
Digital Image Processing Chapter 8: Image Compression-3
Digital Image Processing Chapter 8: Image Compression-3
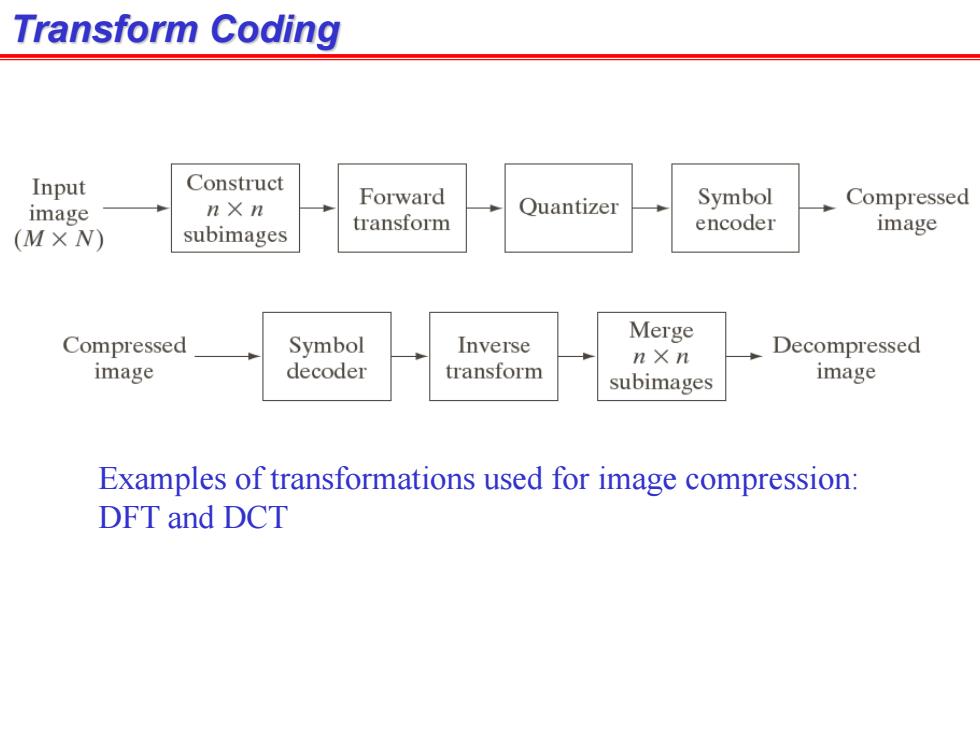
Transform Coding Input Construct n X n Forward Quantizer Symbol Compressed image encoder (M×N) subimages transform image Compressed Symbol Inverse Merge nX n Decompressed image decoder transform subimages image Examples of transformations used for image compression: DFT and DCT
Transform Coding Examples of transformations used for image compression: DFT and DCT
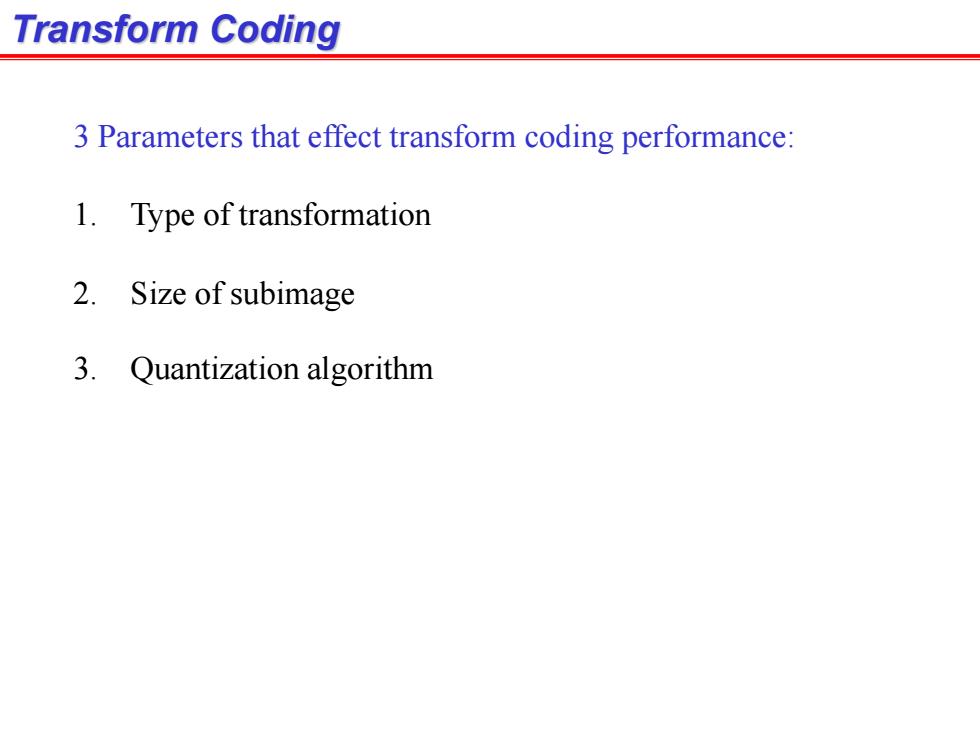
Transform Coding 3 Parameters that effect transform coding performance: 1.Type of transformation 2.Size of subimage 3.Quantization algorithm
Transform Coding 3 Parameters that effect transform coding performance: 1. Type of transformation 2. Size of subimage 3. Quantization algorithm
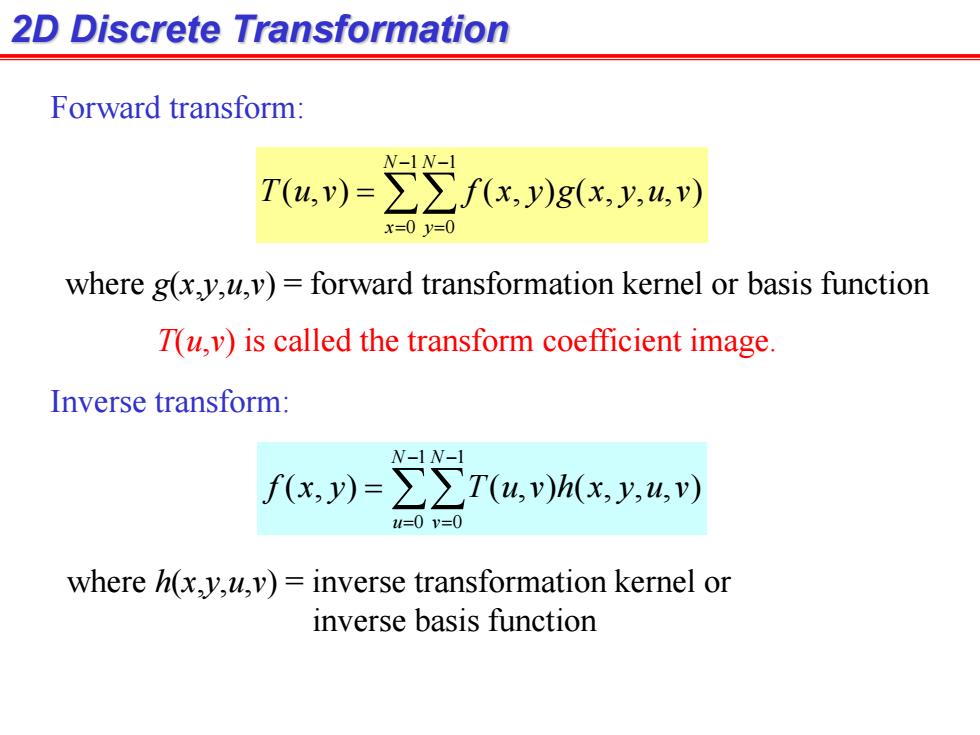
2D Discrete Transformation Forward transform: W-1N- T(4,)=∑∑fx,y)g(x,y,4,) x=0y=0 where g(xy,u,v)=forward transformation kernel or basis function T(u,v)is called the transform coefficient image. Inverse transform: N-1N-1 f(x,y)=∑∑T(u,)h(x,y,4,) 2u=0v=0 where h(x,y,u,v)=inverse transformation kernel or inverse basis function
2D Discrete Transformation 1 0 1 0 ( , ) ( , ) ( , , , ) N x N y T u v f x y g x y u v Forward transform: 1 0 1 0 ( , ) ( , ) ( , , , ) N u N v f x y T u v h x y u v Inverse transform: where g(x,y,u,v) = forward transformation kernel or basis function where h(x,y,u,v) = inverse transformation kernel or inverse basis function T(u,v) is called the transform coefficient image

Transform Example: ·Fourier Transform Walsh-Hadamard Transform Discrete Cosine Transform Karhunen-Loeve Transform
Transform Example: • Fourier Transform • Walsh-Hadamard Transform • Discrete Cosine Transform • Karhunen-Loeve Transform