
Chapter4 Growth and development of craniofacialand dentition in children Department ofPediatric Dentistry Zhang Hongmei vocabulary craniofacial颅面的dentition牙列growth生长development发育 fetus period胎儿期neonatal period新生儿期infancy period婴儿期 toddler period幼儿期preschool age学龄前期schoolage学龄期 adolescent period青春发育期lymphoid淋巴neural神经genital生殖 metabolic新陈代谢的endocrine内分泌的chromosomal染色体的 skeleton骨骼primordial原始的embryos胚胎osteogenic成骨的 intramembranous膜内的endochondral软骨内的ossification成骨 cranium颅parietal颅顶骨的occipital枕骨的sphenoid蝶骨 ethmoid筛骨的temporal bone颞骨hyperplasia增生maxillary上颌骨的 nasal鼻的stroma基质mandible下颌骨condylar髁的cartilage软骨 condyle髁突gems胚芽occlusion咬合lamina薄板intraosseous骨内的 epithelium上皮enamel牙釉质dental papilla牙乳头permanent teeth恒牙 anterior teeth前牙posteriorteeth后牙gestational age胎龄 primitive oral cavity原始口腔deciduous tooth乳牙incisor切牙 canine尖牙premolar tooth前磨牙nolar磨牙symmetrical对称的 mandibular下颌的upper jaws上颌lower jaws下颌primary teeth乳牙 pathological病理的lingual舌的mechanism机制Molecular分子的 lacuna腔隙masticatory咀嚼的malocclusion咬合不正periodontal牙周的 lateral movement横向运动dental arch牙弓proximal近端的distal末端的 primatespace灵长间隙developmental space发育间隙 physiological space生理间隙leeway space剩余间隙 intermaxillary space颌间间隙terminalplane末端平面overbite覆合 overjet覆盖embryonic胚胎的ugly ducking stage胚胎的丑小鸭阶段 labial唇的
Chapter 4 Growth and development of craniofacial and dentition in children Department of Pediatric Dentistry Zhang Hongmei vocabulary : craniofacial 颅面的 dentition 牙列 growth 生长 development 发育 fetus period 胎儿期 neonatal period 新生儿期 infancy period 婴儿期 toddler period 幼儿期 preschool age 学龄前期 school age 学龄期 adolescent period 青春发育期 lymphoid 淋巴 neural 神经 genital 生殖 metabolic 新陈代谢的 endocrine 内分泌的 chromosomal 染色体的 skeleton 骨骼 primordial 原始的 embryos 胚胎 osteogenic 成骨的 intramembranous 膜内的 endochondral 软骨内的 ossification 成骨 cranium 颅 parietal 颅顶骨的 occipital 枕骨的 sphenoid 蝶骨 ethmoid 筛骨的 temporal bone 颞骨 hyperplasia 增生 maxillary 上颌骨的 nasal 鼻的 stroma 基质 mandible 下颌骨 condylar 髁的 cartilage 软骨 condyle 髁突 germs 胚芽 occlusion 咬合 lamina 薄板 intraosseous 骨内的 epithelium 上皮 enamel 牙釉质 dental papilla 牙乳头 permanent teeth 恒牙 anterior teeth 前牙 posterior teeth 后牙 gestational age 胎龄 primitive oral cavity 原始口腔 deciduous tooth 乳牙 incisor 切牙 canine 尖牙 premolar tooth 前磨牙 molar 磨牙 symmetrical 对称的 mandibular 下颌的 upper jaws 上颌 lower jaws 下颌 primary teeth 乳牙 pathological 病理的 lingual 舌的 mechanism 机制 Molecular 分子的 lacuna 腔隙 masticatory 咀嚼的 malocclusion 咬合不正 periodontal 牙周的 lateral movement 横向运动 dental arch 牙弓 proximal 近端的 distal 末端的 primate space 灵长间隙 developmental space 发育间隙 physiological space 生理间隙 leeway space 剩余间隙 intermaxillary space 颌间间隙 terminal plane 末端平面 overbite 覆合 overjet 覆盖 embryonic 胚胎的 ugly ducking stage 胚胎的丑小鸭阶段 labial 唇的

Teaching content: Growthand developmentstages and characteristics ofeach stage The factors influencing growth and development The growth and development ofthe craniofacial skeleton The development oftoothand occlusion Master: The characteristics ofeach growth period thetiming and sequence of dental development growth and development stages oftooth and occlusion Familiar: Influencing factors of growth and development characteristics ofgrowth and development of upper and lower jaw and teeth Understand:Anatomical and physiological changes in dentition and occlusion development Section 1 Stages and Characteristics -、Stages (一)fetus period (二)neonatal period (三)infancy period (四)toddler period (五)preschool period (六)school period (adolescentperiod The relationship between the development and age Lymphoid type Neural type Generaltype Genitaltype
