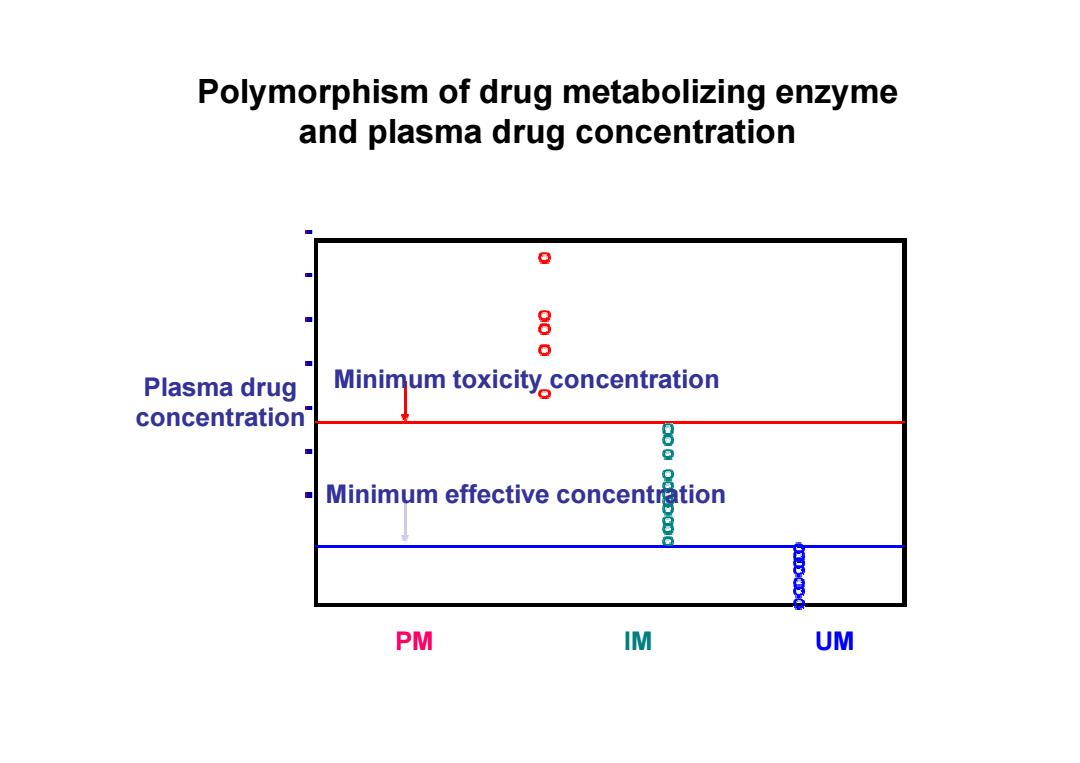
Polymorphism of drug metabolizing enzyme and plasma drug concentration 0 8 Plasma drug Minimum toxicity concentration concentration 8 Minimum effective concentration 8 PM IM UM
Polymorphism of drug metabolizing enzyme and plasma drug concentration Plasma drug Minimum toxicity concentration concentration PM IM UM Minimum toxicity concentration Minimum effective concentration
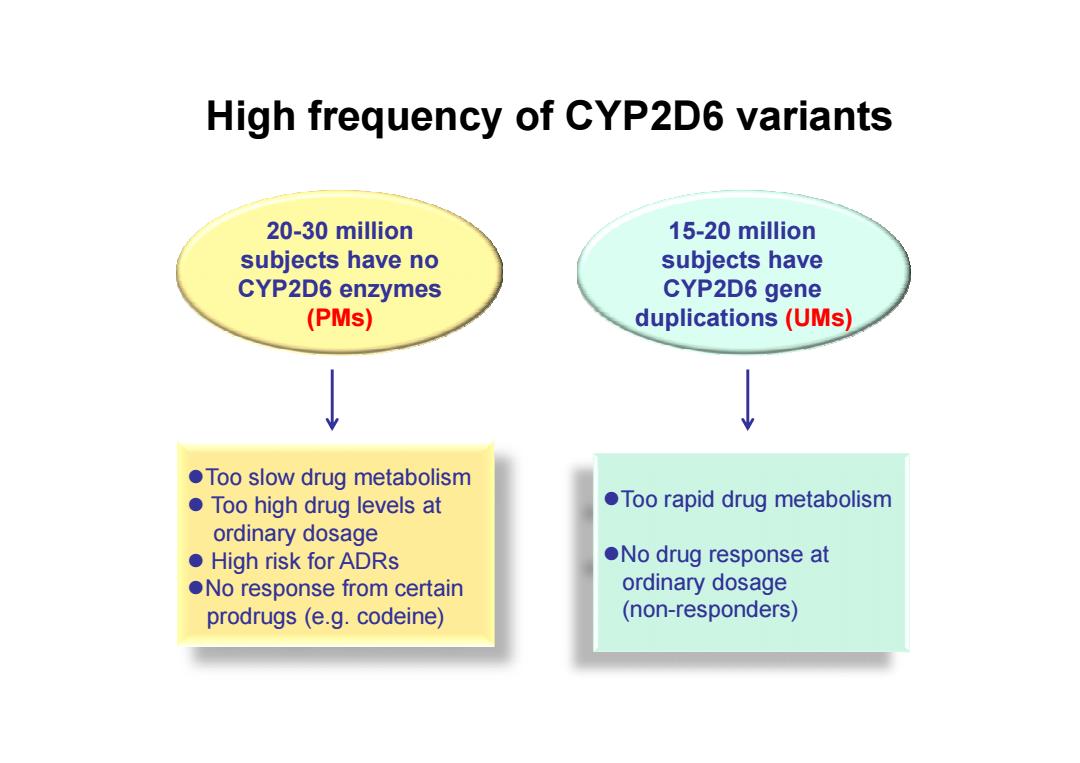
High frequency of CYP2D6 variants 20-30 million 15-20 million subjects have no subjects have CYP2D6 enzymes CYP2D6 gene (PMs) duplications(UMs) Too slow drug metabolism Too high drug levels at Too rapid drug metabolism ordinary dosage ●High risk for ADRs ●No drug response at ONo response from certain ordinary dosage prodrugs(e.g.codeine) (non-responders)
