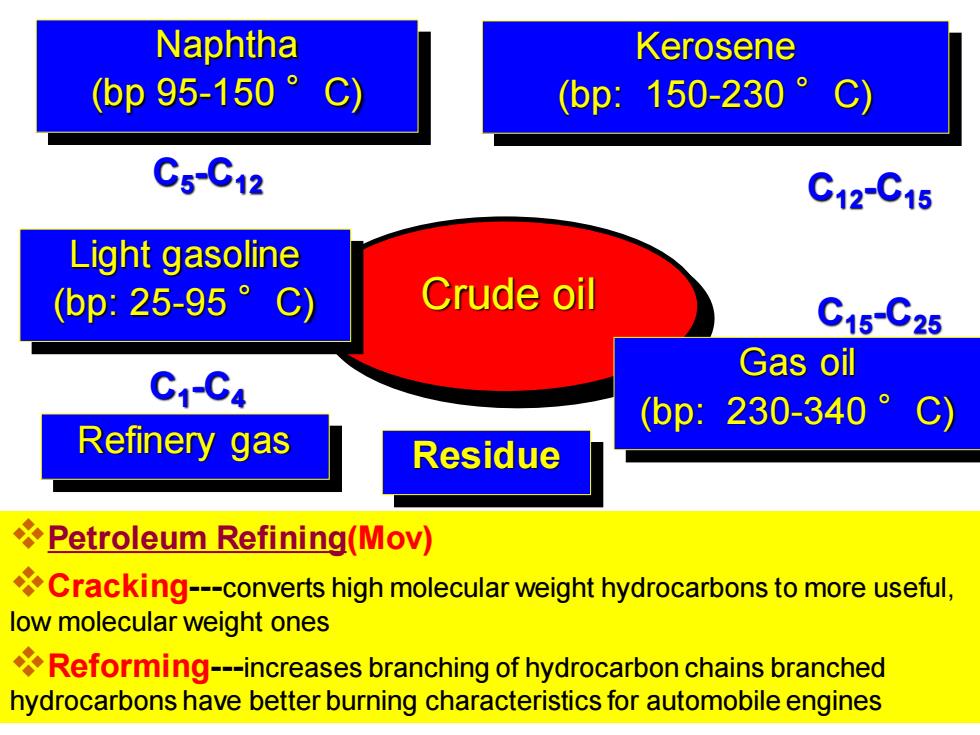
Naphtha Kerosene (bp95-150° C) (bp:150-230° C5C12 C12C15 Light gasoline (bp:25-95。C Crude oil C15-C25 Gas oil C1-C4 bp:230-340°C) Refinery gas Residue Petroleum Refining(Mov) Cracking---converts high molecular weight hydrocarbons to more useful, low molecular weight ones Reforming---increases branching of hydrocarbon chains branched hydrocarbons have better burning characteristics for automobile engines
Crude oil Refinery gas C1 -C4 Light gasoline (bp: 25-95 °C) C5 -C12 Naphtha (bp 95-150 °C) Kerosene (bp: 150-230 °C) C12-C15 Gas oil (bp: 230-340 °C) C15-C25 Residue ❖Petroleum Refining(Mov) ❖Cracking---converts high molecular weight hydrocarbons to more useful, low molecular weight ones ❖Reforming---increases branching of hydrocarbon chains branched hydrocarbons have better burning characteristics for automobile engines