Teaching content: Growth and development stages and characteristics of each stage The factors influencing growth and development The growth and development of the craniofacial skeleton The development of tooth and occlusion Master: The characteristics of each growth period the timing and sequence of dental development growth and development stages of tooth and occlusion Familiar: Influencing factors of growth and development characteristics of growth and development of upper and lower jaw and teeth Understand:Anatomical and physiological changes in dentition and occlusion development Section 1 Stages and Characteristics 一、Stages (一)fetus period (二)neonatal period (三)infancy period (四)toddler period (五)preschool period (六)school period (七)adolescent period The relationship between the development and age Lymphoid type Neural type General type Genital type
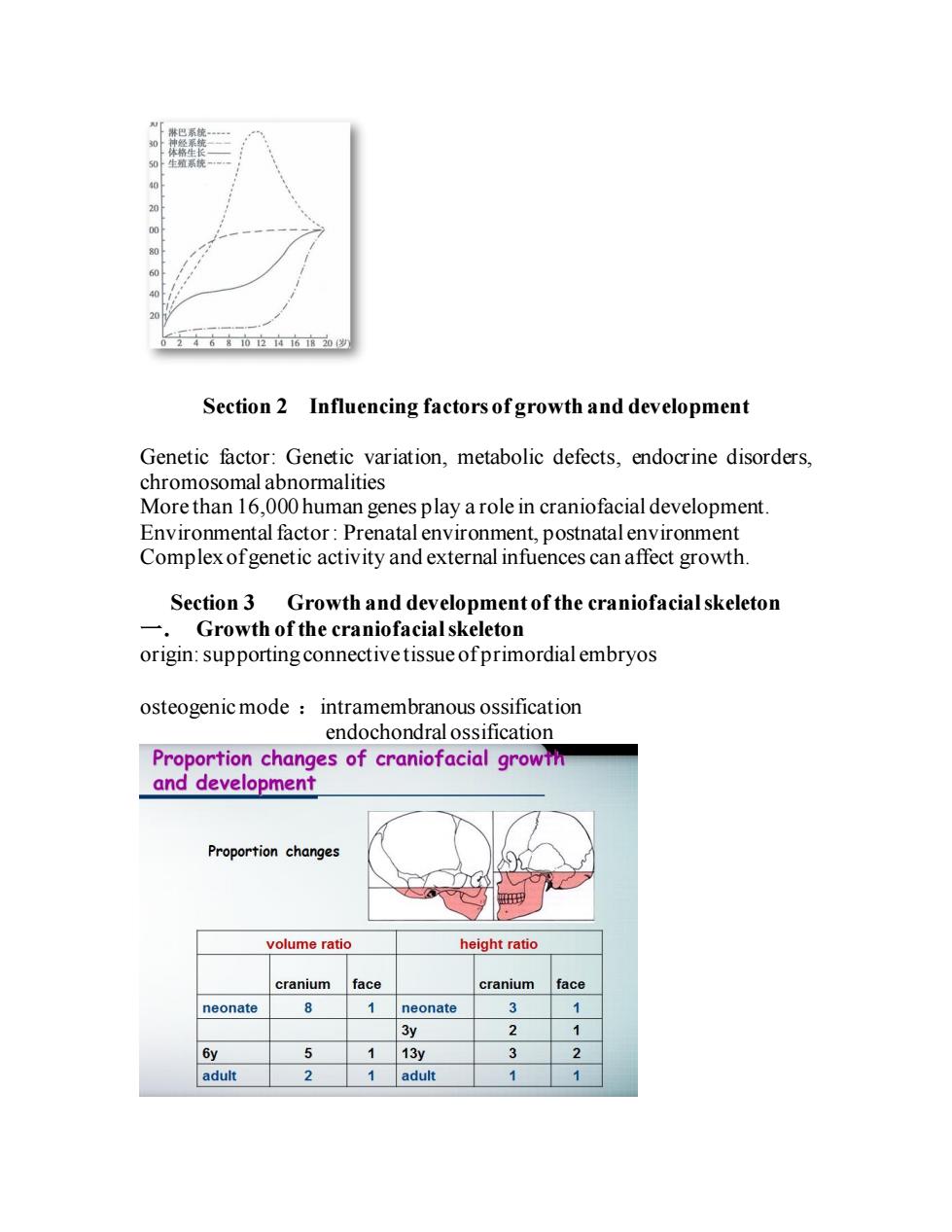
体生 Section 2 Influencing factors of growth and development Genetic factor:Genetic variation,metabolic defects,endocrine disorders, chromosomal abnormalities More than 16,000 human genes play a role in craniofacial development. Environmental factor:Prenatal environment,postnatal environment Complex ofgenetic activity and external infuences can affect growth. Section 3 Growth and development of the craniofacial skeleton -Growth of the craniofacial skeleton origin:supporting connective tissue ofprimordial embryos osteogenic mode intramembranous ossification endochondral ossification Proportion changes of craniofacial growt and development Proportion changes volume ratio height ratio cranium face cranium face neonate 8 neonate 13 adult adult
Section 2 Influencing factors of growth and development Genetic factor: Genetic variation, metabolic defects, endocrine disorders, chromosomal abnormalities More than 16,000 human genes play a role in craniofacial development. Environmental factor : Prenatal environment, postnatal environment Complex of genetic activity and external infuences can affect growth. Section 3 Growth and development of the craniofacial skeleton 一. Growth of the craniofacial skeleton origin: supporting connective tissue of primordial embryos osteogenic mode :intramembranous ossification endochondral ossification

Cranium growth:1-2y(rapidest development),6y(about 90%) Facial growth:1-2y,9-14y (rapidest development),Height>Depth>Width 3.Craniofacial skeleton growth and development Ist period of accelerated growth:postnatal 7m 2nd period of accelerated growth:4y-7y 3rd period of accelerated growth:1ly-13y 4thperiod of accelerated growth:16y-19y 4.Cranium growth intramembranous ossification:cranium,including forehead bone,parietal bone endochondral ossification:occipital bone,sphenoid bone,ethmoid bone. and temporal bone Bone surface hyperplasia is the main form of bone growth,one side new bone deposition and the other side old bone resorption. 5.Facial bonegrowth Three-dimensional growth ofmaxillary (length,width,height):key of facial structure Volume growth mainly depends on bone surface hyperplasia and interstitial stroma hyperplasia. Growth and development of mandible The mandible growth mainly depends on the bone surface proliferation and condylar cartilage osteogenesis. Condyle is the main growth center of mandible,it's the last one to stop developingamong the facial bones. Section 4 Development of tooth and occlusion process of tooth development time oftooth development time and sequence of tootheruption mechanism oftooth eruption succession of deciduousteeth development oftooth and occlusion
