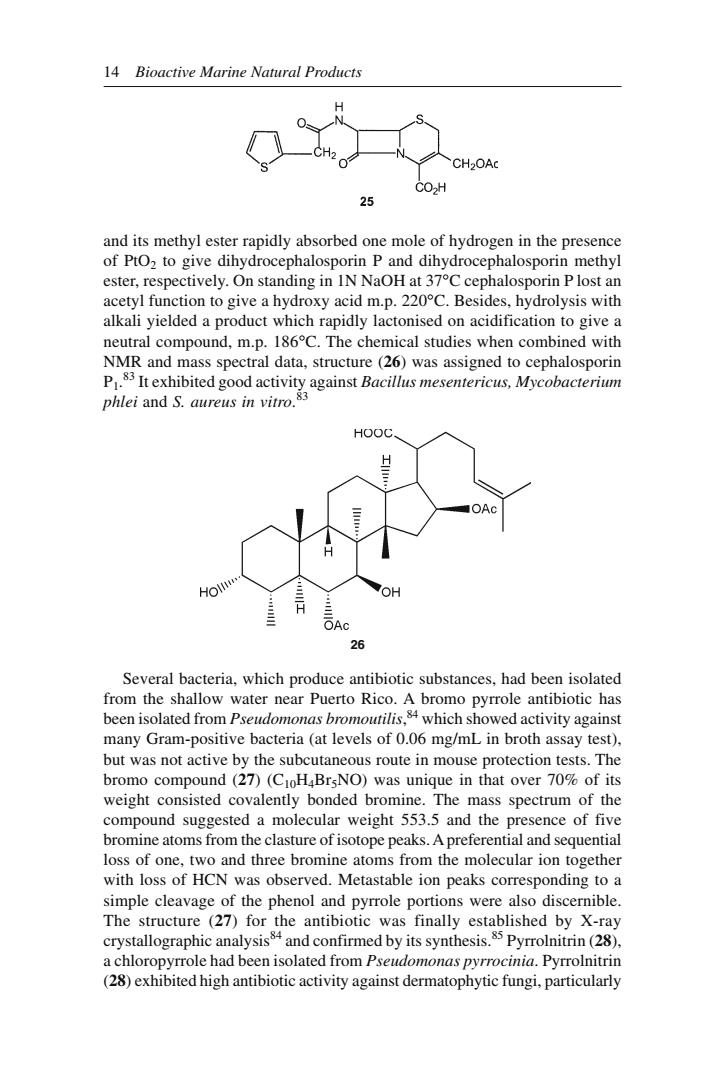
14 Bioactive Marine Natural Products CH2OA 25 and its methyl ester rapidly absorbed one mole of hydrogen in the presence of PtO2 to give dihydrocephalosporin P and dihydrocephalosporin methyl ester,respectively.On standing in IN NaOH at 37C cephalosporin P lost an neutral compound,m.p.186C.The chemical studies when combined with NMR and mass spectral data,structure (26)was assigned to cephalosporin waa,A 2 Several bacteria,which produce antibiotic substances.had been isolated from the shallow water near Puerto Rico.A bromo p pyrrole antibiotic has been isolated from ed activity agains many Gram-positive bacteria(at levels/mLin broth assay test). but was not active by the subcutaneous route in mouse protection tests.The bromo compound(27)(CIoH BrsNO)was unique in that over 70%of its weight consisted covalently bonded bromine.The mass spectrum of the ompound suggested a molecular weight 553.5 and the sence of five bromine atoms from the clasture of isotope peaks.A prefe loss of one,two and three bromine atoms from the molecular ion together with loss of HCN was observed.Metastable ion peaks corresponding to a simple cleavage of the phenol and pyrrole portions were also discernible. The structure (27)for the antibiotic was finally established by x-ray its synthesis.Py trin(28) achloropyrole had been isolated from Pse (28)exhibited high antibiotic activity against dermatophytic fungi,particularly
14 Bioactive Marine Natural Products Several bacteria, which produce antibiotic substances, had been isolated from the shallow water near Puerto Rico. A bromo pyrrole antibiotic has been isolated from Pseudomonas bromoutilis, 84 which showed activity against many Gram-positive bacteria (at levels of 0.06 mg/mL in broth assay test), but was not active by the subcutaneous route in mouse protection tests. The bromo compound (27) (C10H4Br5NO) was unique in that over 70% of its weight consisted covalently bonded bromine. The mass spectrum of the compound suggested a molecular weight 553.5 and the presence of five bromine atoms from the clasture of isotope peaks. A preferential and sequential loss of one, two and three bromine atoms from the molecular ion together with loss of HCN was observed. Metastable ion peaks corresponding to a simple cleavage of the phenol and pyrrole portions were also discernible. The structure (27) for the antibiotic was finally established by X-ray crystallographic analysis84 and confirmed by its synthesis.85 Pyrrolnitrin (28), a chloropyrrole had been isolated from Pseudomonas pyrrocinia. Pyrrolnitrin (28) exhibited high antibiotic activity against dermatophytic fungi, particularly and its methyl ester rapidly absorbed one mole of hydrogen in the presence of PtO2 to give dihydrocephalosporin P and dihydrocephalosporin methyl ester, respectively. On standing in 1N NaOH at 37°C cephalosporin P lost an acetyl function to give a hydroxy acid m.p. 220°C. Besides, hydrolysis with alkali yielded a product which rapidly lactonised on acidification to give a neutral compound, m.p. 186°C. The chemical studies when combined with NMR and mass spectral data, structure (26) was assigned to cephalosporin P1. 83 It exhibited good activity against Bacillus mesentericus, Mycobacterium phlei and S. aureus in vitro. 83 26

Bioactive Metabolites of Marine Algae,Fungi and Bacteria 15 against members of the genus Trychophyton and against many soil borne fungal plant pathogens like and sambucinum and as gainst foliar fungal pathoger ns like Fusarium graminearum. E culmorum and Pyrenophora tritici repentis.This compound was marketed in Japan under the name PYRO-ACE for the treatment of superficial dermatophytic infections.h Its light sensitivity prevented the use of pyrrolnitrin(28)as a fungicide in plant protection.Recently,antimycobacterial activity was reported for (and related compoundsBiological activity of()atow concentrat. demonstrated to be due to the uncoupling of oxidativ phosphorylation in Neurospora crassa and at higher concentrations due to c9opemecmytattp2的eOgyo