Sec 2 Physical Properties -Solubility:hydrophobic -Density:less than 1 g/mL -Boiling points increase with increasing carbons (little less for branched chains). -Melting points increase with increasing carbons(less for odd-number of carbons)
Sec 2 Physical Properties ▪Solubility: hydrophobic ▪Density: less than 1 g/mL ▪Boiling points increase with increasing carbons (little less for branched chains). ▪Melting points increase with increasing carbons (less for odd-number of carbons)
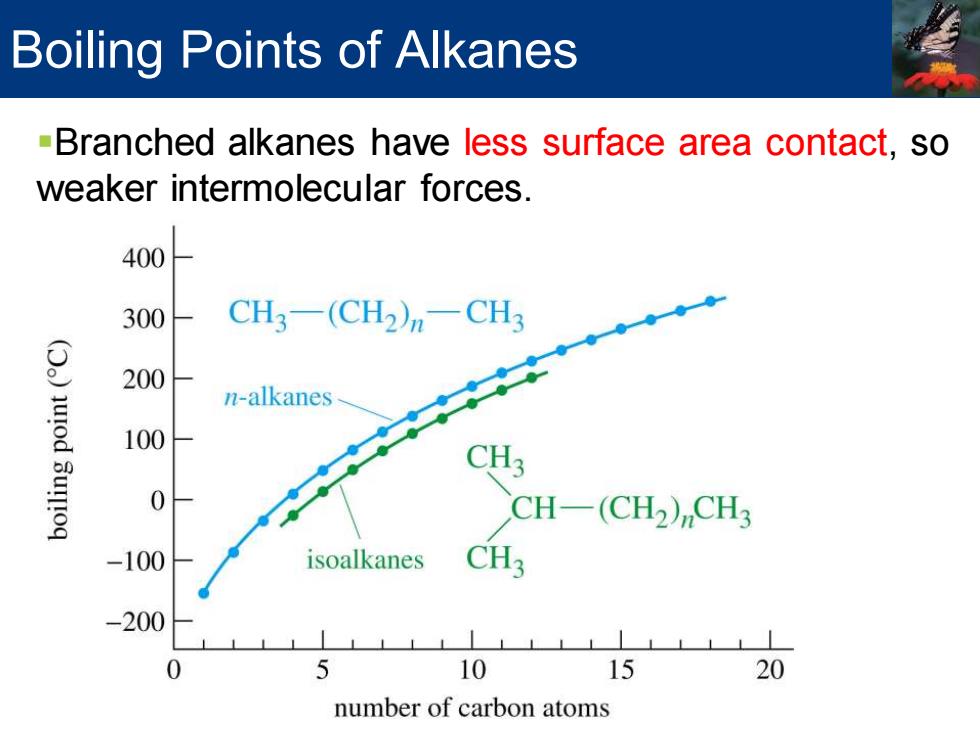
Boiling Points of Alkanes -Branched alkanes have less surface area contact,so weaker intermolecular forces. 400 300 CH3-(CH2)-CH3 200 urod n-alkanes 100 Sur!oq CH3 0 CH-(CH2)CH3 -100 isoalkanes CH3 -200 0 5 10 15 20 number of carbon atoms
Boiling Points of Alkanes ▪Branched alkanes have less surface area contact, so weaker intermolecular forces
