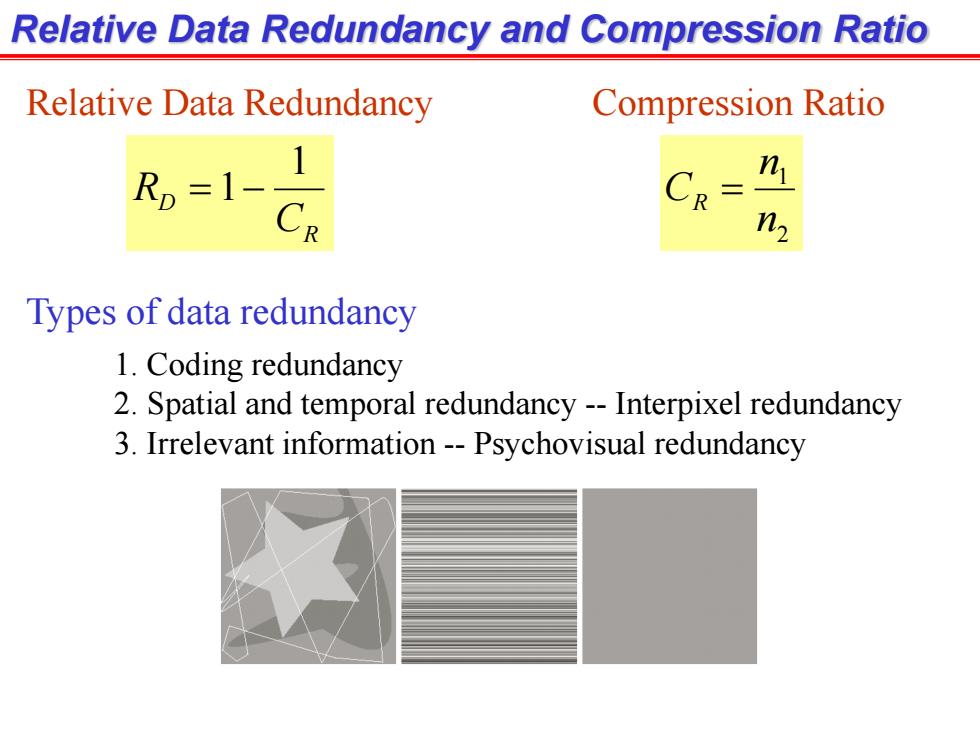
Relative Data Redundancy and Compression Ratio Relative Data Redundancy Compression Ratio R=1- n R n, Types of data redundancy 1.Coding redundancy 2.Spatial and temporal redundancy--Interpixel redundancy 3.Irrelevant information--Psychovisual redundancy
Relative Data Redundancy and Compression Ratio R D C R 1 1 Relative Data Redundancy Compression Ratio 2 1 n n CR Types of data redundancy 1. Coding redundancy 2. Spatial and temporal redundancy -- Interpixel redundancy 3. Irrelevant information -- Psychovisual redundancy
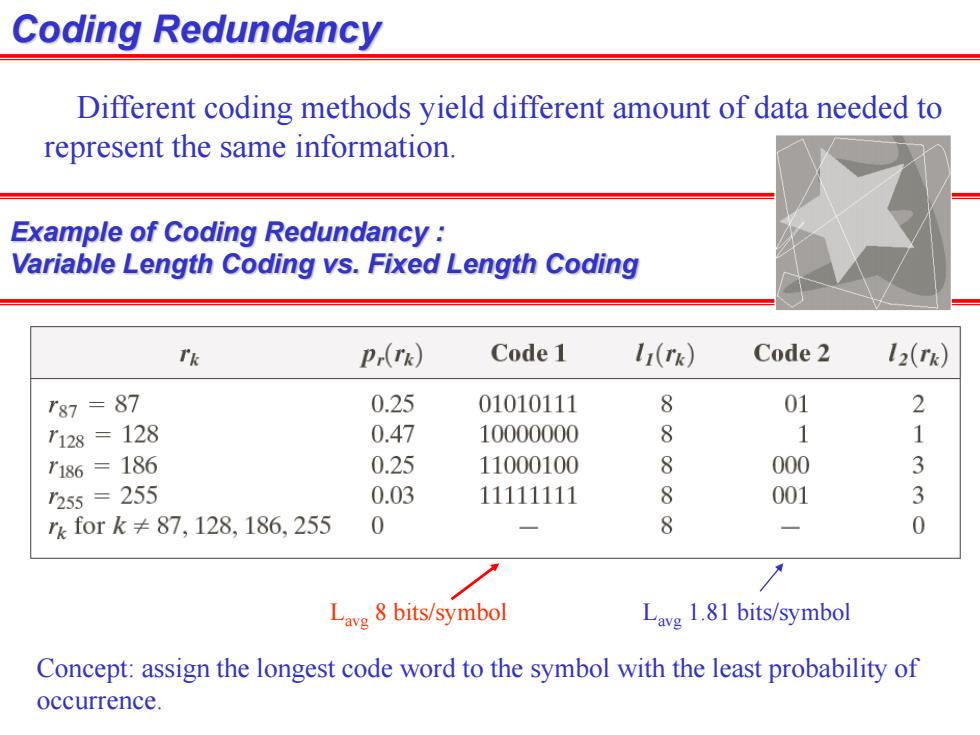
Coding Redundancy Different coding methods yield different amount of data needed to represent the same information. Example of Coding Redundancy Variable Length Coding vs.Fixed Length Coding Tk Pr(rk) Code 1 11(rk) Code2 12(Tk) T87=87 0.25 01010111 8 01 2 7128=128 0.47 10000000 8 1 7186=186 0.25 11000100 8 000 3 255=255 0.03 11111111 8 001 3 rk for k≠87,128,186,255 0 一 8 0 Lav8 bits/symbol Lavg 1.81 bits/symbol Concept:assign the longest code word to the symbol with the least probability of occurrence
Coding Redundancy Different coding methods yield different amount of data needed to represent the same information. Example of Coding Redundancy : Variable Length Coding vs. Fixed Length Coding Lavg 8 bits/symbol Lavg 1.81 bits/symbol Concept: assign the longest code word to the symbol with the least probability of occurrence