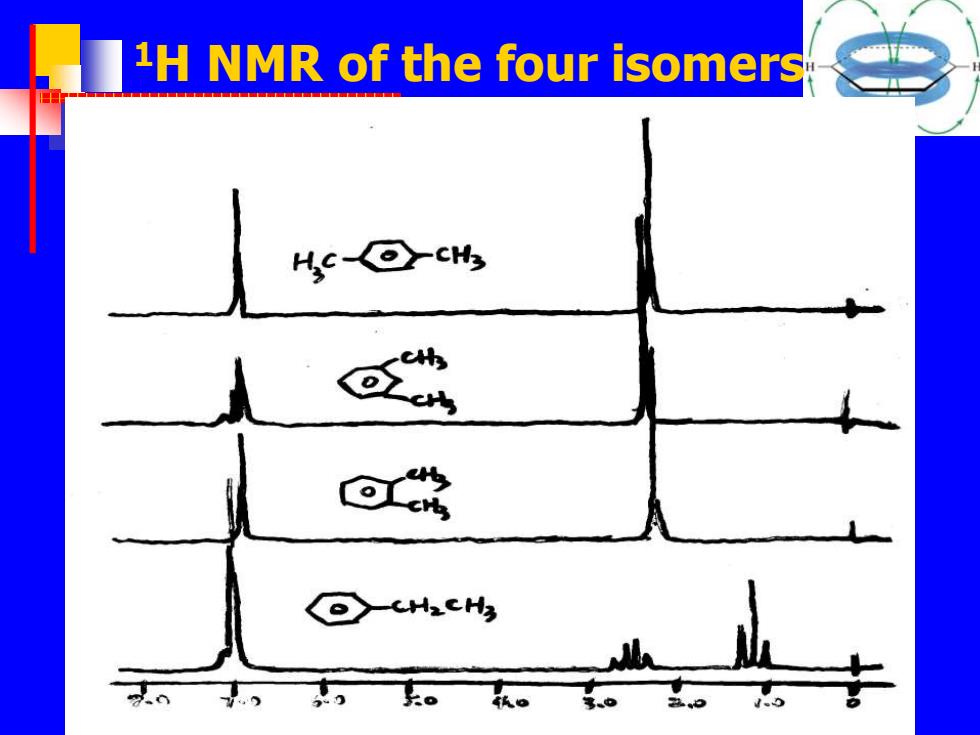
1H NMR of the four isomers Hs⊙ -H.CHg
1H NMR of the four isomers

有机波谱法特点 于 必(1) 样品用量少,一般23mg(可<1mg) (2) 除质谱外,无祥品消耗,可回收 必(3)省时,简便 $(4)配合元素分析(或高分辨质谱), 可准确确定化合物的分子式和立体结构
有 机 波 谱 法 特 点 ❖(1) 样品用量少,一般2~3mg(可<1mg) ❖(2) 除质谱外,无样品消耗,可回收 ❖(3) 省时,简便 ❖(4) 配合元素分析(或高分辨质谱), ❖ 可准确确定化合物的分子式和立体结构

一节Ma5s Spectrum(质谱} HFHHHHHHHHH1HHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHHP 一、 基本原理 In a technique called mass spectroscopy,a molecule is vaporized and then ionized by removing an electron.This produced a molecular ion,which is a radical cation,a species with an unpaired electron and a positive charge.Because of possessing high energy,the molecular ion may break apart into cations,radicals,neutral molecules, and other radical cations
第一节 Mass Spectrum(质谱) ❖一、基本原理 ❖In a technique called mass spectroscopy, a molecule is vaporized and then ionized by removing an electron. This produced a molecular ion, which is a radical cation, a species with an unpaired electron and a positive charge. Because of possessing high energy, the molecular ion may break apart into cations, radicals, neutral molecules, and other radical cations