accumulation and stimulation of triacylglycerol synthesis resulting in leaky cell membra and concom eak down of bic synthetic activity follo ised as 3-chlord (2-nitro-3-chlorophenyl)pyrrole.A synthesis of the antibiotic is reported.7 The formation of antibiotic substances of the types mentioned above gives the indication that the marine microbes are capable of producing new and Peinsalaque saoueisqns onoignue to sadl lensnun would,undo edly,be found useful in medic and pharmacology,while others could become of even greater interest than native product. Serratia marcescens,a widely distributed non-pathogenic bacterium,had furnished a red coloured antibiotic named prodigiosin.It exhibited high precluded its use as a therapeutic agent. Studies on the marine phytoplanktons are few because of difficulty of goebeoaoamcmaloo8omeeoexSs The cultured cells of the dinoflagellate Prychodiscus brevis,yielded brevetoxin B.C and dihydrobrevetoxin B.-107A ique feature of their struct chain of GB-4 and
Bioactive Metabolites of Marine Algae, Fungi and Bacteria 15 against members of the genus Trychophyton and against many soil borne fungal plant pathogens like Rhizoctonia solani and Fusarium sambucinum and against foliar fungal pathogens like Fusarium graminearum, F. culmorum and Pyrenophora tritici repentis. 86 This compound was marketed in Japan under the name PYRO-ACE for the treatment of superficial dermatophytic infections.86h Its light sensitivity prevented the use of pyrrolnitrin (28) as a fungicide in plant protection. Recently, antimycobacterial activity was reported for (28) and related compounds.86i Biological activity of (28) at low concentrations was demonstrated to be due to the uncoupling of oxidative phosphorylation in Neurospora crassa and at higher concentrations due to inhibition of electron transport both in the flavin region and through cytochrome coxidase.86l However, recently it was reported that (28) leads to glycerol accumulation and stimulation of triacylglycerol synthesis resulting in leaky cell membranes and concomitant break down of biosynthetic activity followed by cessation of cell growth.86m It had been characterised as 3-chloro-4- (2-nitro-3-chlorophenyl)pyrrole. A synthesis of the antibiotic is reported.87 The formation of antibiotic substances of the types mentioned above gives the indication that the marine microbes are capable of producing new and unusual types of antibiotic substances than the terrestrial ones. Some of these bioactive substances would, undoubtedly, be found useful in medicine and pharmacology, while others could become of even greater interest than native product. Serratia marcescens, a widely distributed non-pathogenic bacterium, had furnished a red coloured antibiotic named prodigiosin.88-96 It exhibited high order of antibiotic and antifungal activities. The high toxicity of prodigiosin precluded its use as a therapeutic agent. Studies on the marine phytoplanktons are few because of difficulty of growing the organisms and the low yield of secondary metabolites. However, several toxins related to saxitoxin are isolated from Gonyaulax species.97-103 The cultured cells of the dinoflagellate Ptychodiscus brevis, yielded brevetoxin B, C and dihydrobrevetoxin B.103-107 A unique feature of their structure is a chain of eleven, continuous trans-fused ether rings in the form of a flat ladder. P. brevis yielded two phosphorus containing toxins108 GB-4 and 27 28

