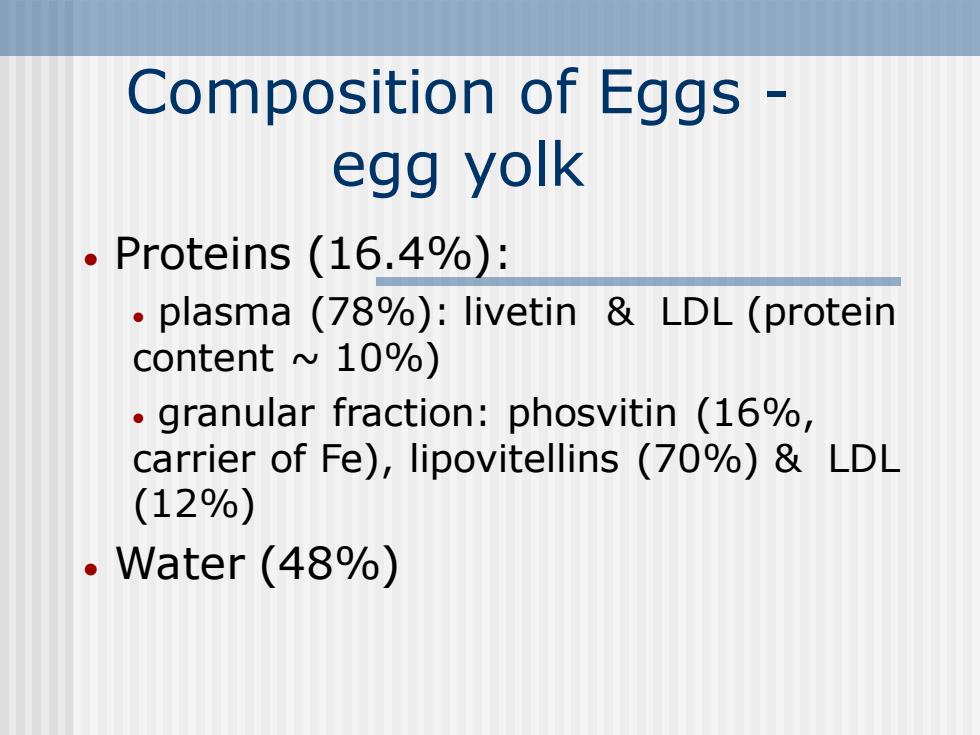
Composition of Eggs - egg yolk • Proteins (16.4%): • plasma (78%): livetin & LDL (protein content ~ 10%) • granular fraction: phosvitin (16%, carrier of Fe), lipovitellins (70%) & LDL (12%) • Water (48%)
Composition of Eggs - egg yolk • Proteins (16.4%): • plasma (78%): livetin & LDL (protein content ~ 10%) • granular fraction: phosvitin (16%, carrier of Fe), lipovitellins (70%) & LDL (12%) • Water (48%)

Composition of Eggs - egg yolk •Lipids (32 to 34%) − triglycerol (66%) − phospholipid (28%) including lecithin − (has remarkable emulsifying ability) − cholesterol (3%, or 250 mg) •The color of yolk depends on the presence of carotenoids. • xanthophylls not carotene (Lutein and zeaxanthin)
Composition of Eggs - egg yolk •Lipids (32 to 34%) − triglycerol (66%) − phospholipid (28%) including lecithin − (has remarkable emulsifying ability) − cholesterol (3%, or 250 mg) •The color of yolk depends on the presence of carotenoids. • xanthophylls not carotene (Lutein and zeaxanthin)


Egg Quality • Commercial grading of eggs according to the USDA standards • External quality: shell characteristics, shape, soundness, cleanliness, & color • Interior quality: size of the air cell, firmness of the white, & the yolk (distinct or flattened during aging) • Evaluated by candling
Egg Quality • Commercial grading of eggs according to the USDA standards • External quality: shell characteristics, shape, soundness, cleanliness, & color • Interior quality: size of the air cell, firmness of the white, & the yolk (distinct or flattened during aging) • Evaluated by candling

Egg quality during storage • The size of the air cell increases − water evaporates from the egg through shell • The egg white becomes thinner − ovomucin undergoes degradation • pH of white increases (from ~ 8 to ~9) − due to the loss of CO2 through the pores
Egg quality during storage • The size of the air cell increases − water evaporates from the egg through shell • The egg white becomes thinner − ovomucin undergoes degradation • pH of white increases (from ~ 8 to ~9) − due to the loss of CO2 through the pores