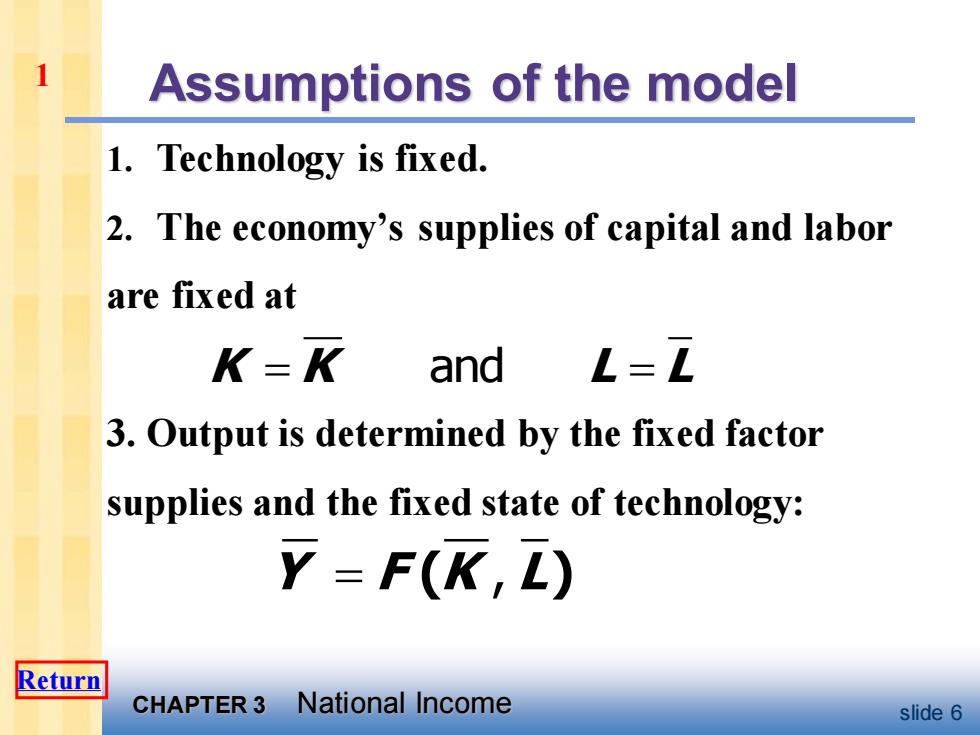
Assumptions of the model 1.Technology is fixed. 2.The economy's supplies of capital and labor are fixed at K=K and L=L 3.Output is determined by the fixed factor supplies and the fixed state of technology: Y=F(K,L) Return CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 6
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 6 Assumptions of the model 1. Technology is fixed. 2. The economy’s supplies of capital and labor are fixed at 3. Output is determined by the fixed factor supplies and the fixed state of technology: K K L L = = and 1 Y F K L = ( ) , Return

The distribution of national income -The distribution of the total income is determined by factor prices,the prices per unit that firms pay for the factors of production. -The wage is the price of L,the rental rate is the price of K. CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 7
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 7 The distribution of national income ▪ The distribution of the total income is determined by factor prices, the prices per unit that firms pay for the factors of production. ▪ The wage is the price of L, the rental rate is the price of K. 2

2 Notation W nominal wage R nominal rental rate P price of output WIP real wage (measured in units of output) R/P real rental rate CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 8
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 8 Notation W = nominal wage R = nominal rental rate P = price of output W/P = real wage (measured in units of output) R/P = real rental rate 2
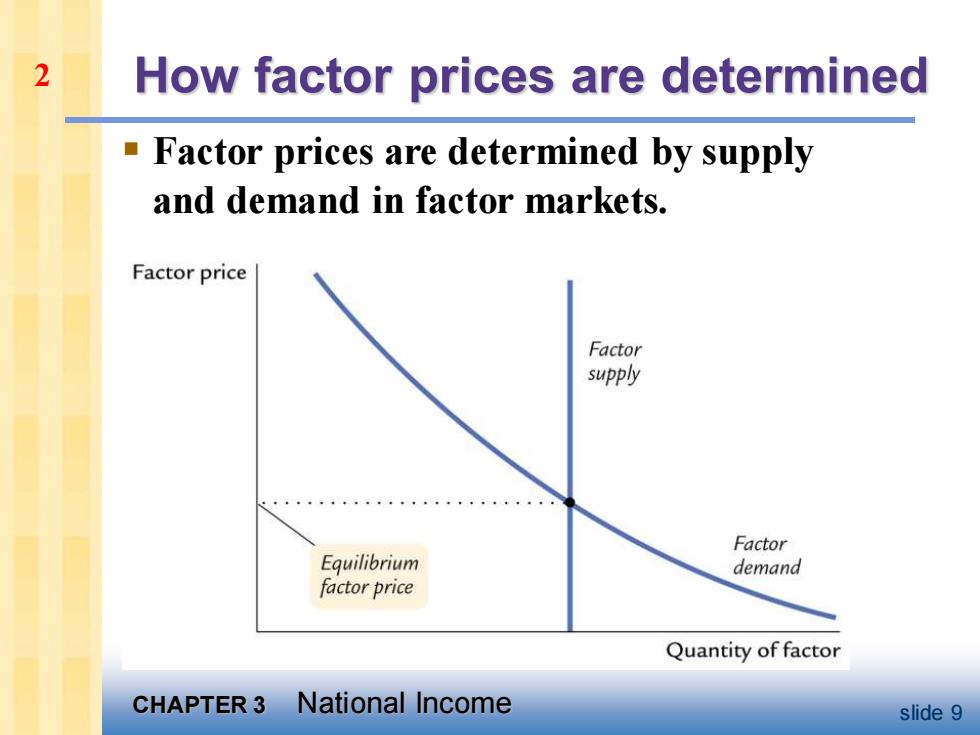
2 How factor prices are determined Factor prices are determined by supply and demand in factor markets. Factor price Factor supply Factor Equilibrium demand factor price Quantity of factor CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 9
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 9 How factor prices are determined ▪ Factor prices are determined by supply and demand in factor markets. 2

2 Demand for labor Assume markets are competitive: each firm takes W,R,and P as given -Basic idea: A firm hires each unit of labor if the cost does not exceed the benefit. cost real wage benefit marginal product of labor MPL F(K,L+1)-F(K,L) CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 10
CHAPTER 3 National Income slide 10 Demand for labor ▪Assume markets are competitive: each firm takes W, R, and P as given ▪Basic idea: A firm hires each unit of labor if the cost does not exceed the benefit. cost = real wage benefit = marginal product of labor ▪ MPL = F (K,L +1) – F (K,L) 2