Cranium growth:1-2y ( rapidest development), 6y ( about 90%) Facial growth:1-2y,9-14y ( rapidest development), Height> Depth> Width 3.Craniofacial skeleton growth and development 1st period of accelerated growth: postnatal 7m 2nd period of accelerated growth:4y-7y 3rd period of accelerated growth:11y-13y 4th period of accelerated growth:16y-19y 4. Cranium growth intramembranous ossification: cranium, including forehead bone, parietal bone endochondral ossification: occipital bone,sphenoid bone, ethmoid bone, and temporal bone Bone surface hyperplasia is the main form of bone growth, one side new bone deposition and the other side old bone resorption. 5. Facial bone growth Three-dimensional growth of maxillary (length、width、height): key of facial structure Volume growth mainly depends on bone surface hyperplasia and interstitial stroma hyperplasia . Growth and development of mandible The mandible growth mainly depends on the bone surface proliferation and condylar cartilage osteogenesis. Condyle is the main growth center of mandible, it's the last one to stop developing among the facial bones. Section 4 Development of tooth and occlusion process of tooth development time of tooth development time and sequence of tooth eruption mechanism of tooth eruption succession of deciduous teeth development of tooth and occlusion

It's about 20 years,including dental germs development,tooth eruption and occlusion establishment. Process of tooth development Dental germs formation (Growth) Dental tissue formation (Calcification) Tootheruption (Eruption) Tooth eruption:pre-eruptive phase eruption phase post-eruptive phase Active eruption:The teeth move towards occlusion and erupt to mouth. Passive eruption:The reduced enamel epithelium separated from the enamel surface,the gums recoiled toward the root,and the clinical crown exposed. Root development: Deciduous teeth need 1-1.5years Permanent teeth need 2-3 years(anterior teeth)/3-5 years(posterior teeth) 二,The time of tooth development Deciduous tooth germ from the 6th week to 10th week ofembryo Permanent tooth germ:from 4 months to 4 years ofage The rule of tootheruption:Certaintime,Certainorder,Left-right symmetrical eruption,Mandibular is earlier than the maxillary. The order oftootheruption is moreclinically significant than thetime of tootheruption. Thereare large individual differences in the timing of tootheruption Influencing factors:genetic factors,environmental factors The order oftootheruptionalso frequently mutates
It's about 20 years, including dental germs development, tooth eruption and occlusion establishment. Process of tooth development Dental germs formation(Growth) Dental tissue formation(Calcification) Tooth eruption(Eruption) Tooth eruption:pre-eruptive phase ;eruption phase ;post-eruptive phase Active eruption:The teeth move towards occlusion and erupt to mouth. Passive eruption:The reduced enamel epithelium separated from the enamel surface, the gums recoiled toward the root, and the clinical crown exposed. Root development : Deciduous teeth need 1 -1 .5years Permanent teeth need 2-3 years (anterior teeth) / 3-5 years (posterior teeth) 二 .The time of tooth development Deciduous tooth germ :from the 6thweek to 10th week of embryo Permanent tooth germ: from 4 months to 4 years of age. The rule of tooth eruption:Certain time,Certain order,Left-right symmetrical eruption,Mandibular is earlier than the maxillary. The order of tooth eruption is more clinically significant than the time of tooth eruption. There are large individual differences in the timing of tooth eruption. Influencing factors: genetic factors, environmental factors The order of tooth eruption also frequently mutates