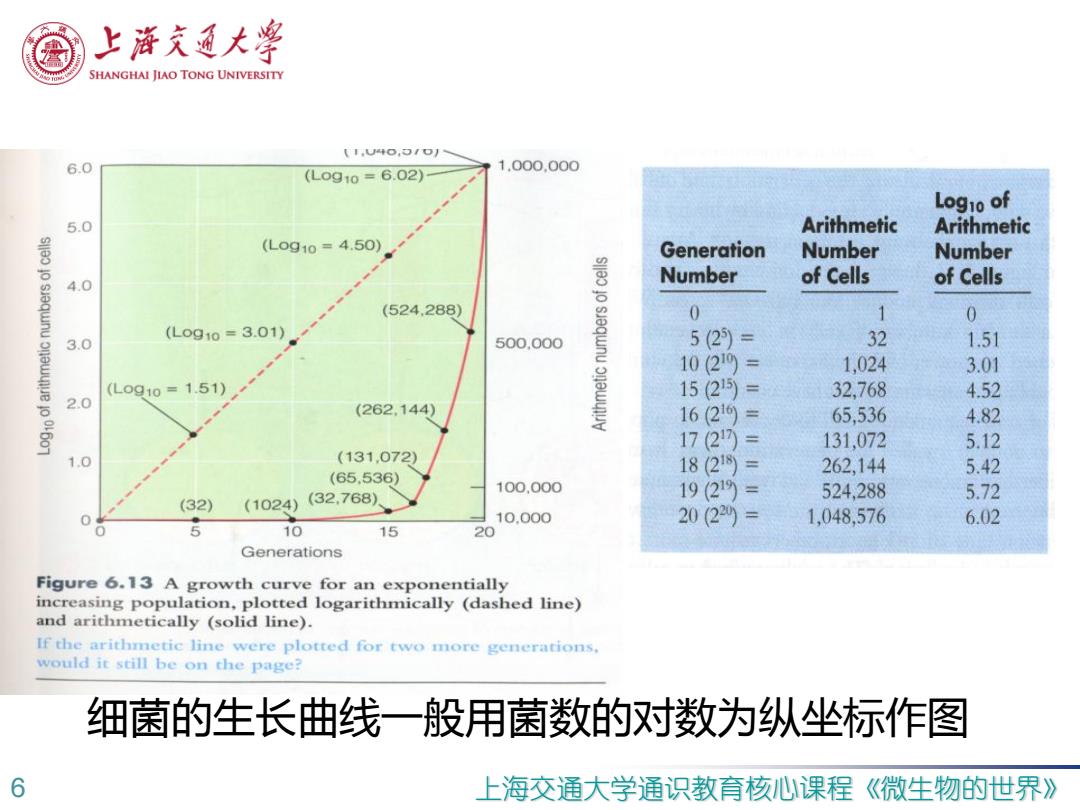
上帝充通大粤 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 【1,U4⊙,▣40) 6.0 1.000.000 (L0g10=6.02) Log1o of 5.0 Arithmetic Arithmetic (Lo910=4.50), Generation Number Number 4.0 Number of Cells of Cells (524,288) (L0910=3.01) 3.0 500.000 sjeqwnu 0 1 0 5(2)= 32 1.51 10(219= 1,024 3.01 (L0910=1.51) 15(25)= 32,768 4.52 2.0 (262.144) 16(216= 65,536 4.82 17(21= 131,072 5.12 1.0 (131,072) 18(21= 262,144 (65.536) 5.42 100.000 (32,768) 19(219= 524,288 5.72 (32) (1024) 10.000 20(220= 1,048,576 6.02 5 10 15 20 Generations Figure 6.13 A growth curve for an exponentially increasing population,plotted logarithmically (dashed line) and arithmetically (solid line). If the arithmetic line were plotted for two more generations, would it still be on the page? 细菌的生长曲线一般用菌数的对数为纵坐标作图 6 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程 《微生物的世界》
6 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程《微生物的世界》 细菌的生长曲线一般用菌数的对数为纵坐标作图