16 Bioactive Marine Natural Products GB-1 which do not appear to be natural products since attempts to incorporate 32P into GB-1 gave ambiquous results.109.110 Two new polycyclic ethers.gB-5 and GB-6 closely related to okadaic acid.a toxin that was first found in in dinoflagellate have been isolated from the cultured ce G.breve an transmits shellfish,toxins that are responsibe for diarrhoetic shellfish poisoning.Lyngbya majuscula known to cause swimmer's itch has furnished Ae mmn yhe depsipeptic majusculam ide-Cisolated from th e orga inhibits thegwth blue-green algae Schizothrix calcicola and Oscillatoria nigroviridis possess antileukaemic activity but their high toxicity precludes their medicinal use. Cytotoxic and fungicidal nucleosides have been isolated from a variety of blue-green algae.30 Anatoxin-a,an exogenic toxin of blue-green alga Anabaena aguaeBisoneofthemostpotentnicotinicreceptoragonisL. is suggested that the analogues of anatoxin-a may be of clinical value for treating disorders associated with defects in cholinergic regions of the central nervous system. leley r lgica m the growth of marine bacteria and fungi,cell division of fertilized sea-urchin eggs and the motility of sea-urchin sperms at I ug/ml Avrainvilleo brominated metabolite of green algae.Avrainvillea longicaulis exhibits high order of antifeedant activity in reef fish and also inhibits the growth of microorganisms.The genera Halimeda,Penicillus and Udotea are found to contain highly active but unstable sesquiterpenoids and dterpenos. of these dit erpe oids xhibit and an Prenylated aroma e relatively common in n brown Dictvpers hyoare isolatedo algae. The function of these hydrocarbons have been studied in detail.140.141 It has been observed that the sperm cells aggregate around the female gametes of brown algae which exude Cuhydr ct the fo and caus them the excited state in the vicinity of the latter.The sex attra from Fucus serratus,multifidene from Culteria multifida,n-butyl-cyclohepta- 2.5-diene from dictvota dichotoma.desmarestene from desmarestia viridis ne from nodosum.Tracing the origin of arsenic in lobsters and in fish,it ha been found that the bro Ecklonia radi concentrates arsenic in the form of arseno-sugars Hydroxydictyodia from Dictyota spinulosa inhibits feeding in the omnivorous fish Tilapia mossambica.45 Three ichthyotoxic and phytotoxic diterpenes are isolated from Dilophus fasciola.Several diterpenes from speciesexhibit significant cytotoxicity.47 Two phlorotar n Eckl urome
16 Bioactive Marine Natural Products GB-1 which do not appear to be natural products since attempts to incorporate 32P into GB-1 gave ambiquous results.109,110 Two new polycyclic ethers, GB-5 and GB-6 closely related to okadaic acid, a toxin that was first found in sponges and later in dinoflagellate have been isolated from the cultured cells of G. breve. 111 The dinoflagellate Dinophysis, produces and transmits shellfish, toxins that are responsibe for diarrhoetic shellfish poisoning.112 Lyngbya majuscula known to cause swimmer’s itch has furnished several class of compounds.113-126 Pukeleimides (A-F) showed activity against Mycobacterium smegmatis and Streptococcus pyrogenes. 113,127,128 Cyclic depsipeptide, majusculamide-C isolated from the organism inhibits the growth of fungal plant pathogen.129 Aplysiatoxins and oscillatoxins isolated from blue-green algae Schizothrix calcicola and Oscillatoria nigroviridis possess antileukaemic activity but their high toxicity precludes their medicinal use. Cytotoxic and fungicidal nucleosides have been isolated from a variety of blue-green algae.130Anatoxin-a, an exogenic toxin of blue-green alga Anabaena flosaquae131 is one of the most potent nicotinic receptor agonist. It is suggested that the analogues of anatoxin-a may be of clinical value for treating disorders associated with defects in cholinergic regions of the central nervous system. Several species of green-algae of the genus Halimeda produce an ichthyotoxin which exhibits diverse biological activities.132-134 It inhibits the growth of marine bacteria and fungi, cell division of fertilized sea-urchin eggs and the motility of sea-urchin sperms at 1 µg/mL. Avrainvilleol, a brominated metabolite of green algae, Avrainvillea longicaulis exhibits high order of antifeedant activity in reef fish and also inhibits the growth of microorganisms. The genera Halimeda, Penicillus and Udotea are found to contain highly active but unstable sesquiterpenoids and diterpenoids. Some of these diterpenoids exhibit cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities.135,136 Prenylated aromatics with small side chains are relatively common in brown algae.137 Several highly unsaturated C11 hydrocarbons are isolated from Dictyopteris plagiogramma and D. australis. 