High frequency of CYP2D6 variants 20-30 million subjects have no CYP2D6 enzymes (PMs) 15-20 million subjects have CYP2D6 gene duplications (UMs) Too slow drug metabolism Too high drug levels at ordinary dosage High risk for ADRs No response from certain prodrugs (e.g. codeine) Too rapid drug metabolism No drug response at ordinary dosage (non-responders)������

Case report 1 62 y.o.man hospitalized for pneumonia ◆Treated with“standard'doses of codeine as a cough suppressant Coma Morphine levels 20x expected levels ◆ CYP2D6 ultra rapid metabolizer NEJM,30 Dec 2004
Case report 1 62 y.o. man hospitalized for pneumonia Treated with “standard” doses of codeine as a cough suppressant Coma Morphine levels 20x expected levels CYP2D6 ultra rapid CYP2D6 ultra rapid metabolizer metabolizer NEJM, 30 Dec 2004�����
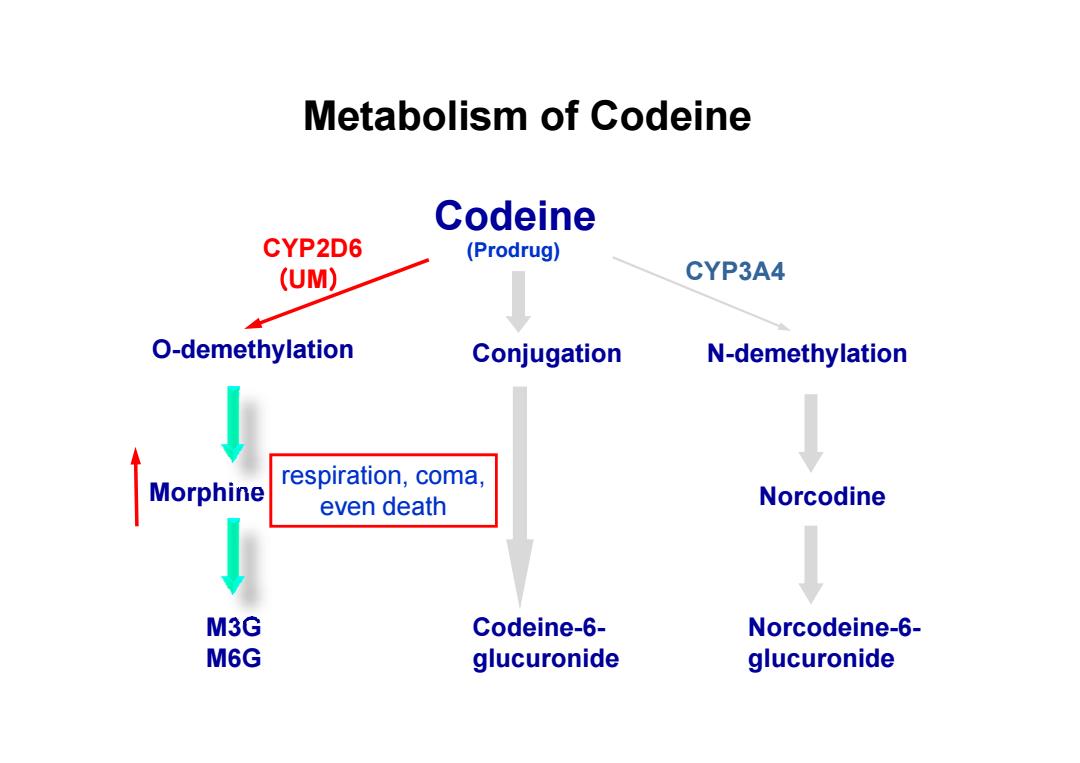
Metabolism of Codeine Codeine CYP2D6 (Prodrug) (UM) CYP3A4 O-demethylation Conjugation N-demethylation respiration,coma, Morphine even death Norcodine M3G Codeine-6- Norcodeine-6- M6G glucuronide glucuronide
