
Speech script “Dental trauma in childhood and adolescence'” Lecture:Jin hua wang Time:2018.11.22 general duction SectionII:diagnosis and treatment of young permanent dentition dental trauma section IIl:injuries to the primary dentition Section IV:dental injuries prevention preface a trauma with accompanying fracture of a permanent incisor is a tragic experience for the young patient.the oral and emotional health of the young patient is involved and the childs appearance must be restored to normal as soon as possible to relieve,the consciousness of being different from other children.sowe should pay attention to the r psychologic well-be ng prognosis of traumatic injuries has improved significantly in the last 20 years,this has been largely due to a greater understanding and knowledge of pulpal procedures.so we should create confidence to treat the dental trauma in childhood and adolescence. Contents To grasp: clinical classification.diagnositic evidence.therapeutic principle and method of Dental trauma in childhood and adolescence. To be familiar: Predilection age and type of Dental trauma in childhood and adolescence.Tracing and To know: Incidence of anterior teeth trauma. Section I general introduction 1.2 epidemiology 1 3 classification 1.4 history and examination 11 defnition childhood and adolescence teeth suffer sharp trauma,especially cause dental,pulp. periodontium trauma due to beating and collisions. 1.2 epidemiology Table 1 dental trauma prevalence in childhood and adolescence
Speech script “Dental trauma in childhood and adolescence” Lecture:Jin hua wang Time : 2018.11.22 This chapter include two sections Section Ⅰ: general introduction SectionⅡ: diagnosis and treatment of young permanent dentition dental trauma section Ⅲ: injuries to the primary dentition Section Ⅳ: dental injuries prevention preface a trauma with accompanying fracture of a permanent incisor is a tragic experience for the young patient,the oral and emotional health of the young patient is involved ,and the child, s appearance must be restored to normal as soon as possible to relieve, the consciousness of being different from other children.so we should pay attention to their psychologic well-being.prognosis of traumatic injuries has improved significantly in the last 20 years,this has been largely due to a greater understanding and knowledge of pulpal procedures.so we should create confidence to treat the dental trauma in childhood and adolescence. Contents To grasp: clinical classification,diagnositic evidence,therapeutic principle and method of Dental trauma in childhood and adolescence. To be familiar: Predilection age and type of Dental trauma in childhood and adolescence.Tracing and restoration evaluation of traumatic teeth. To know: Incidence of anterior teeth trauma. Section Ⅰ : general introduction 1.1 definition. 1.2 epidemiology. 1.3 classification. 1.4 history and examination. 1.1 definition childhood and adolescence teeth suffer sharp trauma, especially cause dental , pulp, periodontium trauma due to beating and collisions. 1.2 epidemiology Table 1 dental trauma prevalence in childhood and adolescence
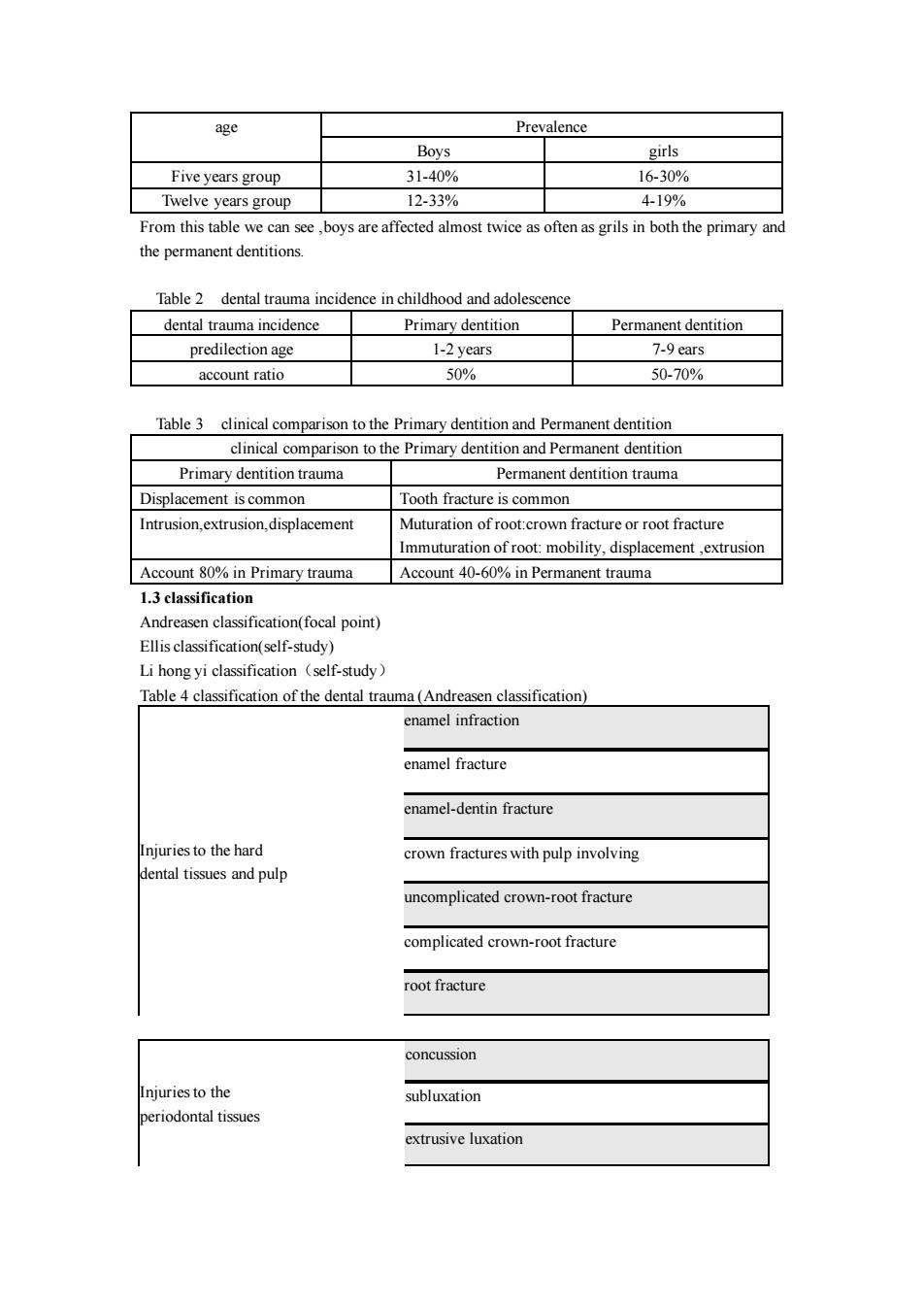
