
上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 如何在生产实践中缩短迟缓期? (1)改变种的遗传特性使迟缓期缩短; (2)利用对数生长期的细胞作为种子; (3)接种前后所使用的培养基组成不要相差太 大; (4)适当扩大接种量 11 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程 《微生物的世界》
11 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程《微生物的世界》 如何在生产实践中缩短迟缓期? (1) 改变种的遗传特性使迟缓期缩短; (2) 利用对数生长期的细胞作为种子; (3) 接种前后所使用的培养基组成不要相差太 大; (4)适当扩大接种量
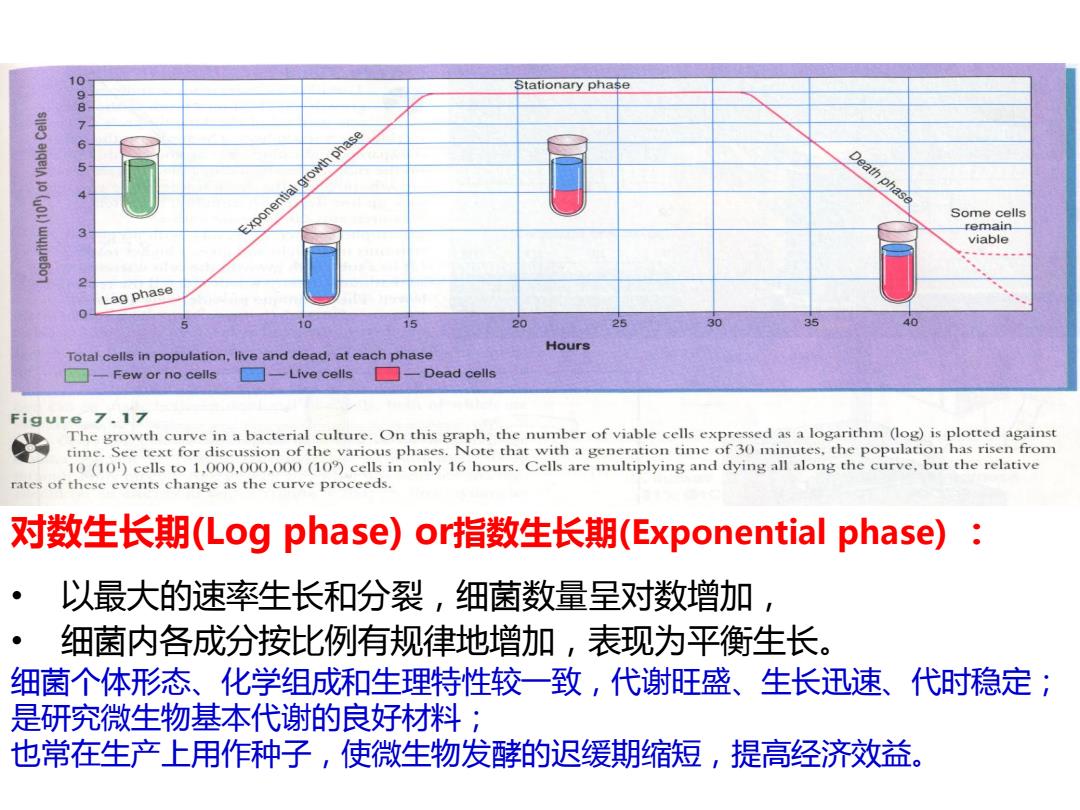
Stationary phase 09876 sle alqeIA 1o (u0L)wywebo Exponential growth phase Death phase Some cells 3 remain viable Lag phase 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Hours Total cells in population,live and dead,at each phase □一Few or no cells ☐-Live cells☐一Dead cells Figure 7.17 The growth curve in a bacterial culture.On this graph,the number of viable cells expressed as a logarithm (log)is plotted against time.See text for discussion of the various phases.Note that with a generation time of 30 minutes,the population has risen from 10(101)cells to 1.000,000.000(10)cells in only 16 hours.Cells are multiplying and dying all along the curve.but the relative rates of these events change as the curve proceeds. 对数生长期(Log phase)or指数生长期(Exponential phase)): 以最大的速率生长和分裂,细菌数量呈对数增加 ● 细菌内各成分按比例有规律地增加,表现为平衡生长。 细菌个体形态、化学组成和生理特性较一致,代谢旺盛、生长迅速、代时稳定; 是研究微生物基本代谢的良好材料; 也常在生产上用作种子,使微生物发酵的迟缓期缩短,提高经济效益
对数生长期(Log phase) or指数生长期(Exponential phase) : • 以最大的速率生长和分裂,细菌数量呈对数增加, • 细菌内各成分按比例有规律地增加,表现为平衡生长。 细菌个体形态、化学组成和生理特性较一致,代谢旺盛、生长迅速、代时稳定; 是研究微生物基本代谢的良好材料; 也常在生产上用作种子,使微生物发酵的迟缓期缩短,提高经济效益
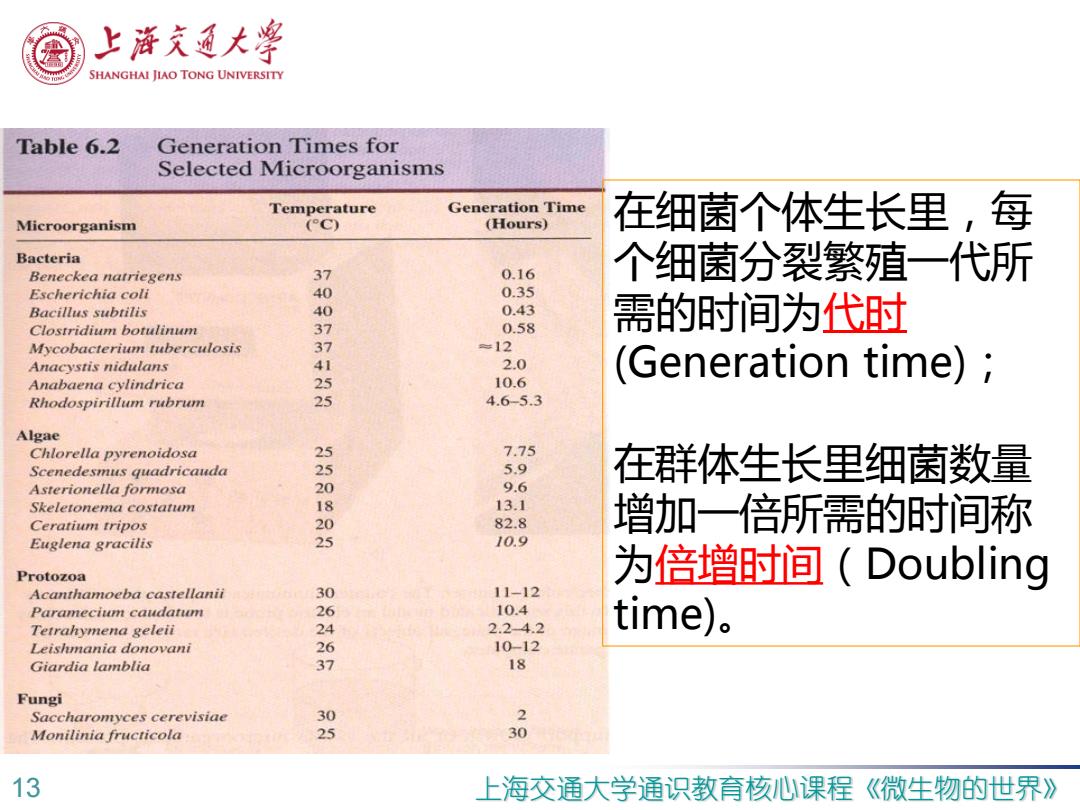
上游充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY Table 6.2 Generation Times for Selected Microorganisms Temperature Generation Time Microorganism (C) (Hours) 在细菌个体生长里,每 Bacteria Beneckea natriegens 7 0.16 个细菌分裂繁殖一代所 Escherichia coli 40 0.35 Bacillus subtilis 0 0.43 Clostridium botulinum 37 0.58 需的时间为代时 Mycobacterium tuberculosis 7 =12 Anacystis nidulans 2.0 10.6 (Generation time); Anabaena cylindrica Rhodospirillum rubrum 25 4.6-5.3 Algae Chlorella pyrenoidosa 2 7.75 Scenedesmus quadricauda 25 5.9 在群体生长里细菌数量 Asterionella formosa 2 9.6 Skeletonema costatum 18 13.1 Ceratium tripos 20 82.8 增加一倍所需的时间称 Euglena gracilis 2 10.9 Protozoa 为倍增时间(Doubling Acanthamoeba castellanii 30 11-12 Paramecium caudatum 26 10.4 Tetrahymena geleii 24 2.24.2 time)。 