Codeine O-demethylation Conjugation N-demethylation CYP2D6 (UM) CYP3A4 Metabolism of Codeine (Prodrug) Morphine M3G M6G Codeine-6- glucuronide Norcodine Norcodeine-6- glucuronide respiration, coma, even death
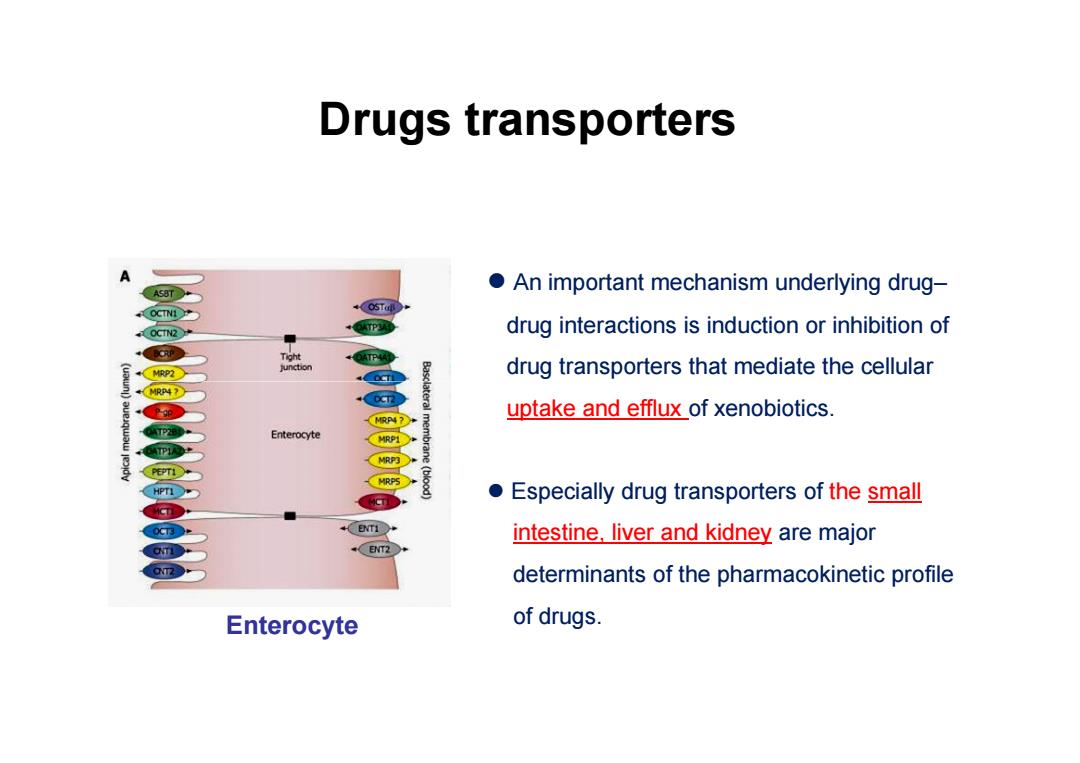
Drugs transporters O An important mechanism underlying drug- +OSTu OCTN2 drug interactions is induction or inhibition of MRP2 drug transporters that mediate the cellular MRP4 0T2 uptake and efflux of xenobiotics. Enterocyte MRP1 MRP3 T1 MRPS Especially drug transporters of the small intestine,liver and kidney are major ENT2 determinants of the pharmacokinetic profile Enterocyte of drugs
An important mechanism underlying drug– drug interactions is induction or inhibition of drug transporters that mediate the cellular Drugs transporters uptake and efflux of xenobiotics. Especially drug transporters of the small intestine, liver and kidney are major determinants of the pharmacokinetic profile of drugs. Enterocyte��