age D Boys Five years group 31-40% 16-30% Twelve years group 12-33% 419% From this table we can see boys are affected amost twice a ften as grils in both the primary and the permanent dentition Table 2 dental trauma incidence in childhood and adolescence dental trauma incidence Primary dentition Permanent dentition ars 7-9ar account ratio 50% 50-70% Table 3 clinical comparison to the Primary dentition and Permanent dentition clinical comparison to the Primary dentition and Permanent dentition Primary dentition trauma Permanent dentition trauma Displacement is common Tooth fracture is common Intrusion extrusion.displacement Muturation of root:crown fracture or root fracture Immuturation of root:mobility. Account 80%in Primary trauma Account 40-60%in Permanent trauma 1.3 classification Andreasen classification(focal point) Ellis classification(self-study) (s-study Table4 classification of the dental trauma (Andreasen classification) enamel infraction enamel fracture enamel-dentin fracture juries to the hard crown fractures with pulp involving dental tissues and pulp uncomplicated crown-root fracture complicated crown-root fracture root fracture concussion juriesto the subluxation riodontal tissues extrusive uxation
age Prevalence Boys girls Five years group 31-40% 16-30% Twelve years group 12-33% 4-19% From this table we can see ,boys are affected almost twice as often as grils in both the primary and the permanent dentitions. Table 2 dental trauma incidence in childhood and adolescence dental trauma incidence Primary dentition Permanent dentition predilection age 1-2 years 7-9 ears account ratio 50% 50-70% Table 3 clinical comparison to the Primary dentition and Permanent dentition clinical comparison to the Primary dentition and Permanent dentition Primary dentition trauma Permanent dentition trauma Displacement is common Tooth fracture is common Intrusion,extrusion,displacement Muturation of root:crown fracture or root fracture Immuturation of root: mobility, displacement ,extrusion Account 80% in Primary trauma Account 40-60% in Permanent trauma 1.3 classification Andreasen classification(focal point) Ellis classification(self-study) Li hong yi classification(self-study) Table 4 classification of the dental trauma (Andreasen classification) Injuries to the hard dental tissues and pulp enamel infraction enamel fracture enamel-dentin fracture crown fractures with pulp involving uncomplicated crown-root fracture complicated crown-root fracture root fracture Injuries to the periodontal tissues concussion subluxation extrusive luxation
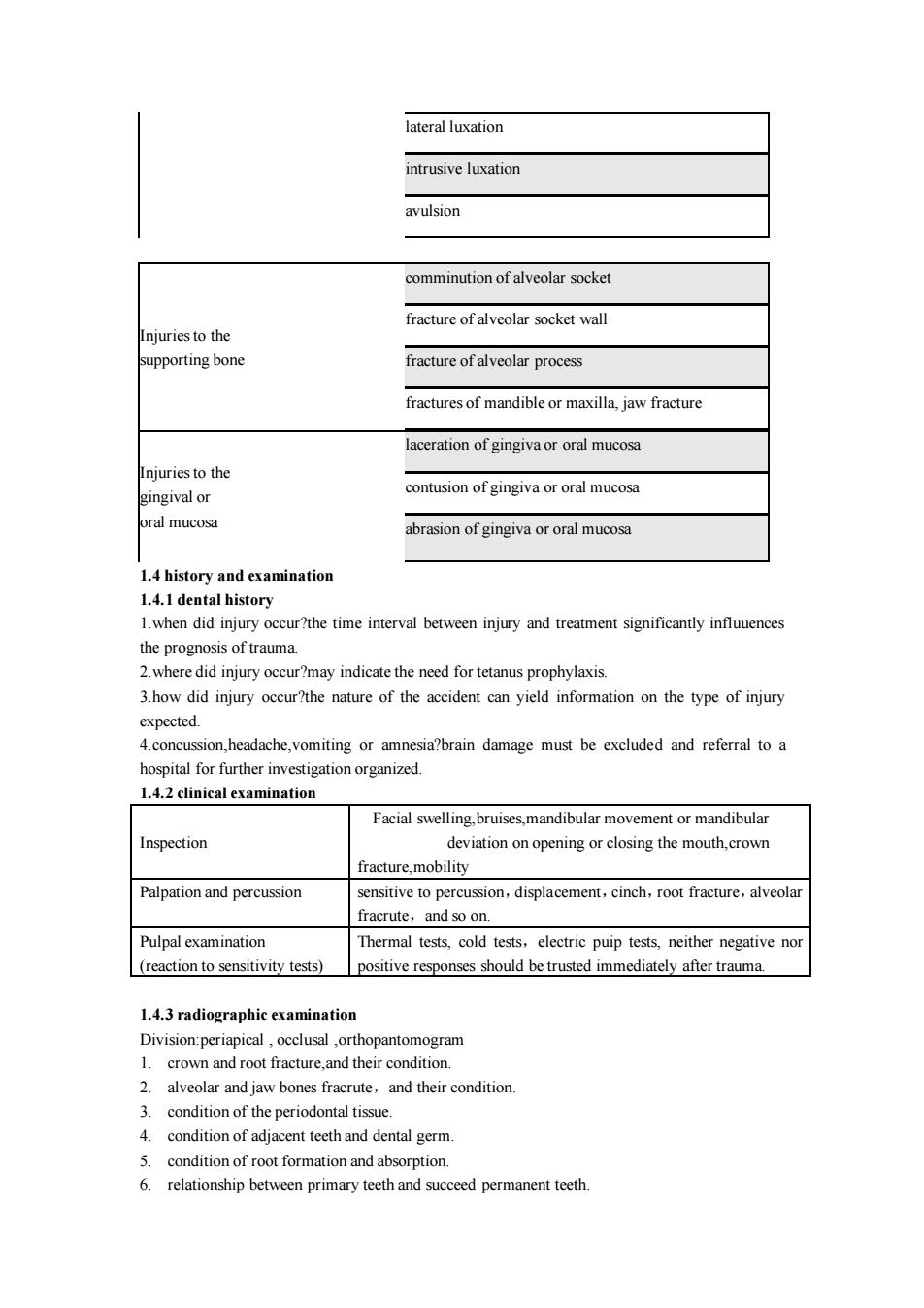
lateral luxation intrusive luxation avulsion comminution of alveolar socket fracture of alveolar socket wall Injuries to the upporting bone fracture ofalveolar process fractures of mandible or maxilla,jaw fracture laceration of gingiva or oral mucosa contusion of gingiva or oral mucosa gingival or oral mucosa rasion of gingiva or oral mucosa 1.4 history and examination 1.4.1 dental history 1.when did injury occur?the time interval between injury and treatment significantly influuences 3.how did injury occur?the nature of the accident can yield information on the type of injury expected. 4.concussion,headache,vomiting or amnesia?brain damage must be excluded and referral to a hospital for further investigation organized. 