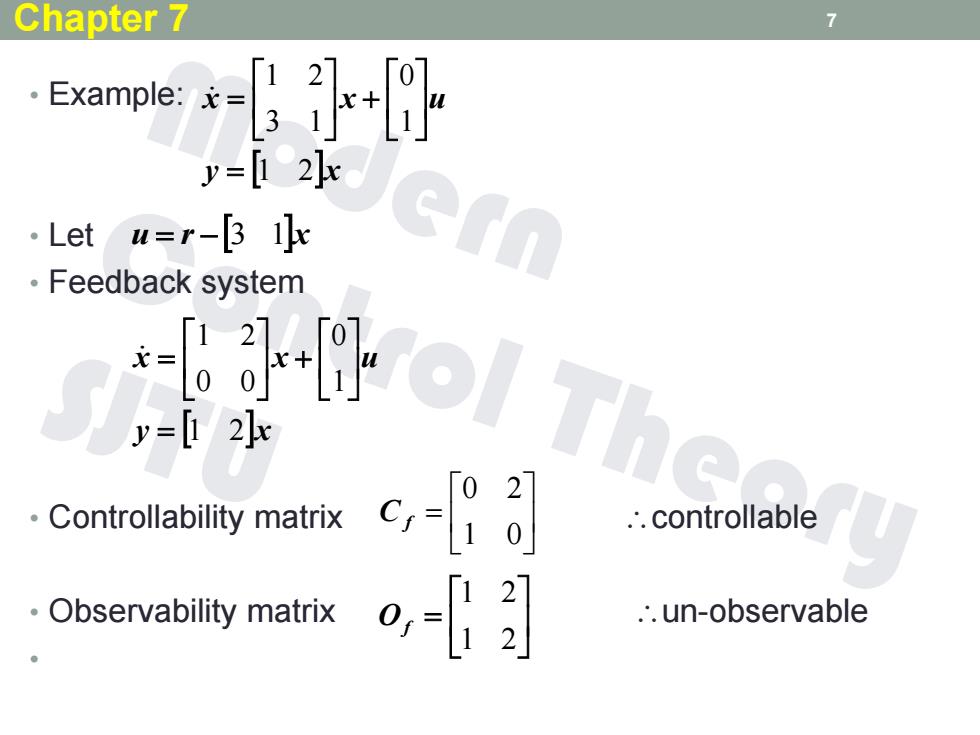
Chapter 7 7 「12].「01 Example:;xgk+ y=[2k .Let u=r-[3 Ik ol The ·Feedback system y=1/2]x Controllability matrix c .∴controllable Observability matrix [121 012 ..un-observable
• Example: • Let • Feedback system • Controllability matrix controllable • Observability matrix un-observable • 7 y x x x u 1 2 1 0 3 1 1 2 u r 3 1x y x x x u 1 2 1 0 0 0 1 2 1 0 0 2 C f 1 2 1 2 Of Chapter 7

Chapter 7 8 7.3 Pole placement and design of feedback matrix State feedback can be used to place eigenvalues(pole)of A in any position if the system is controllable. Pole placement:choosing state feedback gains to place poles in desired positions. Theorem:If the n-dimensional linear system is controllable,then the eigenvalues of 4-BK can arbitrarily assigned by state feedback u=r-Kx,where k is a 1xn real constant vector
7.3 Pole placement and design of feedback matrix • State feedback can be used to place eigenvalues(pole)of A in any position if the system is controllable. • Pole placement: choosing state feedback gains to place poles in desired positions. • Theorem: If the n-dimensional linear system is controllable, then the eigenvalues of A-BK can arbitrarily assigned by state feedback u=r-Kx, where k is a 1n real constant vector. Chapter 7 8

Chapter 7 9 Theorem:Consider the state equation x=Ax+bu,y =cx with n =4 and the characteristic polynomiai △(s)=det(l-A)=s4+4s3+a2s2+4s+&4: If the given state equation is controllable,then it can be transformed by the transformation x=Px with 10%23 Q=P-=[b Ab A2b Ab] 0112 0014 into the controllable canonical form 0001 [-%1-2-%3-4 T1 1 00 0 0 文=Ax+bM= 区+ 01 0 0 0 u.y=Cx=IB B2 B Bx. 001 0 0
Chapter 7 9

Chapter 7 10 Remark:For the case of n=4,from any set of desired eigenvalues,we can readily form Let △(S)=S4+瓦S3+a2s2+as+瓦4 k=[a1-41a2-2a3-a3a4-4l,k=kP where [1%a2% P-=[b Ab AbAb] 01%02 00101 0001 cory
Chapter 7 10

Chapter 7 11 Example: Consider a linear system -6* A(S)=(s-1)2-9=(s-4)(s+2),→S=4,S2=-2 State feedback 店+-[母 4(s)=s2+(k-2)5+(3k-k2-8) New s,s2 is determined by values of k1 and k2
Example: • Consider a linear system 11 x x u 0 1 3 1 1 3 2 1 2 ( ) ( 1) 9 ( 4)( 2), 4, 2 s s s s s s x r k k x u k k x 0 1 3 1 1 3 0 1 3 1 0 0 1 3 1 2 1 2 ( s ) s ( k 2 )s ( 3k k 8 ) 1 1 2 2 State feedback n i n ki xi u r Kx V- k k x r 1 1 New s1 s2 is determined by values of k1 and k2 . Chapter 7