
Chapter 8 2 Chapter 8 Fundamentals of Optimal Control Objectives: Optimal control from Hamilton-Pontryagin Equation Optimal Control Law for Linear System with Quadratic Performance Index Design procedure and examples
Chapter 8 Fundamentals of Optimal Control Objectives: • Optimal control from Hamilton-Pontryagin Equation • Optimal Control Law for Linear System with Quadratic Performance Index • Design procedure and examples Chapter 8 2

Chapter 8 8.1 Optimal Control based on Hamilton-Pontryagin Equation 1.The optimal control problem for feedback control systems. To minimize J=L(X.U)d subject to X(t)=f(X,U) TU X)e∈R" state vector U(t)∈R' the control vector f(X,U) the function vector(Rn+r-R) L(X,U) Rnr→Rn,J is a function 2.Target: Euler-Lagrange Equation>Hamilton-Pontryagin Equation
8.1 Optimal Control based on Hamilton-Pontryagin Equation 1.The optimal control problem for feedback control systems. To minimize T J L X U dt 0 ( , ) subject to X(t) f(X,U) state vector n X(t)R r U(t)R f(X, U) L(X,U) the control vector the function vector(Rn+r→Rn ) Rn+r→Rn , J is a function 2.Target: Euler-Lagrange Equation Hamilton -Pontryagin Equation Chapter 8

Chapter 8 3.The design approach Step 1.Rewrite the state equation -X(t)+f(X(t),U(t)=0 Step 2.Set up the augment functional J[L(X,U)+A"(f(X,U)-x)]dt =L(X,U)+A"f-A"x)]dt Define: F=L(X,U)+Af(X,U)-A'X Step 3.Define a scalar function-Hamiltonian H(X,U,A)=L(X,U)+A'f(X,U) then F=H(X,U,A)-A"X
3.The design approach Step 1. Rewrite the state equation X(t) f(X(t),U(t)) 0 Step 2. Set up the augment functional T T T T T L dt J L dt 0 0 [ ( , ) )] [ ( , ) ( ( , ) )] X U Λ f Λ X X U Λ f X U X Define: X U Λ T f X U Λ T X F L( , ) ( , ) Step 3. Define a scalar function —Hamiltonian (X,U, Λ) (X,U) Λ f(X,U) T H L then F H X U Λ Λ T X ( , , ) Chapter 8

Chapter 8 Step 4.Applying Euler-Lagrange Equation to this problem OF d oF 0 dt ox OF d =00 aU d而 OF d oF =0 an dt a Step 5.By substituting into the equation above aH(X,A,U)d=0 Furthermore OH 1(0= OX dt ox aH(X,A,U) 0 OH =0 aU aU F(&,A,U,X-0 X=fX,U) aA Hamilton-Pontryagin equation------The necessary condition for optimizing control systems
Step 4. Applying Euler-Lagrange Equation to this problem 0 0 0 Λ Λ U U X X F dt F d F dt F d F dt F d Step 5. By substituting into the equation above 0 ( , , , ) 0 ( , , ) 0 ( , , ) Λ X Λ U X U X Λ U Λ X X Λ U F H dt H d Furthermore X f(X,U) U H X H Λ(t) 0 Hamilton-Pontryagin equation------The necessary condition for optimizing control systems. Chapter 8
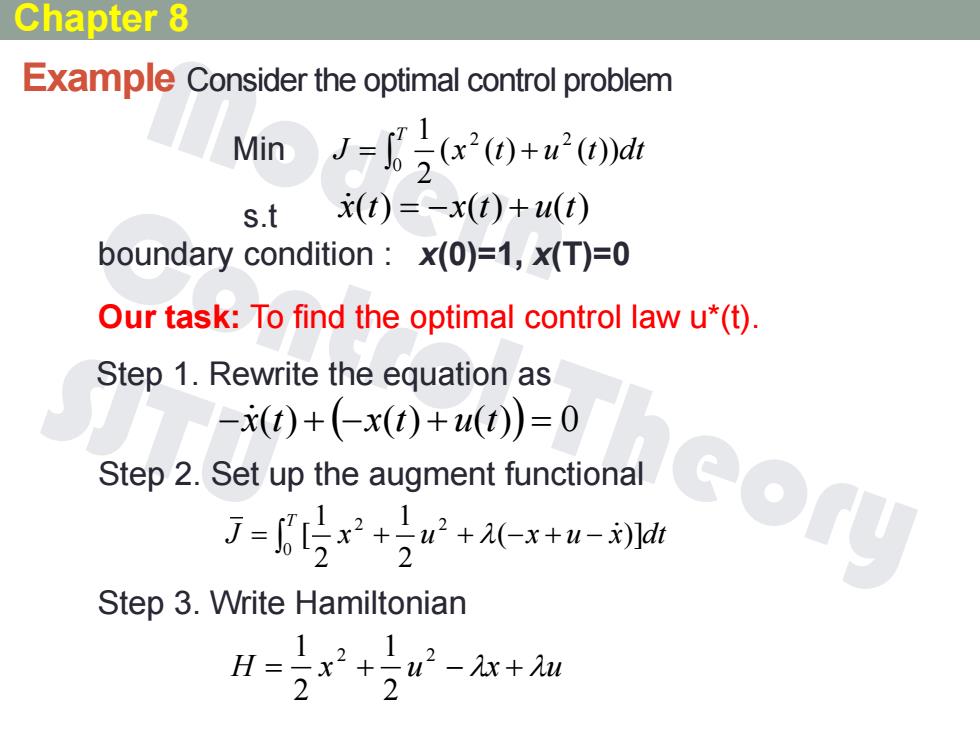
Chapter 8 Example Consider the optimal control problem Min J+(dr s.t (t)=-x(t)+u(t) boundary condition x(0)=1,x(T)=0 Our task:To find the optimal control law u*(t). Step 1.Rewrite the equation as -x(t)+(-x(t)+u(t)=0 Step 2.Set up the augment functional J-r++ex*- eory Step 3.Write Hamiltonian 2+2-x+ H=x 2 2
Example Consider the optimal control problem Min T J x t u t dt 0 2 2 ( ( ) ( )) 2 1 s.t x (t) x(t) u(t) boundary condition : x(0)=1, x(T)=0 Our task: To find the optimal control law u*(t). Step 1. Rewrite the equation as x (t) x(t) u(t) 0 Step 2. Set up the augment functional T J x u x u x dt 0 2 2 ( )] 2 1 2 1 [ Step 3. Write Hamiltonian H x u x u 2 2 2 1 2 1 Chapter 8