
1966 Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Design Lecture 1:Introduction The Fabrics The Fabrics
EE141 The Fabrics Advanced Digital Integrated Circuits Design Lecture 1: Introduction & The Fabrics

Agenda 1966 ▣l.1 Introduction 1.2 Overview on Manufacturing Process 1.3 The MOS(FET)Transistor 1.3.1 I-V/C-V characteristics (self-learning) ▣1.3.2 SPICE Models 1.4 Process variations The Fabrics
EE141 The Fabrics Agenda ❑ 1.1 Introduction ❑ 1.2 Overview on Manufacturing Process ❑ 1.3 The MOS(FET) Transistor ❑ 1.3.1 I-V/C-V characteristics (self-learning) ❑ 1.3.2 SPICE Models ❑ 1.4 Process Variations

Agenda 1966 ▣l.1 Introduction 1.2 Overview on Manufacturing Process 1.3 The MOS(FET)Transistor 1.3.1 I-V/C-V characteristics (self-learning ▣1.3.2 SPICE Models 1.4 Process variations The Fabrics
EE141 The Fabrics Agenda ❑ 1.1 Introduction ❑ 1.2 Overview on Manufacturing Process ❑ 1.3 The MOS(FET) Transistor ❑ 1.3.1 I-V/C-V characteristics (self-learning) ❑ 1.3.2 SPICE Models ❑ 1.4 Process Variations