1.4.2 clinical examination Facial swelling.bruises,mandibular movement or mandibular Inspection deviation on opening or closing the mouth,crown fracture mobility Palpation and percussion ensitive to percussion.displacement.cinch.root fracture.alveolar rute Pulpal examination Thermal tests,cold tests,electric puip tests,neither negative nor (reaction to sensitivity tests)positive responses should be trusted immediately after trauma. 1.4.3 radiographic examination crown and root fracture,and their condition. 2.alveolar and jaw bones fracrute,and their condition. 3 condition of the periodontal tissue 4.condition of adjacent teeth and dental germ 5. conditio n of 6.relationship between primary teeth and succeed permanent teeth
lateral luxation intrusive luxation avulsion Injuries to the supporting bone comminution of alveolar socket fracture of alveolar socket wall fracture of alveolar process fractures of mandible or maxilla, jaw fracture Injuries to the gingival or oral mucosa laceration of gingiva or oral mucosa contusion of gingiva or oral mucosa abrasion of gingiva or oral mucosa 1.4 history and examination 1.4.1 dental history 1.when did injury occur?the time interval between injury and treatment significantly influuences the prognosis of trauma. 2.where did injury occur?may indicate the need for tetanus prophylaxis. 3.how did injury occur?the nature of the accident can yield information on the type of injury expected. 4.concussion,headache,vomiting or amnesia?brain damage must be excluded and referral to a hospital for further investigation organized. 1.4.2 clinical examination Inspection Facial swelling,bruises,mandibular movement or mandibular deviation on opening or closing the mouth,crown fracture,mobility Palpation and percussion sensitive to percussion,displacement,cinch,root fracture,alveolar fracrute,and so on. Pulpal examination (reaction to sensitivity tests) Thermal tests, cold tests,electric puip tests, neither negative nor positive responses should be trusted immediately after trauma. 1.4.3 radiographic examination Division:periapical , occlusal ,orthopantomogram 1. crown and root fracture,and their condition. 2. alveolar and jaw bones fracrute,and their condition. 3. condition of the periodontal tissue. 4. condition of adjacent teeth and dental germ. 5. condition of root formation and absorption. 6. relationship between primary teeth and succeed permanent teeth

7.if there are root absorption and modus to the old trauma section II:Diagnosis and treatment of dental trauma In the young permanent dentition 1.enamel infraction and crown fracture 2.crown-root fracture 3.root fracture 4.tooth luxation injuries 5.tooth avulsion 6.prognosis assessment 1.1 crown fracture:it was the commonest in the tooth fracture,it was predilected in incisal angle and incisal edge. It was divided into merely enamel fracture,enamel fracture with dentin exposed,crown fracture with pulp exposed. 1.1.1 merely e amel fractur cinicalstuationtwsprodtlectodinincidlangleandincidedge,andentindidnitepoe Treatment: No disposal. Grinding and polishing to restore in the near future for the small areas 1.1.2 enamel fracture with dentin exposed clinical situation:dentin exposed,and they were sensitive to the caloric stimulation,it was essential to pulp protection. Treatment: Took indireet pulp cappin ng to protect pulp mobility not obviously:direct repair. mobility obviously:repair temporary with Complex resin,then to restore permanently after mobility vanishing. modulate occlusion follow-up review periodic 1.1.fracture with pulp exposd clinical situation:crown fracture with pulp exposed,they were sensitive to the caloric stimulation,and affected to take food.it could be infected and pulp hyperblastosis if it didn't treat. Treatment Take direct pulp capping (it was difficult). Take apexification(root immaturating) Take root canal therapy(root maturating). 