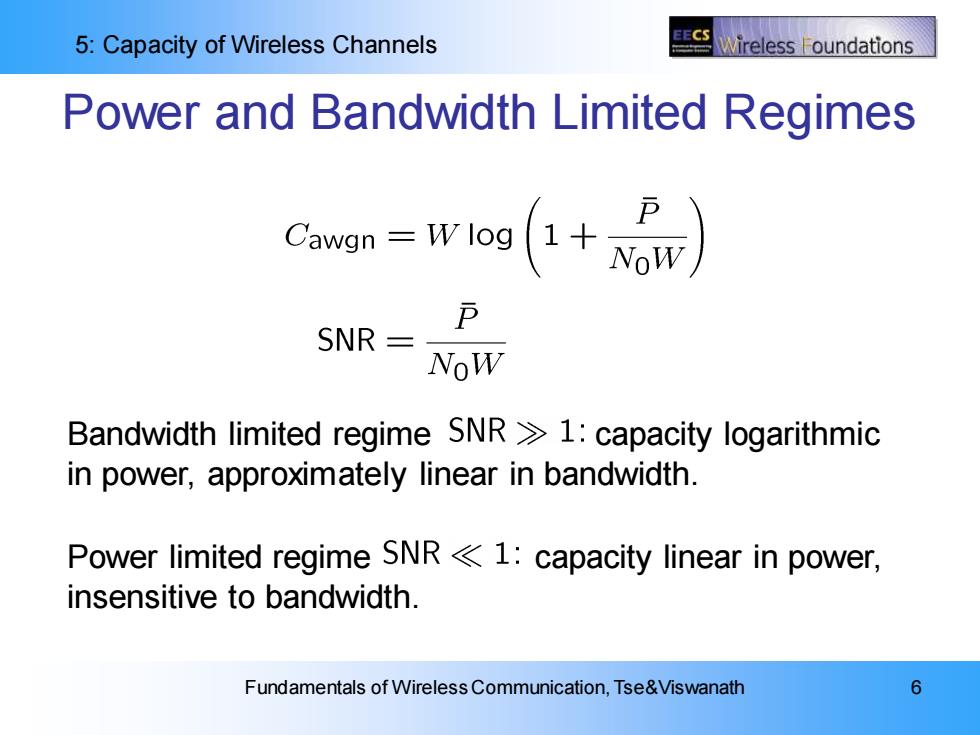
5:Capacity of Wireless Channels Vireless oundations Power and Bandwidth Limited Regimes SNR= NoW Bandwidth limited regime SNR1:capacity logarithmic in power,approximately linear in bandwidth. Power limited regime SNR<1:capacity linear in power, insensitive to bandwidth. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 6
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 6 Power and Bandwidth Limited Regimes Bandwidth limited regime capacity logarithmic in power, approximately linear in bandwidth. Power limited regime capacity linear in power, insensitive to bandwidth
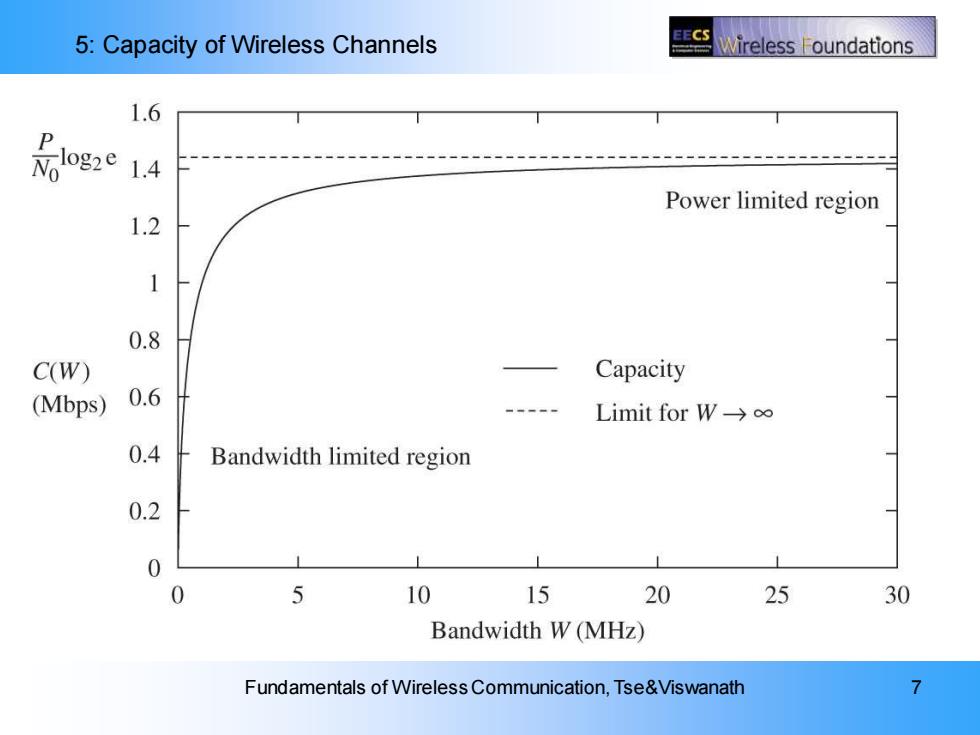
5:Capacity of Wireless Channels CS Wireless F oundations 1.6 P 1.4 Power limited region 1.2 0.8 C(W) Capacity (Mbps) 0.6 Limit for W→o∞ 0.4 Bandwidth limited region 0.2 0 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 Bandwidth W(MHz) Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 7
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 7

5:Capacity of Wireless Channels Vireless oundations Example 1:Impact of Frequency Reuse Different degree of frequency reuse allows a tradeoff between SINR and degrees of freedom per user. Users in narrowband systems have high link SINR but small fraction of system bandwidth. Users in wideband systems have low link SINR but full system bandwidth. 。 Capacity depends on both SINR and d.o.f.and can provide a guideline for optimal reuse. Optimal reuse depends on how the out-of-cell interference fraction f(p)depends on the reuse factor p. Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 8
