
Multiple Halogenations Cl2 c OH,H2O The a-haloketone produced is more reactive than ketone because the enolate ion is stabilized by the electron-withdrawing halogen. The second halogenation occurs faster than the first. Because of the tendency for multiple halogenations this base-promoted halogenation is not widely used to prepare monohalogenated ketones. Chapter 22 16
Chapter 22 16 Multiple Halogenations ▪ The a-haloketone produced is more reactive than ketone because the enolate ion is stabilized by the electron-withdrawing halogen. ▪ The second halogenation occurs faster than the first. ▪ Because of the tendency for multiple halogenations this base-promoted halogenation is not widely used to prepare monohalogenated ketones. O H Cl Cl2 OH , H2O _ O Cl Cl O Cl C Cl l O Cl C Cl l Cl

Bromoform Reaction R-C-CH, excess X2.OH a methyl ketone (X2=Cl2.Br2.or I2) HCX, a trihalomethyl ketone a carboxylate a haloform (not isolated) -A methyl ketone reacts with a halogen under strongly basic conditions to give a carboxylate ion and a molecule of haloform. The trihalomethyl intermediate is not isolated. Chapter 22 17
Chapter 22 17 Bromoform Reaction ▪ A methyl ketone reacts with a halogen under strongly basic conditions to give a carboxylate ion and a molecule of haloform. ▪ The trihalomethyl intermediate is not isolated

Mechanism of Haloform Formation :0 R -CX :OH R- CX2R一 oH :CX3→R-( HCX, :OH nucleophilic acyl substitution a carboxylate ion a haloform Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The trihalomethyl ketone reacts with hydroxide ion to give a carboxylic acid. A fast proton exchange gives a carboxylate ion and a haloform. When Cl2 is used,chloroform is formed;Br2 forms bromoform and 12 forms iodoform. Chapter 22 18
Chapter 22 18 Mechanism of Haloform Formation ▪ The trihalomethyl ketone reacts with hydroxide ion to give a carboxylic acid. ▪ A fast proton exchange gives a carboxylate ion and a haloform. ▪ When Cl2 is used, chloroform is formed; Br2 forms bromoform ; and I2 forms iodoform

Positive lodoform Test for Alcohols OH RCH-CH +2 -OH R-C-0-+HCI, (one less carbon) Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The iodine oxidizes the alcohol to a methyl ketone and it will give a positive iodoform test. lodoform (CHla)is a yellow solid that will precipitate out of solution. Chapter 22 19
Chapter 22 19 Positive Iodoform Test for Alcohols ▪ The iodine oxidizes the alcohol to a methyl ketone and it will give a positive iodoform test. ▪ Iodoform (CHI3) is a yellow solid that will precipitate out of solution
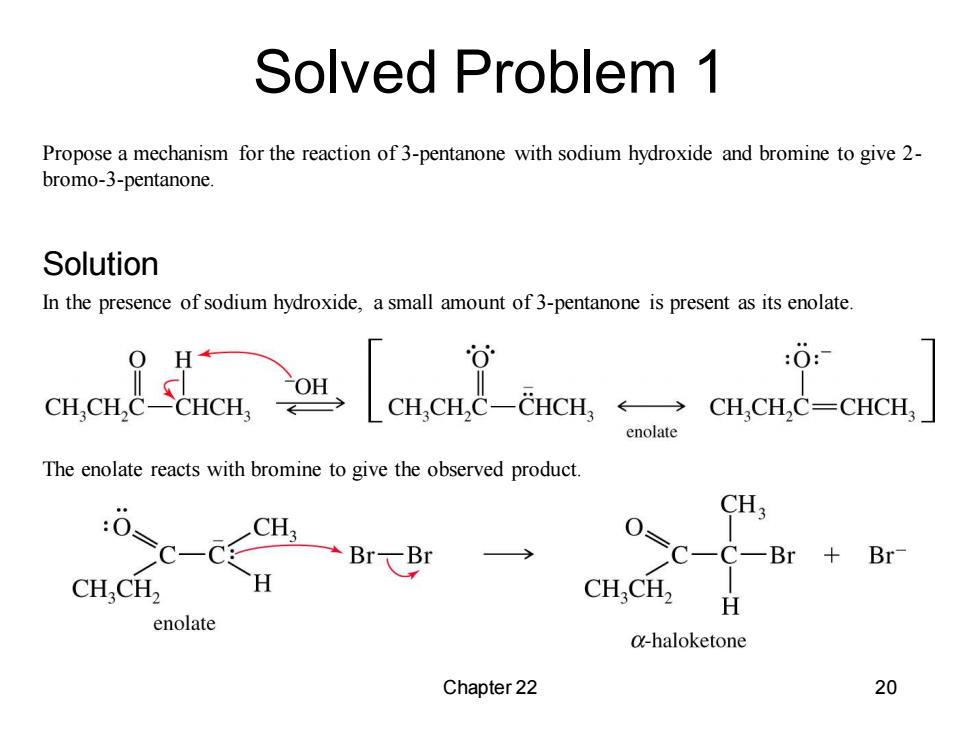
Solved Problem 1 Propose a mechanism for the reaction of 3-pentanone with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give 2- bromo-3-pentanone. Solution In the presence of sodium hydroxide,a small amount of 3-pentanone is present as its enolate. CHCH.C CHCH :0: CH.CH.C-CHCH ←→ CH,CH,C=CHCH enolate The enolate reacts with bromine to give the observed product CH3 0=C-C CH C-C-B Br CH.CH2 H CH,CH2 H enolate @-haloketone Chapter 22 20
Chapter 22 20 Propose a mechanism for the reaction of 3-pentanone with sodium hydroxide and bromine to give 2- bromo-3-pentanone. In the presence of sodium hydroxide, a small amount of 3-pentanone is present as its enolate. The enolate reacts with bromine to give the observed product. Solved Problem 1 Solution