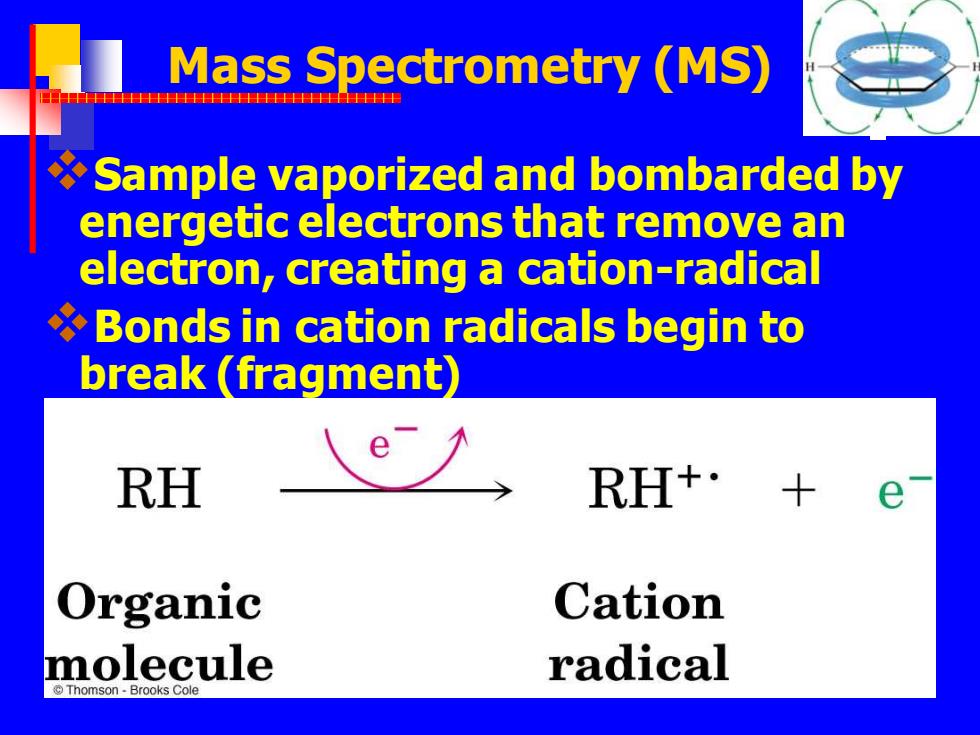
Mass Spectrometry (MS) 串 Sample vaporized and bombarded by energetic electrons that remove an electron,creating a cation-radical Bonds in cation radicals begin to break (fragment RH RH+: 十 Organic Cation molecule radical Thomson-Brooks Cole
Mass Spectrometry (MS) ❖Sample vaporized and bombarded by energetic electrons that remove an electron, creating a cation-radical ❖Bonds in cation radicals begin to break (fragment)
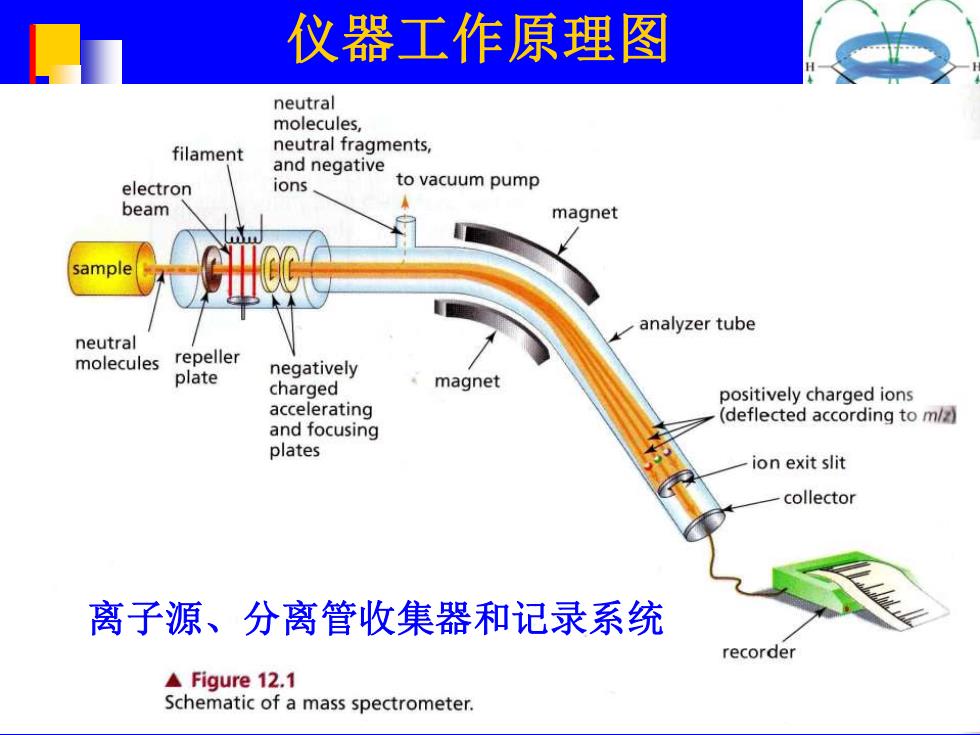
仪器工作原理图 neutral molecules, filament neutral fragments, and negative electron ions to vacuum pump beam magnet analyzer tube neutral molecules repeller plate negatively charged magnet positively charged ions accelerating (deflected according to m/z) and focusing plates ion exit slit collector 离子源、分离管收集器和记录系统 recorder A Figure 12.1 Schematic of a mass spectrometer
仪器工作原理图 离子源、分离管收集器和记录系统