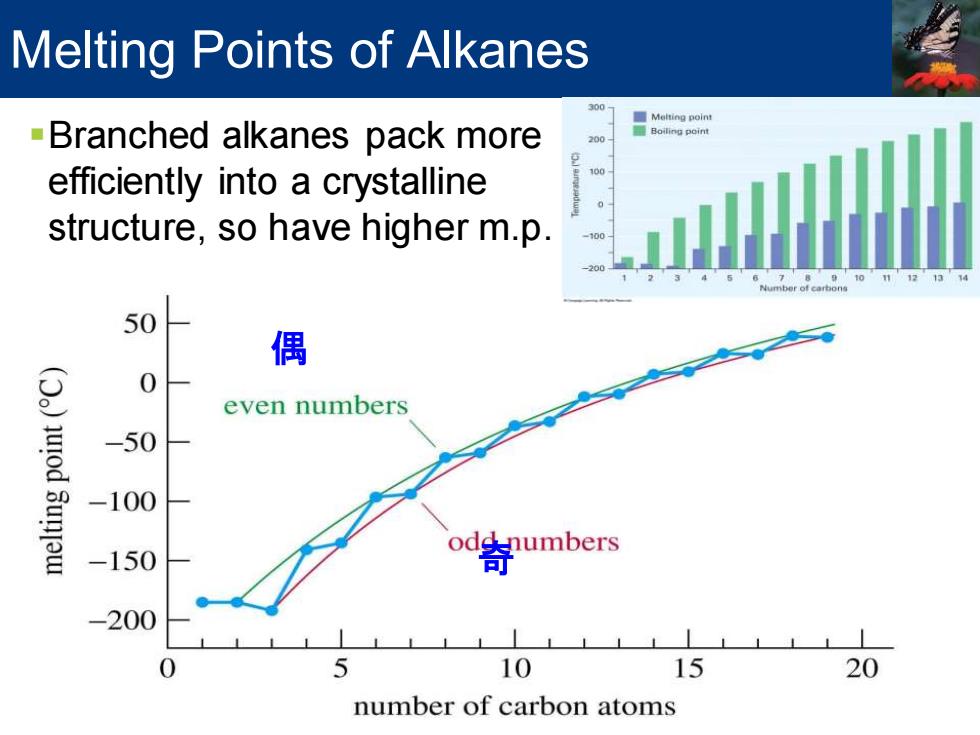
Melting Points of Alkanes Meiting point -Branched alkanes pack more 200 2 efficiently into a crystalline structure,so have higher m.p. 50 偶 0 even numbers od 3un -50 -100 odd numbers -150 -200 0 5 10 15 20 number of carbon atoms
Melting Points of Alkanes ▪Branched alkanes pack more efficiently into a crystalline structure, so have higher m.p. 偶 奇
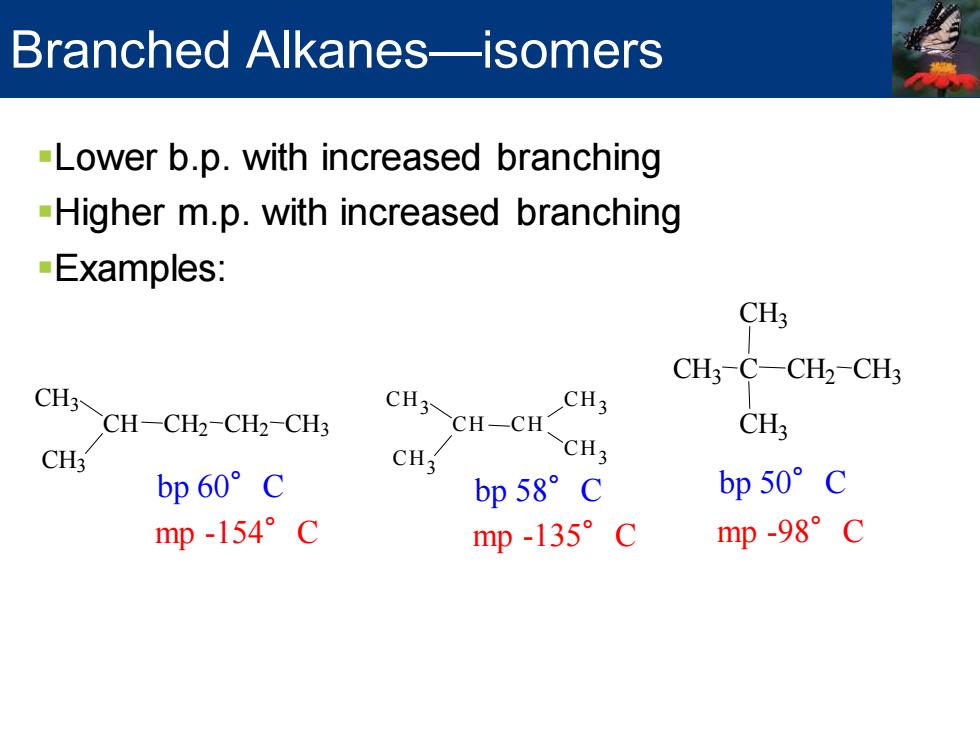
Branched Alkanes-isomers -Lower b.p.with increased branching -Higher m.p.with increased branching Examples: CH3 CH3-C-CH2-CH3 CHCH-CH2-CH2-CHs CH3CH-CH CH3 CH3 CH; CH3 CH3 bp60°C bp58°c bp50°c mp-154°C mp-135°C mp-98°c
Branched Alkanes—isomers ▪Lower b.p. with increased branching ▪Higher m.p. with increased branching ▪Examples: H CH3 CH CH3 CH2 CH2 CH3 bp 60°C mp -154°C CH3 CH CH3 CH CH3 CH3 bp 58°C mp -135°C bp 50°C mp -98°C CH3 C C 3 CH3 CH2 CH3