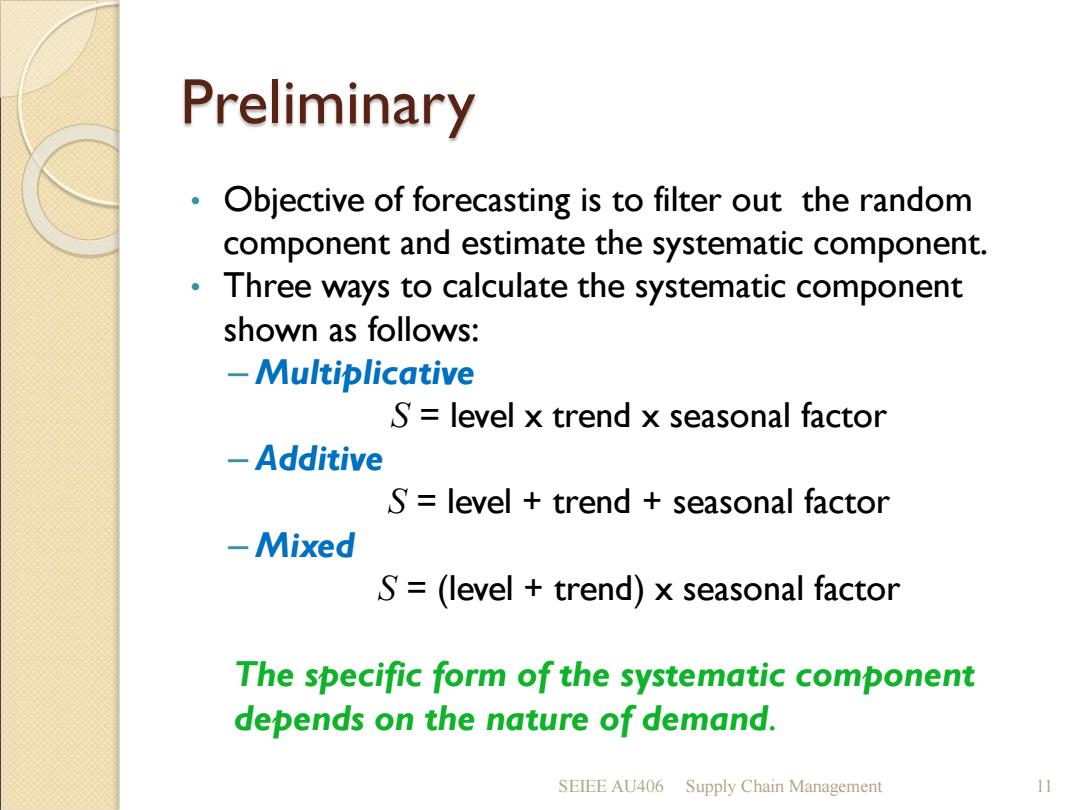
Preliminary Objective of forecasting is to filter out the random component and estimate the systematic component. Three ways to calculate the systematic component shown as follows: Multiplicative S=level x trend x seasonal factor -Additive S level trend seasonal factor -Mixed S=(level trend)x seasonal factor The specific form of the systematic component depends on the nature of demand. SEIEE AU406 Supply Chain Management 11
Preliminary • Objective of forecasting is to filter out the random component and estimate the systematic component. • Three ways to calculate the systematic component shown as follows: – Multiplicative S = level x trend x seasonal factor – Additive S = level + trend + seasonal factor – Mixed S = (level + trend) x seasonal factor The specific form of the systematic component depends on the nature of demand. SEIEE AU406 Supply Chain Management 11
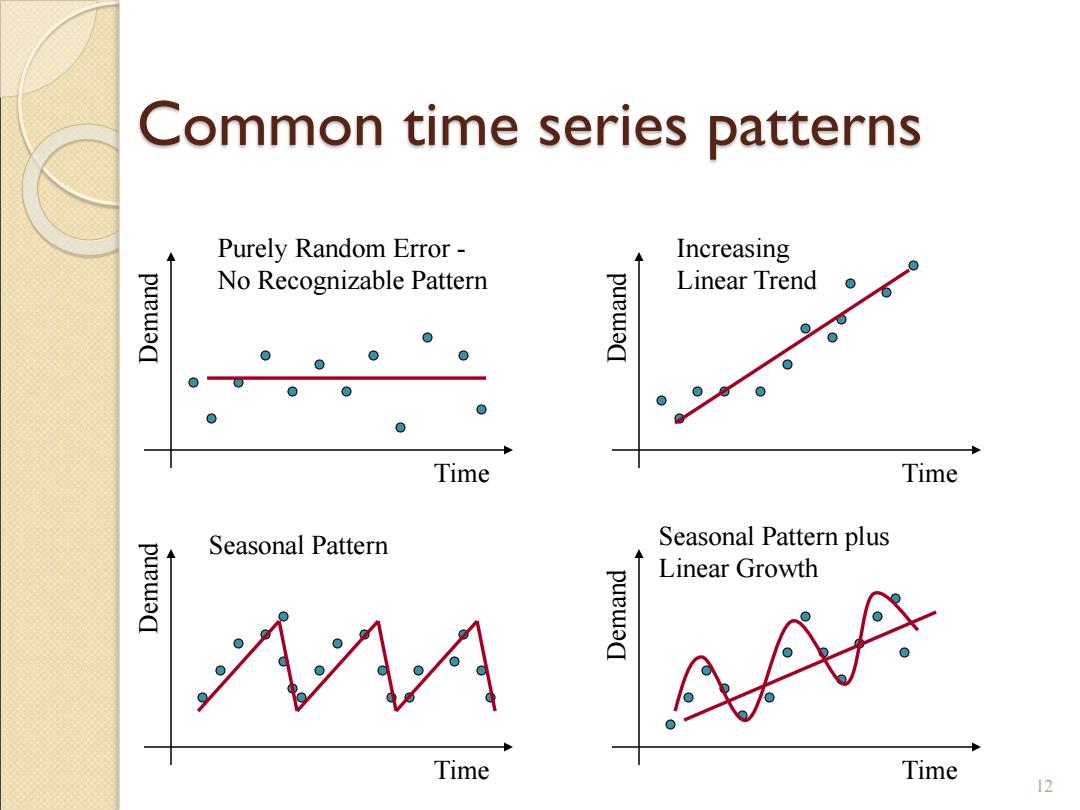
Common time series patterns Purely Random Error- Increasing Linear Trend puewa No Recognizable Pattern puewa 0 Time Time Seasonal Pattern Seasonal Pattern plus puew Linear Growth puew Time Time 12
12 Common time series patterns Time Time Time Demand Time Demand Demand Demand Purely Random Error - No Recognizable Pattern Increasing Linear Trend Seasonal Pattern Seasonal Pattern plus Linear Growth
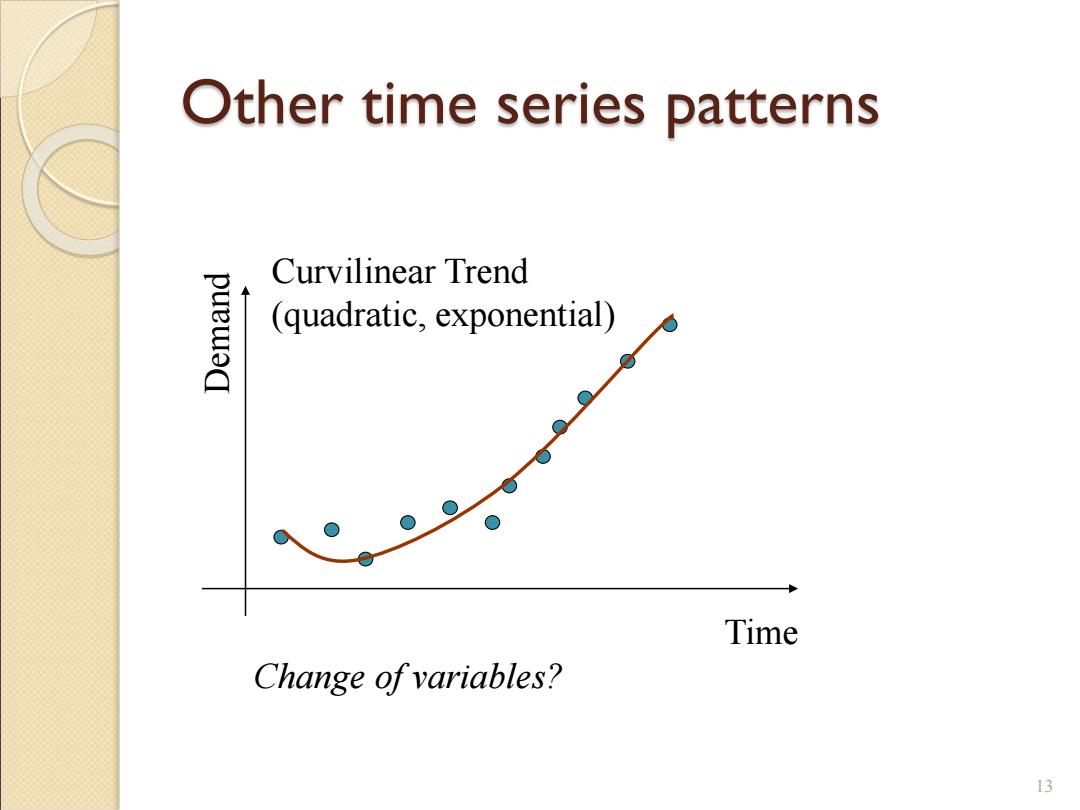
Other time series patterns Curvilinear Trend puew d (quadratic,exponential) Time Change ofvariables? 13
