
Tutorial 11:Limit Theorems Baoxiang Wang Yihan Zhang bxwang,yhzhang@cse.cuhk.edu.hk April 10,2017
Tutorial 11: Limit Theorems Baoxiang Wang & Yihan Zhang bxwang, yhzhang@cse.cuhk.edu.hk April 10, 2017 1

Outline The Central Limit Theorem(CLT) Normal Approximation Based on CLT De Moivre-Laplace Approximation to the Binomial Problems and solutions
Outline • The Central Limit Theorem (CLT) • Normal Approximation Based on CLT • De Moivre-Laplace Approximation to the Binomial • Problems and solutions
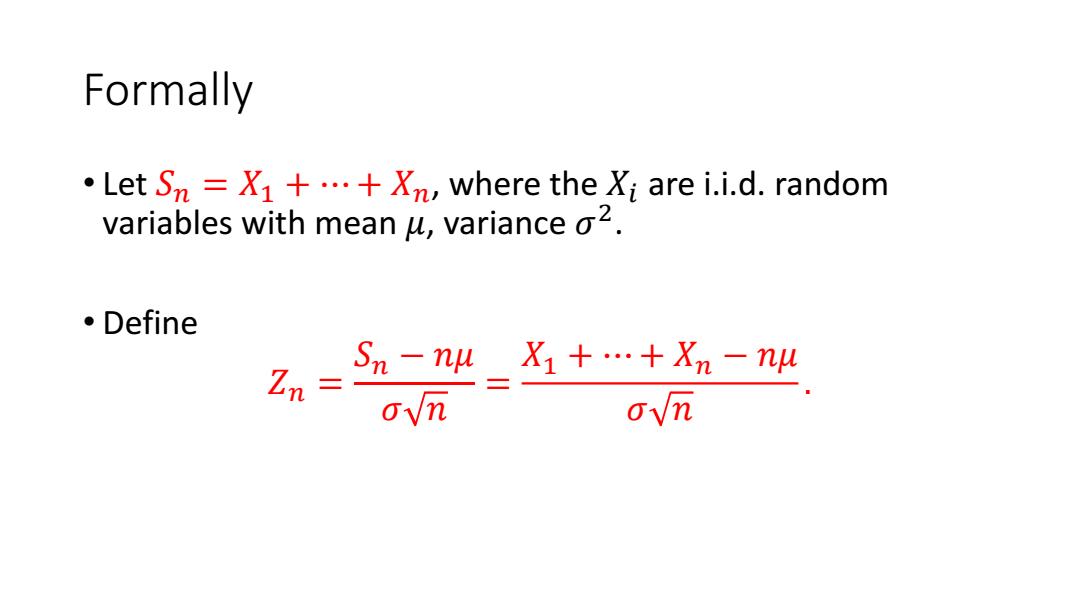
Formally .Let Sm=X1+..+Xn,where the Xi are i.i.d.random variables with mean u,variance o2. 。Define Sn-nW_X1+…+Xn-nw Zn= 0√m
Formally • Let 𝑆𝑛 = 𝑋1 + ⋯ + 𝑋𝑛, where the 𝑋𝑖 are i.i.d. random variables with mean 𝜇, variance 𝜎 2 . • Define 𝑍𝑛 = 𝑆𝑛 − 𝑛𝜇 𝜎 𝑛 = 𝑋1 + ⋯ + 𝑋𝑛 − 𝑛𝜇 𝜎 𝑛

Zero mean and unit variance An easy calculation yields E[X1+…+XnJ-nw E[Zn] 二0 ovn ·For variance,we have var(X1+…+Xn) no2 var(Zn)= (Vm列)
Zero mean and unit variance • An easy calculation yields E[𝑍𝑛] = E 𝑋1 + ⋯ + 𝑋𝑛 − 𝑛𝜇 𝜎 𝑛 = 0 • For variance, we have var 𝑍𝑛 = var 𝑋1 + ⋯ + 𝑋𝑛 𝜎 𝑛 2 = 𝑛𝜎 2 𝑛𝜎 2 = 1
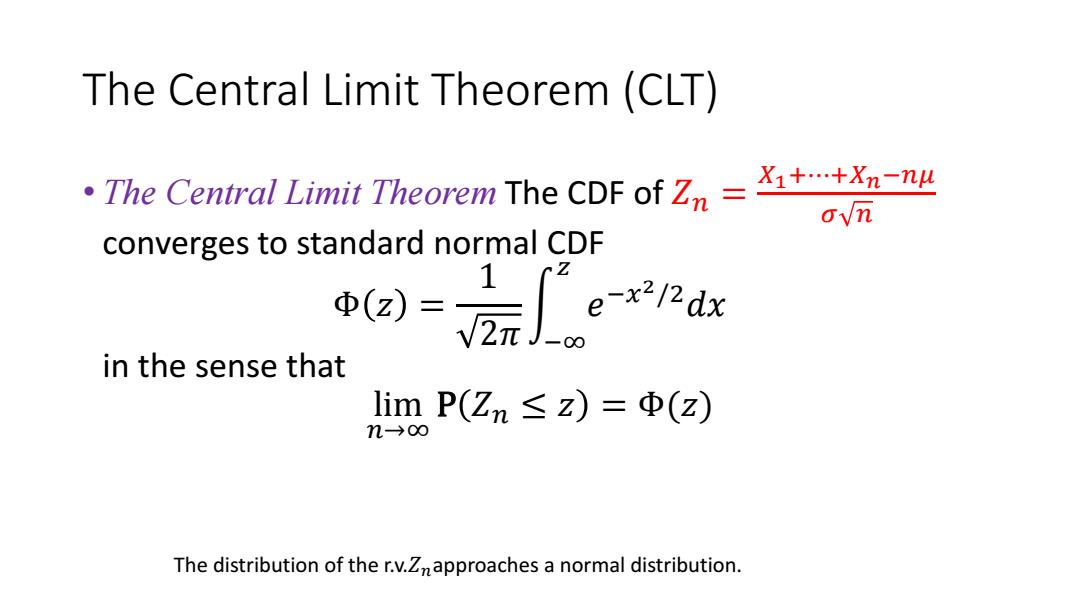
The Central Limit Theorem (CLT) .The Central Limit Theorem The CDF ofZn= X1+.+Xn-nu ovn converges to standard normal CDF in the sense that limP(Zn≤z)=Φ(z) n-→o∞ The distribution of the r.v.Znapproaches a normal distribution
The Central Limit Theorem (CLT) • The Central Limit Theorem The CDF of 𝑍𝑛 = 𝑋1+⋯+𝑋𝑛−𝑛𝜇 𝜎 𝑛 converges to standard normal CDF Φ 𝑧 = 1 2𝜋 න −∞ 𝑧 𝑒 −𝑥 2/2𝑑𝑥 in the sense that lim 𝑛→∞ P 𝑍𝑛 ≤ 𝑧 = Φ(𝑧) The distribution of the r.v.𝑍𝑛approaches a normal distribution