
Economic importance of bacterial diseases (细菌病害的经济重要性) Causing diseases throughout the whole range of families of higher plants. ● A number of bacterial diseases are of major economic importance. Direct financial loss due to decreased agricultural production Indirect loss due to the implementation of expensive control measures. Total losses on all susceptible crops were estimated to be $50-100 million annually,on a world-wide basis. 11
11 Economic importance of bacterial diseases (细菌病害的经济重要性) ⚫ Causing diseases throughout the whole range of families of higher plants. ⚫ A number of bacterial diseases are of major economic importance. ⚫ Direct financial loss due to decreased agricultural production ; Indirect loss due to the implementation of expensive control measures. ⚫ Total losses on all susceptible crops were estimated to be $50-100 million annually, on a world-wide basis

Contents(教学内容) Vhat are Prokaryotes(原核生物的概念) Characteristics of Prokaryotes(原核生物的一般性状) How Phytopathogenic Prokaryotes are classfied (植物病原原核生物的分类) Important groups of Phytopathogenic Prokaryotes (植物病原原核生物的重要类群) Diseases caused by Phytopathogenic Prokaryotes (植物病原原核生物所致的重要病害) 12
12 Contents(教学内容) ⚫ What are Prokaryotes(原核生物的概念) ⚫ Characteristics of Prokaryotes (原核生物的一般性状) ⚫ How Phytopathogenic Prokaryotes are classfied (植物病原原核生物的分类) ⚫ Important groups of Phytopathogenic Prokaryotes (植物病原原核生物的重要类群) ⚫ Diseases caused by Phytopathogenic Prokaryotes (植物病原原核生物所致的重要病害)

What are Prokaryotes Very small,relatively simple,single-celled organisms genetic material not enclosed in a special nuclear membrane. ●Including Bacteria(Cell wall(细菌,有细胞壁) Spiroplasma(Cell wall-less)(螺原体,无细胞壁) Phytoplasma(Cell wall-less)(植原体,无细胞壁) Saprophytes(most)(大部分腐生) 13
13 What are Prokaryotes ⚫ Very small, relatively simple, single-celled organisms, genetic material not enclosed in a special nuclear membrane. ⚫ Including Bacteria (Cell wall) (细菌,有细胞壁) Spiroplasma (Cell wall-less)(螺原体,无细胞壁) Phytoplasma (Cell wall -less)(植原体,无细胞壁) ⚫ Saprophytes (most)(大部分腐生)
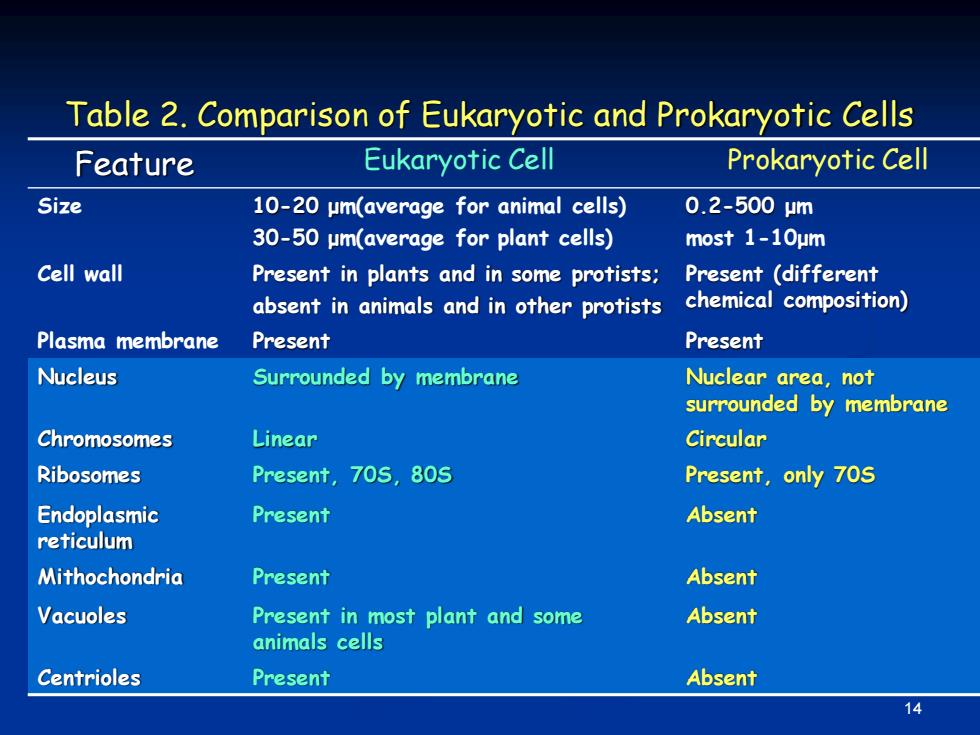
Table 2.Comparison of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells Feature Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell Size 10-20 um(average for animal cells) 0.2-500m 30-50 um(average for plant cells) most 1-10um Cell wall Present in plants and in some protists;Present (different absent in animals and in other protists chemical composition) Plasma membrane Present Present Nucleus Surrounded by membrane Nuclear area,not surrounded by membrane Chromosomes Linear Circular Ribosomes Present,70S,805 Present,only 70S Endoplasmic Present Absent reticulum Mithochondria Present Absent Vacuoles Present in most plant and some Absent animals cells Centrioles Present Absent
14 Feature Eukaryotic Cell Prokaryotic Cell Size 10-20 μm(average for animal cells) 30-50 μm(average for plant cells) 0.2-500 μm most 1-10μm Cell wall Present in plants and in some protists; absent in animals and in other protists Present (different chemical composition) Plasma membrane Present Present Nucleus Surrounded by membrane Nuclear area, not surrounded by membrane Chromosomes Linear Circular Ribosomes Present, 70S, 80S Present, only 70S Endoplasmic reticulum Present Absent Mithochondria Present Absent Vacuoles Present in most plant and some animals cells Absent Centrioles Present Absent Table 2. Comparison of Eukaryotic and Prokaryotic Cells

Characteristics of Prokaryotes 1.Cell shape and structure(形态、结构) 2.Cell stain reaction(细胞染色反应) 3.Growth(生长条件) 4.Reproduction(繁殖》 5.Inheritance and Variation(遗传和变异) 15
15 Characteristics of Prokaryotes 1. Cell shape and structure(形态、结构) 2. Cell stain reaction(细胞染色反应) 3. Growth(生长条件) 4. Reproduction(繁殖) 5. Inheritance and Variation(遗传和变异)