138,139 The function of these hydrocarbons have been studied in detail.140,141 It has been observed that the sperm cells aggregate around the female gametes of brown algae which exude C11 hydrocarbons that attract the former and cause them to remain in the excited state in the vicinity of the latter. The sex attractants that have been identified are: ectocarpene from Ectocarpus siliculosus, 142 fucoserratene from Fucus serratus, multifidene from Culteria multifida, n-butyl-cyclohepta- 2,5-diene from Dictyota dichotoma, desmarestene from Desmarestia viridis and tinavarrene from Ascophyllum nodosum. Tracing the origin of arsenic in lobsters and in fish, it has been found that the brown algae Ecklonia radiata concentrates arsenic in the form of arseno-sugars.143,1444 Hydroxydictyodial from Dictyota spinulosa inhibits feeding in the omnivorous fish Tilapia mossambica. 145 Three ichthyotoxic and phytotoxic diterpenes are isolated from Dilophus fasciola. 146,147 Several diterpenes from Dictyota species exhibit significant cytotoxicity.147 Two phlorotannins from Ecklonia kurome exhibit

Bioactive Metabolites of Marine Algae,Fungi and Bacteria 17 pharmacological ties of ninine has been studied.It has been found that the compound at high doses does have a hypotensive action as a result of a ganglion blocking effect. Marine red algae have yielded a vast array of halogenated lipids,some of these exhibit CNS-depressant and hypotensive activities.Three brominated acetylenic compounds squito larvae have been obtained Laurentic nipponic Trihydroxy benzyl I ethers having actectvity against Bacills subiiis are isolated from Grateloupid Enantioselective synthesis of (-)-kainic acid possessing anthelmintic,insecticidal and neuroexcitatory activities,have been achieved. The symmetrical bisbenzyl ether from svmphvocladia latiuscula showed gal activity.5-lodo-5'-deox usual nucleoside has been from Hypnea valentid e caused pronounce relaxation of muscles,hypothermia in mice and blocked polysynaptic and monosynaptic reflexes. 5.Micro Algae Micro algae represent a subset of single cell microorganisms that generally grow autotropically using CO2 as the sole carbon source and light as energy. These algae are ubiquitous in nature.Aquatic micro algae have been isolated in areas ranging from hot springs to glacial ice flows.There are over 50.000 of which only a few have been characterised. Micro algae represent a majo untapped resource of genetic c potential fo valuable bioactive agents and biochemicals.Phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are produced by cyanobateria(Spirulina).and recently have been used as fluorescent labelling agents.They are proteinaceous in structure and exhibit a high extinction coefficient.One future commercial application of micro could be in the pro oduction of spe cial lipids The omega-3-fatty acids found n the water marinefishare to responsible to reduce incidence of coronary heart disease.These fatty acids are likely to originate from the phytoplankton in food chain.Many of these phytoplankton species are found to be rich in reserves of oils containing various amounts of eicosapentaenoic acid(EPA)and docosahexaenoic acid DHA)Exploiti g a o algae ed for the This involy of triti ted wate B3HO]for H2O or 14CO2 for "CO,and results in the production of radioactively labelled biochemicals.Deuterium labelled compounds and also compounds labelled with C are made using heavy water [D2O]and 3CO2. espe ectively one can produce enrichment levels upto 100%der nding on th pe ent of the c labelled bic are of high value.Uses of the stable isotopically labelled compounds inclu production of very high stability deuterated lubricants.The most attractive source of the C and2H-labelled compounds are autotrophic micro algae.If diagnostic tests are developed using these compounds,the market will increase