2.1 root fracture:it occur most frequently in the middle or the apical third of the root we can diagnose by radiograph and varying
7. if there are root absorption and modus to the old trauma. sectionⅡ: Diagnosis and treatment of dental trauma In the young permanent dentition 1. enamel infraction and crown fracture 2. crown-root fracture 3. root fracture 4. tooth luxation injuries 5. tooth avulsion 6. prognosis assessment 1.1 crown fracture:it was the commonest in the tooth fracture,it was predilected in incisal angle and incisal edge. It was divided into merely enamel fracture,enamel fracture with dentin exposed ,crown fracture with pulp exposed. 1.1.1 merely enamel fracture clinical situation:it was predilected in incisal angle and incisal edge,and dentin didn't expose. Treatment: No disposal. Grinding and polishing. to restore in the near future for the small areas. to restore after viewing for the large areas. 1.1.2 enamel fracture with dentin exposed clinical situation: dentin exposed,and they were sensitive to the caloric stimulation,it was essential to pulp protection. Treatment: Took indirect pulp capping to protect pulp. mobility not obviously: direct repair. mobility obviously: repair temporary with Complex resin,then to restore permanently after mobility vanishing. modulate occlusion. follow-up review periodic 1.1.3 crown fracture with pulp exposed clinical situation:. crown fracture with pulp exposed, they were sensitive to the caloric stimulation,and affected to take food.it could be infected and pulp hyperblastosis if it didn't treat. Treatment: Take direct pulp capping (it was difficult to success). Take palpotomy(root immaturating). .Take apexification(root immaturating). Take root canal therapy(root maturating). 2.1 root fracture:it occur most frequently in the middle or the apical third of the root.we can diagnose by radiograph and varying projection angle

2.1.1 It can be divided into three types: coronal third root fracture. midlehirdrofracture apical third root fracture 2.1.2 clinical manifestation: tooth mobility dental crown lenghen slihtly articulaliontaum 2.1.3 therapeutic principle reset to broken ends of fractured root splint tooth(2-3mouths). eliminate occlusion trauma 2.1.4 therapy thod corol third:extract the coronl fragment and retain the remaining root by extirpate gingive and strip alveolar bone partly.if the root was immature,we can Take apexification,keep the teeth interspace and Take root canal therapy when the root was mature.if the root was mature.we take root canal therapy directly.then draw root out of alveolar crest.this is root canal-orthodontic reatment.clinical middle third:replacement and splintingit can be fixed for 2-3mouths then review condition of broken ends healing and pulp vitality recovery.if take place pulp necrosis,we can adopt root canal therapy when broken ends healing otherwise we place retention post in root canal. apical third:prognosis is better than other root fracture,if the root fracture is almost immobility.wecan let alone.if there are mobility obviously.we can fix itif take place root tip athological es or calcify,w commit apicc oot tip rever 3.:,caementum fracture simultaneously when teeth traum take place.it can be divided into two types:simple crown-root fracture and complicated crown-root fracture. 