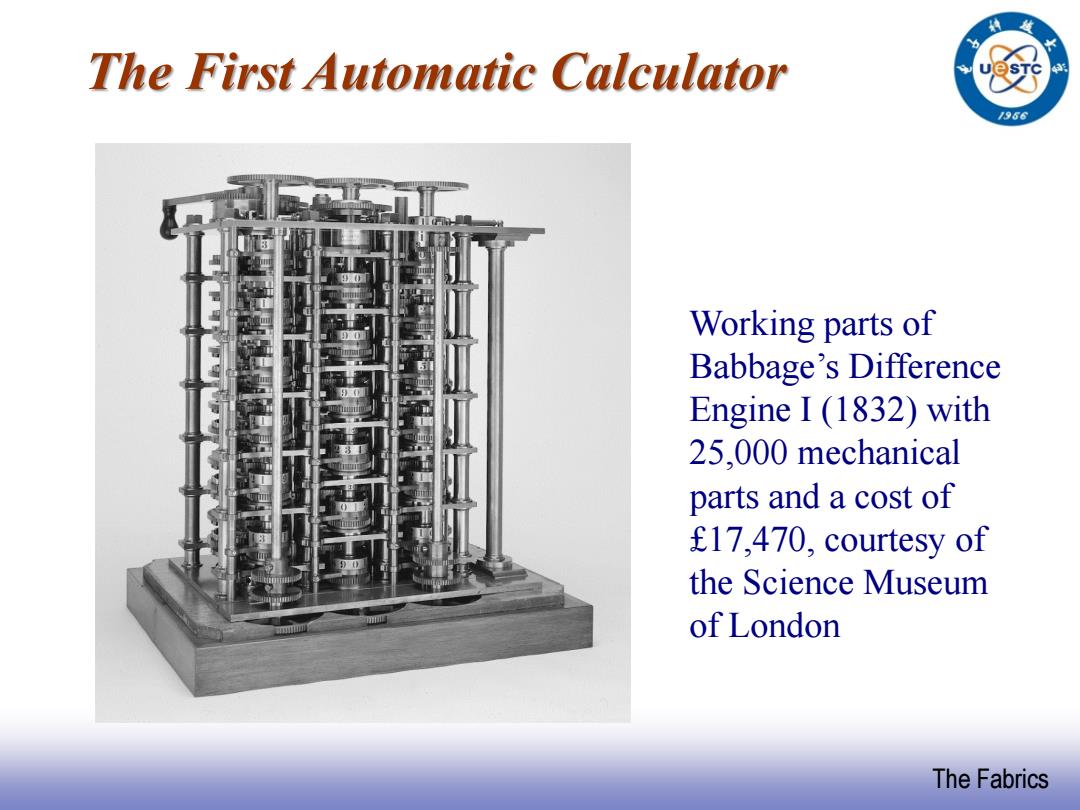
The First Automatic Calculator 1966 Working parts of Babbage's Difference Engine I (1832)with 25,000 mechanical parts and a cost of £17,470,courtesy of the Science Museum of London The Fabrics
EE141 The Fabrics Working parts of Babbage’s Difference Engine I (1832) with 25,000 mechanical parts and a cost of £17,470, courtesy of the Science Museum of London The First Automatic Calculator
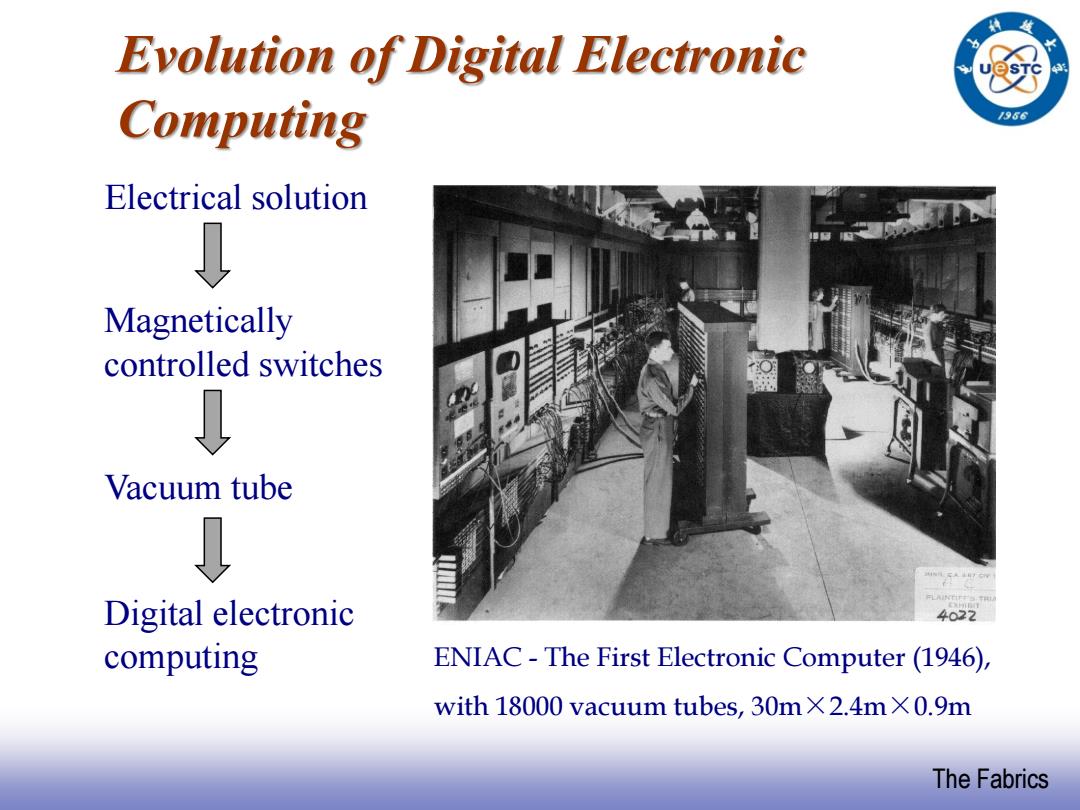
Evolution of Digital Electronic Computing 1966 Electrical solution Magnetically controlled switches Vacuum tube Digital electronic 4022 computing ENIAC-The First Electronic Computer(1946), with18000 vacuum tubes,30m×2.4m×0.9m The Fabrics
EE141 The Fabrics Evolution of Digital Electronic Computing ENIAC - The First Electronic Computer (1946), with 18000 vacuum tubes, 30m×2.4m×0.9m Electrical solution Vacuum tube Magnetically controlled switches Digital electronic computing