Bioactive Metabolites of Marine Algae, Fungi and Bacteria 17 antiplasmin inhibitory activity.148-152 The pharmacological properties of laminine has been studied. It has been found that the compound at high doses does have a hypotensive action as a result of a ganglion blocking effect. Marine red algae have yielded a vast array of halogenated lipids, some of these exhibit CNS-depressant and hypotensive activities. Three brominated acetylenic compounds active against mosquito larvae have been obtained from Laurentia nipponica. 153 Trihydroxy benzyl methyl ethers having antibacterial activity against Bacillus subtilis are isolated from Grateloupia filicina. 154,155 Enantioselective synthesis of (–)-kainic acid possessing anthelmintic, insecticidal and neuroexcitatory activities, have been achieved. The symmetrical bisbenzyl ether from Symphyocladia latiuscula showed antifungal activity. 5-Iodo-5′-deoxytubercidin, an unusual nucleoside has been isolated from Hypnea valentiae. 156 The nucleoside caused pronounced relaxation of muscles, hypothermia in mice and blocked polysynaptic and monosynaptic reflexes. 5. Micro Algae Micro algae represent a subset of single cell microorganisms that generally grow autotropically using CO2 as the sole carbon source and light as energy. These algae are ubiquitous in nature. Aquatic micro algae have been isolated in areas ranging from hot springs to glacial ice flows. There are over 50,000 different species of micro algae of which only a few have been characterised. Micro algae represent a major untapped resource of genetic potential for valuable bioactive agents and biochemicals. Phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are produced by cyanobateria (Spirulina), and recently have been used as fluorescent labelling agents. They are proteinaceous in structure and exhibit a high extinction coefficient. One future commercial application of micro algae could be in the production of special lipids. The omega-3-fatty acids found in the oils of certain cold-water marine fish are considered to be responsible to reduce incidence of coronary heart disease. These fatty acids are likely to originate from the phytoplankton in food chain. Many of these phytoplankton species are found to be rich in reserves of oils containing various amounts of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA). Exploiting autotrophy, micro algae are being used for the production of labelled biochemicals. This involves the substitution of tritiated water [ 3 H2O] for 1 H2O or 14CO2 for 12CO2 and results in the production of radioactively labelled biochemicals. Deuterium labelled compounds and also compounds labelled with 13C are made using heavy water [D2O] and 13CO2, respectively. One can produce enrichment levels upto 100% depending on the isotope enrichment of the culture medium. These labelled biochemicals are of high value. Uses of the stable isotopically labelled compounds include production of very high stability deuterated lubricants. The most attractive source of the 13C and 2H-labelled compounds are autotrophic micro algae. If diagnostic tests are developed using these compounds, the market will increase

18 Bioactive Marine Natural Products dramatically.Micro algae can also provide a "designer oil.specially tailored to the food industry.Further,commercial scale production of EPA from micro algae is an attractive proposition.Micro algae are also expected to isoAIDS.antibiotic and other bioci The extract of cyanobacterium Planktothrix sp.exhibite ce r f ody e、n Several leptosins were isolated from the marine alga Leptosphaeria sp.and their biological neon antinammatory macrolides again Ha ore ve n cancer cell line Brominated anisoles and cresols were detected for the first time in the red marine alga Polysiphonia sphaerocarpa.169 The sulfated polysaccharide of the red microalga Porphyridium sp.showed high order of antiviral activity against herpes simplex virus (HSV-and both mpd Peidantated ion in the growth of lewis lung carcinoma and B16 melanom in mice.Antitumo and immunomodulation activities were found in different molecular