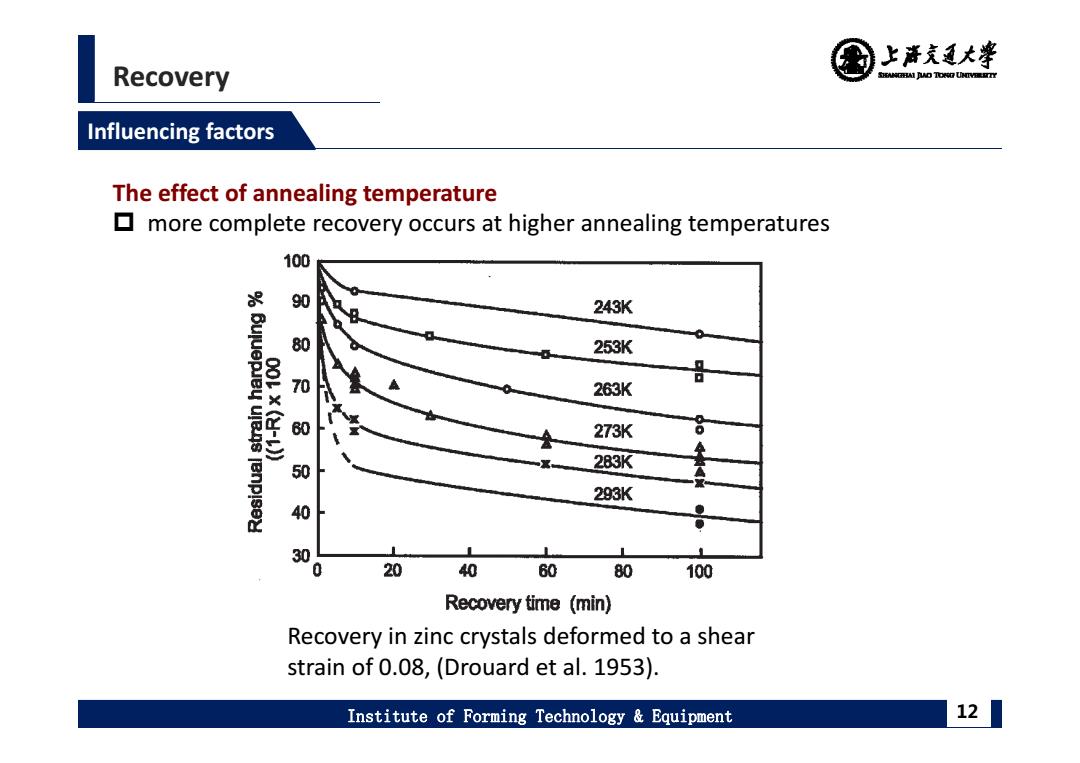
上清充通大米 Recovery SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Influencing factors The effect of annealing temperature more complete recovery occurs at higher annealing temperatures 100 90 243K 80 253K 70 263K 273K 8 283K 50 293K 4 30 20 40 60 80 100 Recovery time (min) Recovery in zinc crystals deformed to a shear strain of 0.08,(Drouard et al.1953). Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 12
Recovery Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 12 Influencing factors The effect of annealing temperature more complete recovery occurs at higher annealing temperatures Recovery in zinc crystals deformed to a shear strain of 0.08, (Drouard et al. 1953)

上产充毛大睾 Recovery SHEAMGRAI DUAD TONO UNTVEEETTY Influencing factors The effect of the nature of the material The stacking fault energy VsFE,affecting dislocations dissociate,the rate of dislocation climb and cross slip(the mechanisms for controlling the rate of recovery). In metals of low stacking fault energy such as copper,a-brass and austenitic stainless steel,climb is difficult,and little recovery of the dislocation structure normally occurs prior to recrystallization. In metals of high stacking fault energy such as aluminium and a-iron,climb is rapid,and significant recovery may occur. ▣ Solutes may influence recovery by their effect on the stacking fault energy, by pinning dislocations,or by affecting the concentration and mobility of vacancies.Solute pinning of dislocations will both inhibit dynamic recovery, resulting in a higher stored energy than for a solute-free material,and also inhibit static recovery. Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 13
Recovery Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 13 Influencing factors The effect of the nature of the material The stacking fault energy γSFE, affecting dislocations dissociate, the rate of dislocation climb and cross slip (the mechanisms for controlling the rate of recovery). In metals of low stacking fault energy such as copper, α‐brass and austenitic stainless steel, climb is difficult, and little recovery of the dislocation structure normally occurs prior to recrystallization. In metals of high stacking fault energy such as aluminium and α‐iron, climb is rapid, and significant recovery may occur. Solutes may influence recovery by their effect on the stacking fault energy, by pinning dislocations, or by affecting the concentration and mobility of vacancies. Solute pinning of dislocations will both inhibit dynamic recovery, resulting in a higher stored energy than for a solute‐free material, and also inhibit static recovery

