
Anaerobic cultivation Anaerobic chamber
Anaerobic cultivation Anaerobic chamber
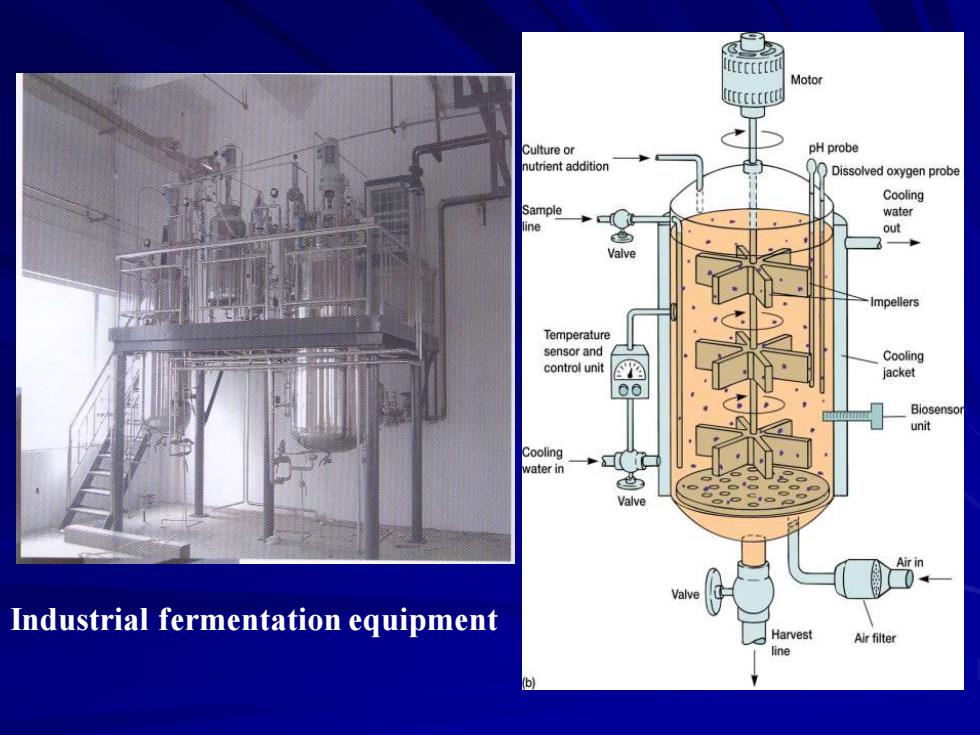
Motor Culture or pH probe nutrient addition Dissolved oxygen probe Cooling water ne out Valve Impellers Temperature sensor and Cooling control unit jacket Biosenso unit Cooling water in Valve Industrial fermentation equipment Air filter
Industrial fermentation equipment

Measurement of microbial growth -Measure of cell numbers 1.Direct count methods do not distinguish between living and dead cells,and may be accomplished by direct microscopic observation on specially etched slides (such as Petroff-Hausser chambers or hemacytometers)or by using electronic counters (such as Coulter Counters,which count microorganisms as they flow through a small hole or orifice)】 2.Viable cell counts involve plating diluted samples (using a pour plate or spread plate) onto suitable growth media and monitoring colony formation;this type of method counts only those cells that are reproductively active;because it is not possible to be certain that each colony arose from a single cell,results are usually expressed as colony forming units (CFU) 3.Microbial numbers are frequently determined from counts of colonies growing on membrane filters having pores small enough to trap bacteria -Measure of cell mass may be used to approximate the number of microorganisms if a suitable parameter proportional to the number of microorganisms present is used (suitable parameters may be dry weight,light scattering in liquid solutions,or biochemical determinations of specific cellular constituents such as protein,DNA,or ATP)
Measurement of microbial growth -Measure of cell numbers 1. Direct count methods do not distinguish between living and dead cells, and may be accomplished by direct microscopic observation on specially etched slides (such as Petroff-Hausser chambers or hemacytometers) or by using electronic counters (such as Coulter Counters, which count microorganisms as they flow through a small hole or orifice) 2. Viable cell counts involve plating diluted samples (using a pour plate or spread plate) onto suitable growth media and monitoring colony formation; this type of method counts only those cells that are reproductively active; because it is not possible to be certain that each colony arose from a single cell, results are usually expressed as colony forming units (CFU) 3. Microbial numbers are frequently determined from counts of colonies growing on membrane filters having pores small enough to trap bacteria -Measure of cell mass may be used to approximate the number of microorganisms if a suitable parameter proportional to the number of microorganisms present is used (suitable parameters may be dry weight, light scattering in liquid solutions, or biochemical determinations of specific cellular constituents such as protein, DNA, or ATP)
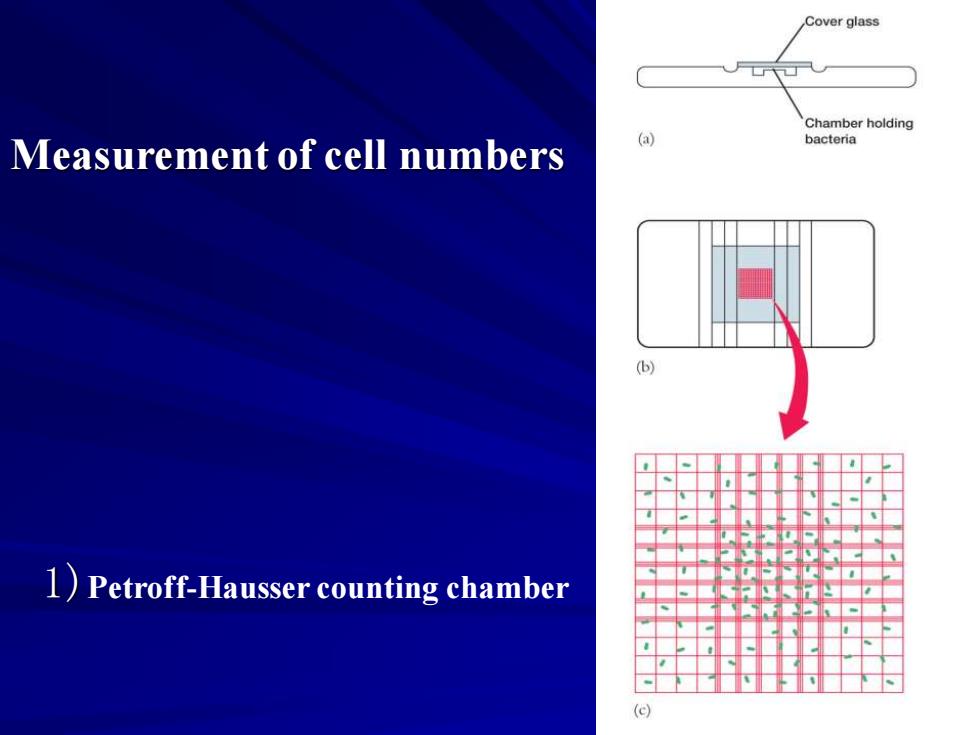
Cover glass Chamber holding Measurement of cell numbers (A bacteria (b) 1)Petroff-Hausser counting chamber
Measurement of cell numbers 1)Petroff-Hausser counting chamber

2)Filtration 裤年时女 spr可glded damp Finned Memhrane f -Clne plaform Biw 民ahr再e
2) Filtration