13 Other time series patterns Time Demand Curvilinear Trend (quadratic, exponential) Change of variables?
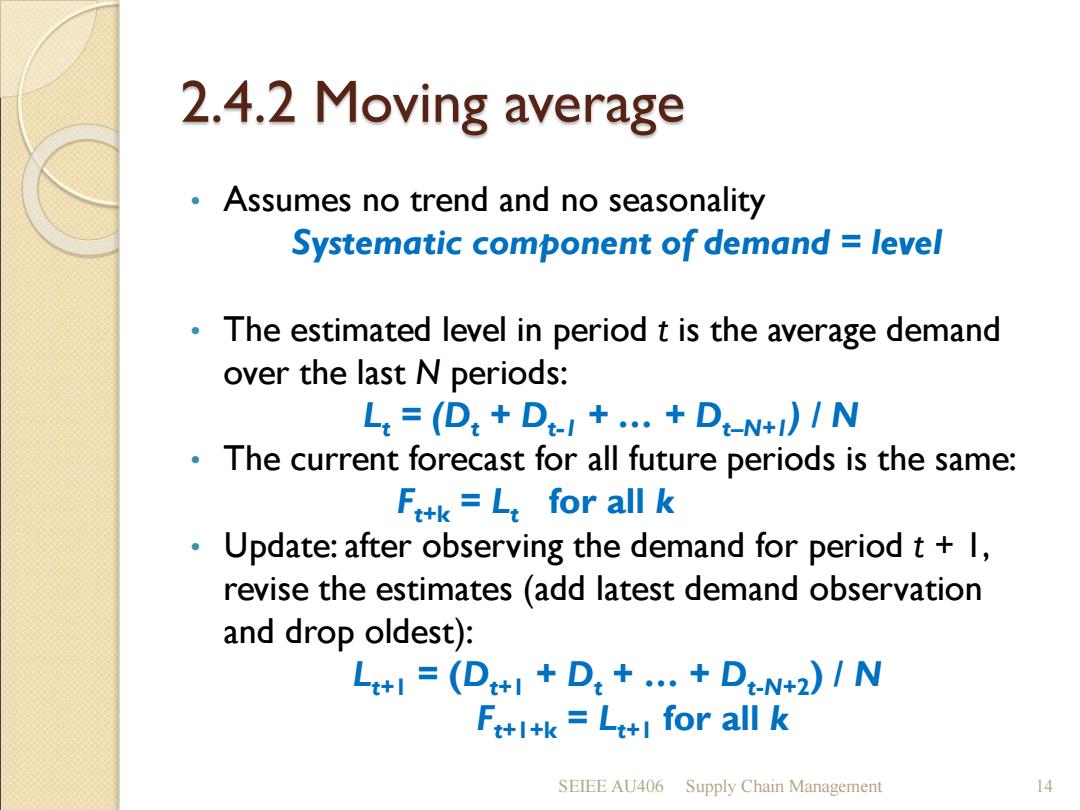
2.4.2 Moving average Assumes no trend and no seasonality Systematic component of demand level The estimated level in period t is the average demand over the last N periods: L,=(D:+D1+.+D-N+)1N The current forecast for all future periods is the same: Fttk=L:for all k Update:after observing the demand for period t+l, revise the estimates (add latest demand observation and drop oldest): L+l=(D+1+D:+…+DN+2IN F+l+k=Le+l for all k SEIEE AU406 Supply Chain Management 14
2.4.2 Moving average SEIEE AU406 Supply Chain Management 14 • Assumes no trend and no seasonality Systematic component of demand = level • The estimated level in period t is the average demand over the last N periods: Lt = (Dt + Dt-1 + … + Dt–N+1) / N • The current forecast for all future periods is the same: Ft+k = Lt for all k • Update: after observing the demand for period t + 1, revise the estimates (add latest demand observation and drop oldest): Lt+1 = (Dt+1 + Dt + … + Dt-N+2) / N Ft+1+k = Lt+1 for all k
