
Pathogenesis of E. coliE coli is a member of the normal intestinal florasometimes found in small numbers as part of the normal flora of theupper respiratory and genital tractsEcoligenerally donot cause disease, and in the intestine theymay even contribute to normal function and nutritionIt become pathogenic only when it reaches tissues outside of theintestinal or other normal flora sitesThe most frequent sites of clinically important infection are the urinarytract, biliary tract, and other sites in the abdominal cavitybut any anatomic site (eg, bacteremia, prostate gland lung, bonemeninges) can be the site of diseaseBut some species of E coli are regular pathogens+Cause exogenous infectionsSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Pathogenesis of E. coli E coli is a member of the normal intestinal flora sometimes found in small numbers as part of the normal flora of the upper respiratory and genital tracts E coli generally do not cause disease, and in the intestine they may even contribute to normal function and nutrition It become pathogenic only when it reaches tissues outside of the intestinal or other normal flora sites The most frequent sites of clinically important infection are the urinary tract, biliary tract, and other sites in the abdominal cavity but any anatomic site (eg, bacteremia, prostate gland, lung, bone, meninges) can be the site of disease But some species of E coli are regular pathogens Cause exogenous infections SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Diseases Caused by E. coli Intestinal tract infectionsDiarhea Caused by regular pathogenic E coli Infections outside intestinal tract Urinary tract infectionSepsisMeningitis Caused by translocation of Normal flora E coliSHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Diseases Caused by E. coli Intestinal tract infections Diarrhea Caused by regular pathogenic E coli Infections outside intestinal tract Urinary tract infection Sepsis Meningitis Caused by translocation of Normal flora E coli SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

E coli-Associated Diarrheal DiseasesE coli that cause diarrhea are extremely common worldwide中These E coli are classified by the characteristics of theivirulence propertiesEPECEnteropathogenic E coliETECEnterotoxigenic E coliEHECEnterohemorrhagic EcoliEIECEnteroinvasive E coliEAECEnteroaggregative E colidiffusely adherent E. coli (DAEC) ?Each group causes disease by a different mechanismThe intestinal epithelial cell adherence properties and thetoxins are encoded by genes on plasmids or phagesSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
E coli-Associated Diarrheal Diseases E coli that cause diarrhea are extremely common worldwide These E coli are classified by the characteristics of their virulence properties Enteropathogenic E coli EPEC Enterotoxigenic E coli ETEC Enterohemorrhagic E coli EHEC Enteroinvasive E coli EIEC Enteroaggregative E coli EAEC diffusely adherent E. coli (DAEC) ? Each group causes disease by a different mechanism The intestinal epithelial cell adherence properties and the toxins are encoded by genes on plasmids or phages SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
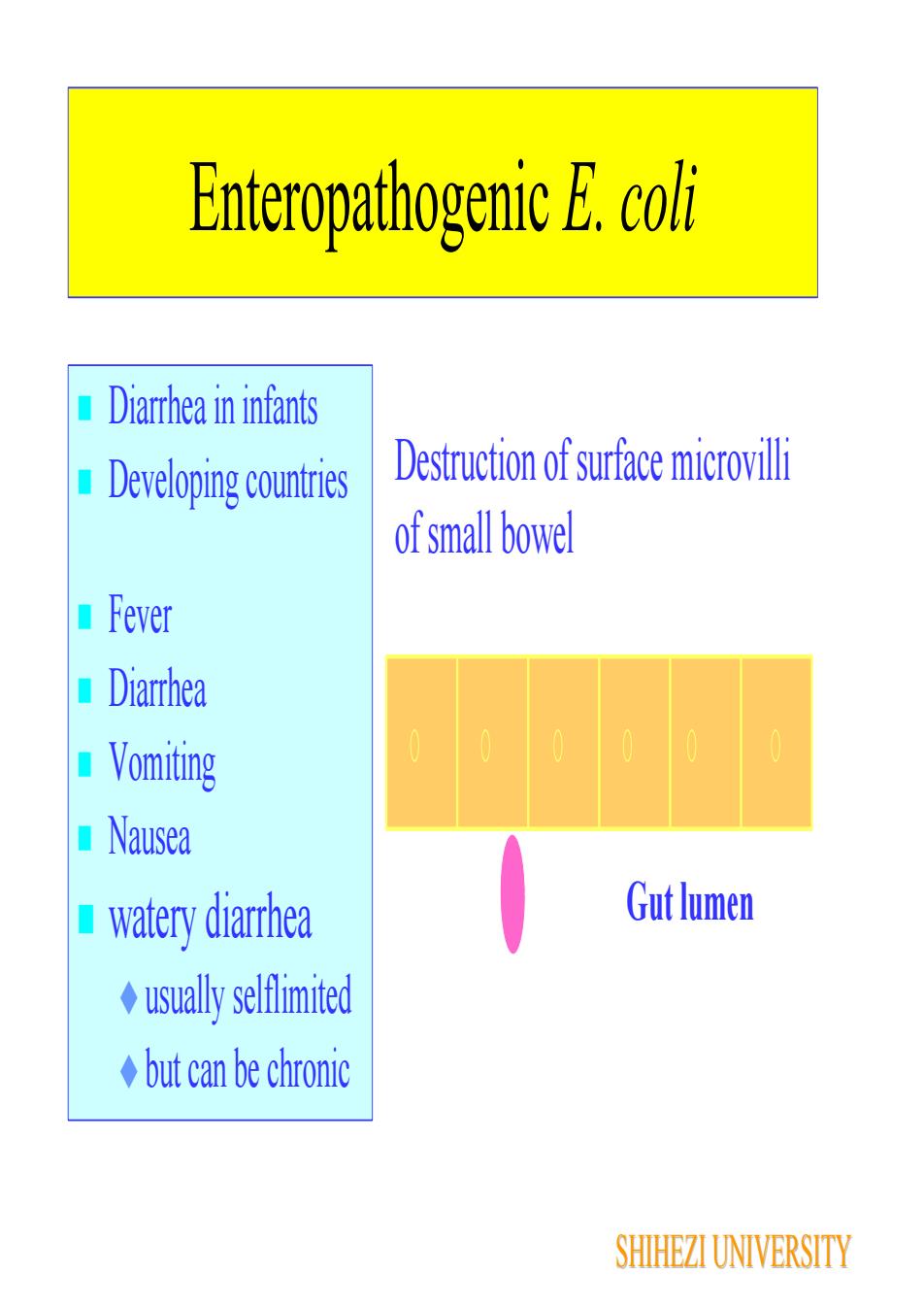
Enteropathogenic E. coliDiarrhea in infantsDestruction of surface microvilli1 Developing countriesof small bowelFeverDiarrhea0 Vomiting NauseaGut lumenwatery diarrhea+ usually selflimited+ but can be chronicSHIHEZI UNIVERSITY
Destruction of surface microvilli of small bowel Gut lumen Enteropathogenic E. coli Diarrhea in infants Developing countries Fever Diarrhea Vomiting Nausea watery diarrhea usually selflimited but can be chronic SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY

Enterotoxigenic E. coli Diarrhea like choleramilder Travellers’ diarrheaMajor virulence factors in ETECAdherence+ Adhesive fimbriaeToxin Heat-labile toxin (LT)Heat-stable toxin (ST)SHIHEZIUNIVERSITY
Enterotoxigenic E. coli Diarrhea like cholera milder Travellers’diarrhea Major virulence factors in ETECAdherence Adhesive fimbriae Toxin Heat-labile toxin (LT) Heat-stable toxin (ST) SHIHEZI UNIVERSITY