3.1.I clinical manifestation fracture and vertica fractur Horiontal meddistal direction,dental rown labia surface droop partly,lingual surface connected with gingive sometimes.it may be take on gingive and pulp stimulus aching vertical fracture there is only single band fracture line usually and it is few in clinical. 3.1.2 therapy method emergency treat ment:fixed tempo simple crown-root fracture:cemental repai vertical fracture:stickiness treatment. Systemical therapy Reparation after removing dental crown fragment. 4.1 it can be divided into five types Concussion subluxation
2.1.1 It can be divided into three types: coronal third root fracture. middle third root fracture. apical third root fracture. 2.1.2 clinical manifestation: tooth mobility dental crown lengthen slightly articulation trauma 2.1.3 therapeutic principle reset to broken ends of fractured root. splint tooth(2-3mouths). eliminate occlusion trauma. 2.1.4 therapy method coronal third:extract the coronal fragment and retain the remaining root by extirpate gingive and strip alveolar bone partly.if the root was immature,we can Take apexification,keep the teeth interspace ,and Take root canal therapy when the root was mature, if the root was mature,we take root canal therapy directly,then draw root out of alveolar crest, this is root canal- orthodontic treatment,clinical prognosis was worse middle third:replacement and splinting,it can be fixed for 2-3mouths,then review condition of broken ends healing and pulp vitality recovery.if take place pulp necrosis,we can adopt root canal therapy when broken ends healing,otherwise we place retention post in root canal. apical third:prognosis is better than other root fracture,if the root fracture is almost immobility,we can let alone;if there are mobility obviously,we can fix it ;if take place root tip pathological changes or calcify,we can commit apiectomy and root tip reverse filling. 3.1 Crown-root fracture:enamel,dentin, caementum fracture simultaneously when teeth trauma take place,it can be divided into two types:simple crown-root fracture and complicated crown-root fracture. 3.1.1 clinical manifestation Horizontal fracture and vertical fracture Horizontal fracture:it is common in clinical,display med-distal direction,dental crown labial surface droop partly,lingual surface connected with gingive sometimes.it may be take on gingive and pulp stimulus aching. vertical fracture:there is only single band fracture line usually,and it is few in clinical. 3.1.2 therapy method emergency treatment:fixed temporary. simple crown-root fracture: cemental repair. vertical fracture: stickiness treatment. Systemical therapy: Reparation after removing dental crown fragment. Remove dental crown fragment and assist gingivectomy and remove alveolar bone. root canal- orthodontic combined treatment. 4.1 it can be divided into five types Concussion subluxation