上清充通大¥ Recovery SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Recovery kinetics The extent of the recovery(R)was defined in terms of the yield stress of the recovered crystals(o),the yield stress of the as-deformed crystal (om) and the yield stress of the undeformed crystal (oo)as R=(on-o,)/(On-Go) The relationship between the amount of recovery,time and temperature was found,over a wide range of conditions to be R=c Int- kT 里30 The amount of work hardening which is 20 recovered in 3hrs at room temperature in Cu- Al203 crystals oriented for single slip,and deformed at 77K,(Humphreys and Hirsch 1976). 0.05 0.0 0.15 Shear Strain Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 14
Recovery Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 14 Recovery kinetics R mr m 0 The extent of the recovery (R) was defined in terms of the yield stress of the recovered crystals (σ), the yield stress of the as‐deformed crystal (σm) and the yield stress of the undeformed crystal (σ0) as The relationship between the amount of recovery, time and temperature was found, over a wide range of conditions to be 1 ln Q Rc t kT The amount of work hardening which is recovered in 3hrs at room temperature in Cu– Al2O3 crystals oriented for single slip, and deformed at 77K, (Humphreys and Hirsch 1976)
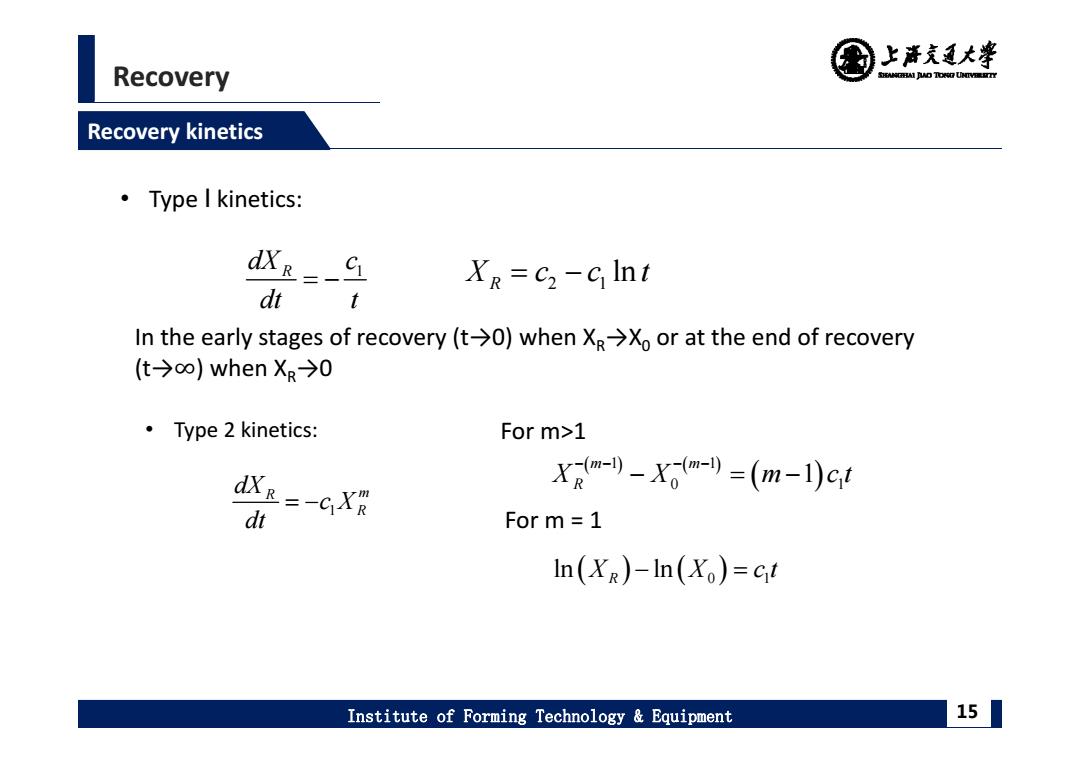
国上清充大¥ Recovery SHEAMGHAI DUD TONO UHTVEREETTY Recovery kinetics 。Type I kinetics: dXr-_C XR=c2-c Int dtt In the early stages of recovery(t->0)when Xg>Xo or at the end of recovery (t-→o)when X.→0 ·Type2 kinetics: For m>1 XR--CXR X君m--Xm-=(m-1)ct d For m=1 In(XR)-In(Xo)=ct Institute of Forming Technology Equipment 15
Recovery Institute of Forming Technology & Equipment 15 Recovery kinetics R 1 dX c dt t • Type Ⅰ kinetics: 2 1 ln X cct R In the early stages of recovery (t→0) when XR→X0 or at the end of recovery (t→∞) when XR→0 • Type 2 kinetics: 1 R m R dX c X dt For m>1 1 1 0 1 1 m m XR X m ct For m = 1 ln ln XR X ct 0 1