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 8 Example 1: Impact of Frequency Reuse • Different degree of frequency reuse allows a tradeoff between SINR and degrees of freedom per user. • Users in narrowband systems have high link SINR but small fraction of system bandwidth. • Users in wideband systems have low link SINR but full system bandwidth. • Capacity depends on both SINR and d.o.f. and can provide a guideline for optimal reuse. • Optimal reuse depends on how the out-of-cell interference fraction f() depends on the reuse factor

5:Capacity of Wireless Channels EECS Wireless F oundations Numerical Examples Linear cellular system Hexagonal system 14 12 Rate bite//H 0.6 Frequency reuse factor 1 0.4 0. 12 Prequency reuse factor 1 0.2 /2… 04 51015 2025 30 -10 5 0 51015 202530 Cell edge SNR(dB) Cell edge SNR (dB) Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 9
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 9 Numerical Examples Linear cellular system Hexagonal system
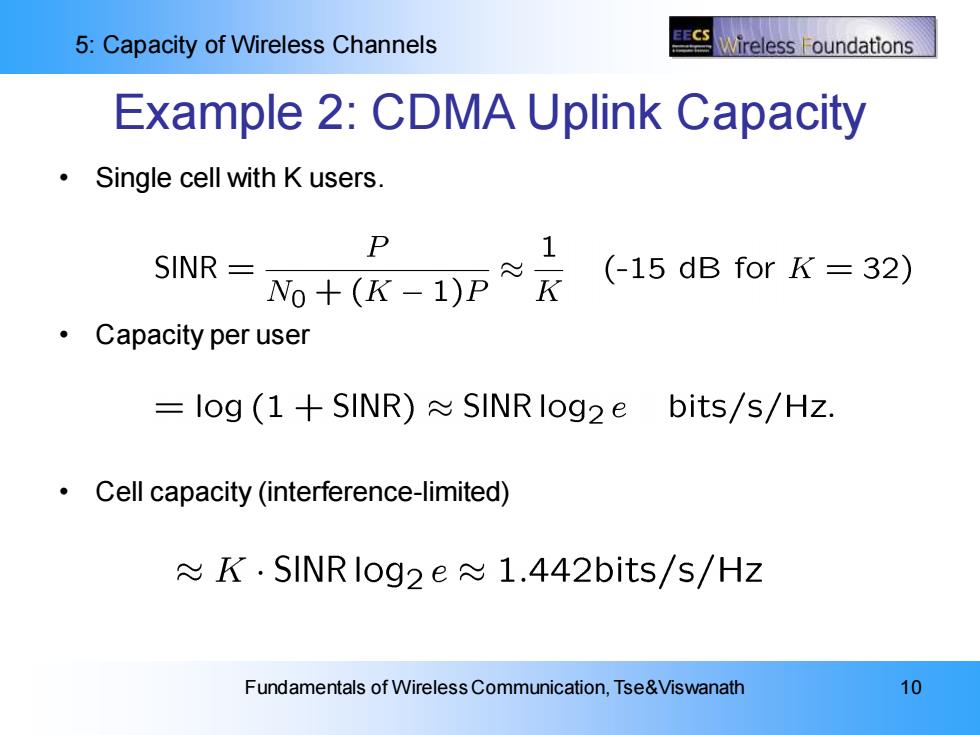
EECS 5:Capacity of Wireless Channels Wireless oundations Example 2:CDMA Uplink Capacity 。 Single cell with K users. P 1 SINR o+(K-1)P≈ (-15 dB for K=32) ·Capacity per user =log (1+SINR)SINRlog2e bits/s/Hz. Cell capacity (interference-limited) K.SINRlog2e 1.442bits/s/Hz Fundamentals of Wireless Communication,Tse&Viswanath 10
5: Capacity of Wireless Channels Fundamentals of Wireless Communication, Tse&Viswanath 10 Example 2: CDMA Uplink Capacity • Single cell with K users. • Capacity per user • Cell capacity (interference-limited)