上游充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 10 Stationary phase 98 7 Exponential growth phase Death phase Some cells 3 remain viable Lag phase 0 15 20 25 30 35 40 Hours Total cells in population,live and dead,at each phase -Few or no cells -Live cells☐一Dead cells Figure 7.17 The growth curve in a bacterial culture.On this graph,the number of viable cells expressed as a logarithm (log)is plotted against time.See text for discussion of the various phases.Note that with a generation time of 30 minutes,the population has risen from 10(101)cells to 1,000,000,000(10)cells in only 16 hours.Cells are multiplying and dying all along the curve.but the relative rates of these events change as the curve proceeds. 典型的生长曲线:迟缓期,对数期,稳定期和衰亡期等四 个生长时期 7 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程 《微生物的世界》
7 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程《微生物的世界》 典型的生长曲线:迟缓期,对数期,稳定期和衰亡期等四 个生长时期
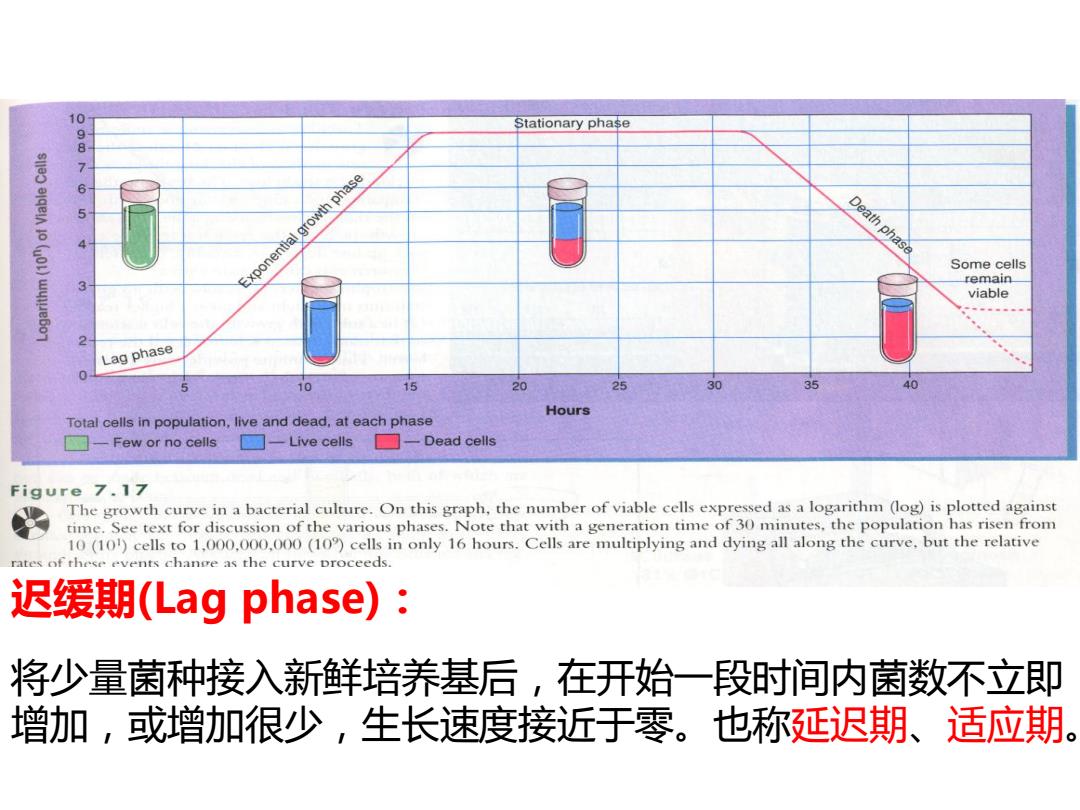
0987 Stationary phase 5 Exponentlal growth phase Death phase Some cells remain viable Lag phase 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 Hours Total cells in population,live and dead,at each phase □-Few or no cells ☐-Live cells☐-Dead cells Figure 7.17 The growth curve in a bacterial culture.On this graph,the number of viable cells expressed as a logarithm (log)is plotted against time.See text for discussion of the various phases.Note that with a generation time of 30 minutes,the population has risen from 10(10)cells to 1,000.000,000(10)cells in only 16 hours.Cells are multiplying and dying all along the curve.but the relative rates of these events change as the curve proceeds. 迟缓期(Lag phase): 将少量菌种接入新鲜培养基后,在开始 一段时间内菌数不立即 增加,或增加很少,生长速度接近于零。也称延迟期、适应期
迟缓期(Lag phase): 将少量菌种接入新鲜培养基后,在开始一段时间内菌数不立即 增加,或增加很少,生长速度接近于零。也称延迟期、适应期

上游充通大学 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 迟缓期的特点:分裂迟缓、代谢活跃 细胞形态变大或增长; 细胞内RNA,尤其是rRNA含量增高,合成代谢活跃。 对外界不良条件反应敏感。 以上特征说明细胞处于活跃生长中,只是分裂迟缓。 在此阶段后期,少数细胞开始分裂,曲线略有上升。 9 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程 《微生物的世界》
9 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程《微生物的世界》 迟缓期的特点:分裂迟缓、代谢活跃 • 细胞形态变大或增长; • 细胞内RNA,尤其是rRNA含量增高,合成代谢活跃。 • 对外界不良条件反应敏感。 以上特征说明细胞处于活跃生长中,只是分裂迟缓。 在此阶段后期,少数细胞开始分裂,曲线略有上升

上游充通大警 SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIVERSITY 迟缓期出现的原因:调整代谢 微生物接种到一个新的环境,调整代谢需要一段适应期 迟缓期的长短与菌种的遗传性、菌龄以及移种前后所处的 环境条件等因素有关(几分钟 数小时) 10 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程 《微生物的世界》
10 上海交通大学通识教育核心课程《微生物的世界》 迟缓期出现的原因:调整代谢 微生物接种到一个新的环境,调整代谢需要一段适应期 迟缓期的长短与菌种的遗传性、菌龄以及移种前后所处的 环境条件等因素有关(几分钟——数小时)