Leishmania donovani 26 10-12 Giardia lamblia 37 18 Fungi Saccharomyces cerevisiae 30 2 Monilinia fructicola 25 30 13 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程 《微生物的世界》
13 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程 《微生物的世界 》 在细菌个体生长里,每 个细菌分裂繁殖一代所 需的时间为代时 (Generation time) ; 在群体生长里细菌数量 增加一倍所需的时间称 为倍增时间(Doubling time)

上游充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 影响微生物倍增时间(代时)的因素: 1)菌种,不同的微生物及微生物的不同菌株代时不同; 2)营养成分,在营养丰富的培养基中生长代时短 3)营养物浓度,在一定范围内,生长速率与营养物浓度呈正比, Rate and Only yield affected yield affected Growth Growth rate yield 处于较低浓度范围内,可影 响生长速率的营养物成分, 3 Nutrient concentration(mg/ml) 就称为生长限制因子。 4)温度,在一定范围,生长速率与培养温度呈正相关。 14 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程 《微生物的世界》
14 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程《微生物的世界》 影响微生物倍增时间(代时)的因素: 1)菌种,不同的微生物及微生物的不同菌株代时不同; 2)营养成分,在营养丰富的培养基中生长代时短 3)营养物浓度,在一定范围内,生长速率与营养物浓度呈正比, 处于较低浓度范围内,可影 响生长速率的营养物成分, 就称为生长限制因子。 4)温度,在一定范围,生长速率与培养温度呈正相关

上游充通大 10 Stationary phase 987 Exponential growth phase Death phase Some cells remain viable Lag phase 0 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Hours Total cells in population,live and dead,at each phase □-Few or no cells □-Live cells☐一Dead cells Figure 7.17 The growth curve in a bacterial culture.On this graph,the number of viable cells expressed as a logarithm (log)is plotted against time.See text for discussion of the various phases.Note that with a generation time of 30 minutes,the population has risen from 10(10)cells to 1,000,000.000(10)cells in only 16 hours.Cells are multiplying and dying all along the curve.but the relative rates of these events change as the curve proceeds. 稳定生长期(Stationary phase): 1)营养物质消耗,2)代谢产物积累、3)pH变化→→逐步不适宜于细 菌生长→→生长速率降低至零(隐性生长状态:细菌分裂增加的数 量等于细菌死亡数)。 15 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程 《微生物的世界》
15 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程《微生物的世界》 稳定生长期(Stationary phase): 1)营养物质消耗,2)代谢产物积累、3)pH变化→→逐步不适宜于细 菌生长→→生长速率降低至零(隐性生长状态:细菌分裂增加的数 量等于细菌死亡数)