
Mutation lonizing radiation (X rays and gamma rays)causes the formation of ions that can react with nucleotides and the deoxyribose-phosphate backbone. Nucleotide excision repairs mutations
• Ionizing radiation (X rays and gamma rays) causes the formation of ions that can react with nucleotides and the deoxyribose-phosphate backbone. • Nucleotide excision repairs mutations Mutation
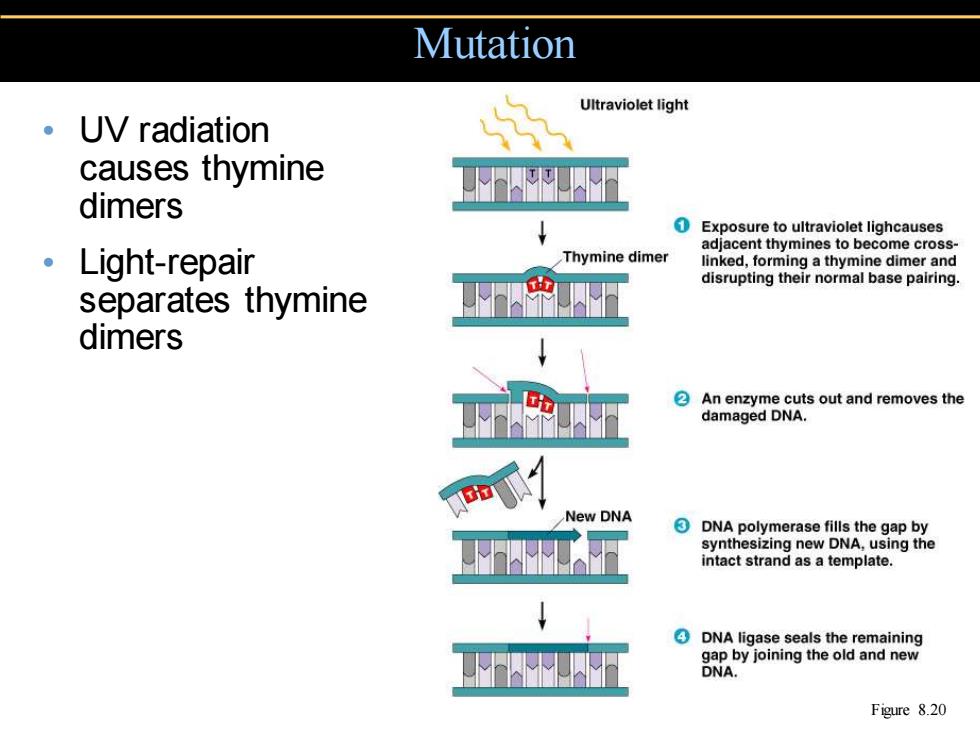
Mutation Ultraviolet light 。 UV radiation causes thymine dimers Exposure to ultraviolet lighcauses adjacent thymines to become cross 。Light-repair Thymine dimer linked,forming a thymine dimer and disrupting their normal base pairing. separates thymine dimers An enzyme cuts out and removes the damaged DNA. New DNA DNA polymerase fills the gap by synthesizing new DNA,using the intact strand as a template. DNA ligase seals the remaining gap by joining the old and new DNA. Figure 8.20
• UV radiation causes thymine dimers • Light-repair separates thymine dimers Mutation Figure 8.20

The Frequency of Mutation Spontaneous mutation rate 1 in 109 replicated base pairs or 1 in 106 replicated genes Mutagens increase to 10-5 or 10-3 per replicated gene
• Spontaneous mutation rate = 1 in 109 replicated base pairs or 1 in 106 replicated genes • Mutagens increase to 10–5 or 10–3 per replicated gene The Frequency of Mutation