weight o- carrangeenans from Chondrusocellatus.3 1-Hydroxy monocyclic carotenoid 3,4-dehydrogenase from a marine bacterium that produces myxol was identified.74 This unique type of crt D is a valuable tool for obtaining 1' HO-34'-didehydr enoids.Anta cgcenanhhiodgah 6.Concluding Remarks e variety of bioactive metabolites.Some of ebacteria prod some e of the e m potent toxins such as saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin.The sulphated polysaccharides obtained from seaweeds are economically most important products.These are extensively used in food and medicine.The red algae are the source of agar and agarose.Although these polysaccharides have no direct medicinal use,howe their use in biomedical research is well known.Alginic acid obtained from brown seaweeds has several uses.The largest use of odium alginate is in the manufacturing of ice cream.However,the most significant property of sodium alginate of biomedical value is that it has the ability to remove strontium 85 and strontium 87 from the body without seriously affecting the availability of Ca.na or k in the body
18 Bioactive Marine Natural Products dramatically. Micro algae can also provide a “designer oil”, specially tailored to the food industry. Further, commercial scale production of EPA from micro algae is an attractive proposition. Micro algae are also expected to furnish potent antiviral, antiAIDS, antibiotic and other bioactive agents. The extract of cyanobacterium Planktothrix sp. exhibited embryotoxicity.157 Changes in the culture conditions of Lyngbya majuscula had the greatest effect on production of its secondary metabolites.158-165 Several leptosins were isolated from the marine alga Leptosphaeria sp. and their biological activity evaluated. Of these leptosin M exhibited significant cytotoxicity against human cancer cell lines.166 Two new antiinflammatory macrolides, lobophorin A and B were isolated from a marine bacterium.167 Water extract of marine diatom Haslea ostrearia exhibited anticoagulant activity.168 Brominated anisoles and cresols were detected for the first time in the red marine alga Polysiphonia sphaerocarpa. 169 The sulfated polysaccharide of the red microalga Porphyridium sp. showed high order of antiviral activity against herpes simplex virus (HSV-1 and 2) both in vitro and in vivo. 170 Ten new sesquiterpenoids were isolated from the fungus Drechslera dematioidea. Of these drechserine E and G exhibited antiplasmodial activity against Plasmodium falciparum strains K1 and NF54.171 Fucoidan, a sulfated polysaccharide from brown seaweed displayed anticoagulant and antithrombotic activities. It also had inhibitory action in the growth of Lewis lung carcinoma and B16 melanoma in mice.172 Antitumor and immunomodulation activities were found in different molecular weight α- carrangeenans from Chondrus ocellatus. 173 1-Hydroxy monocyclic carotenoid 3,4-dehydrogenase from a marine bacterium that produces myxol was identified.174 This unique type of crt D is a valuable tool for obtaining 1′- HO-3′,4′-didehydromonocyclic carotenoids. Antarctic bacteria inhibited growth of food-borne microorganisms at low temperature.175 6. Concluding Remarks Marine algae have yielded a large variety of bioactive metabolites. Some of them have biomedical potential. Marine bacteria produce some of the most potent toxins such as saxitoxin and tetrodotoxin. The sulphated polysaccharides obtained from seaweeds are economically most important products. These are extensively used in food and medicine. The red algae are the source of agar and agarose. Although these polysaccharides have no direct medicinal use, however, their use in biomedical research is well known. Alginic acid obtained from brown seaweeds has several uses. The largest use of sodium alginate is in the manufacturing of ice cream. However, the most significant property of sodium alginate of biomedical value is that it has the ability to remove strontium 85 and strontium 87 from the body without seriously affecting the availability of Ca, Na or K in the body