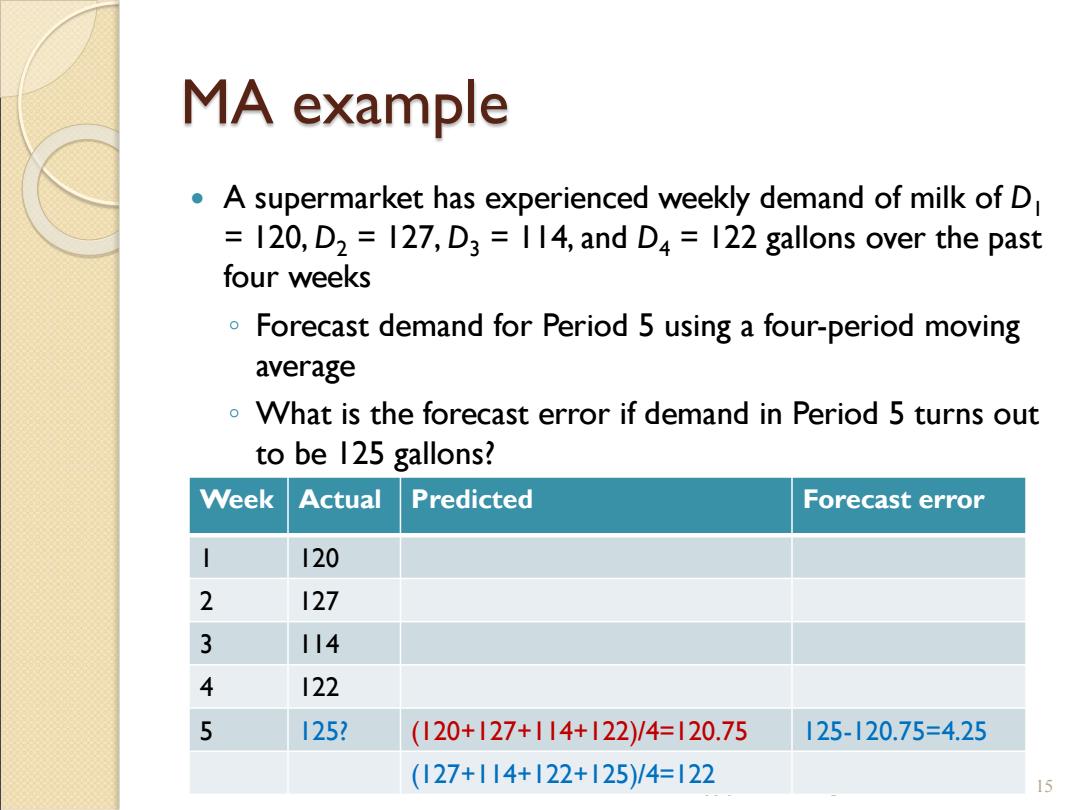
MA example A supermarket has experienced weekly demand of milk of D 120,D2 127,D3 114,and D4=122 gallons over the past four weeks Forecast demand for Period 5 using a four-period moving average What is the forecast error if demand in Period 5 turns out to be 125 gallons? Week Actual Predicted Forecast error I20 2 127 3 川4 4 122 5 1252 (120+127+114+122)/4=120.75 125-120.75=4.25 (127+14+122+125)/4=I22 15
MA example A supermarket has experienced weekly demand of milk of D1 = 120, D2 = 127, D3 = 114, and D4 = 122 gallons over the past four weeks ◦ Forecast demand for Period 5 using a four-period moving average ◦ What is the forecast error if demand in Period 5 turns out to be 125 gallons? SEIEE AU406 Supply Chain Management 15 Week Actual Predicted Forecast error 1 120 2 127 3 114 4 122 5 125? (120+127+114+122)/4=120.75 125-120.75=4.25 (127+114+122+125)/4=122