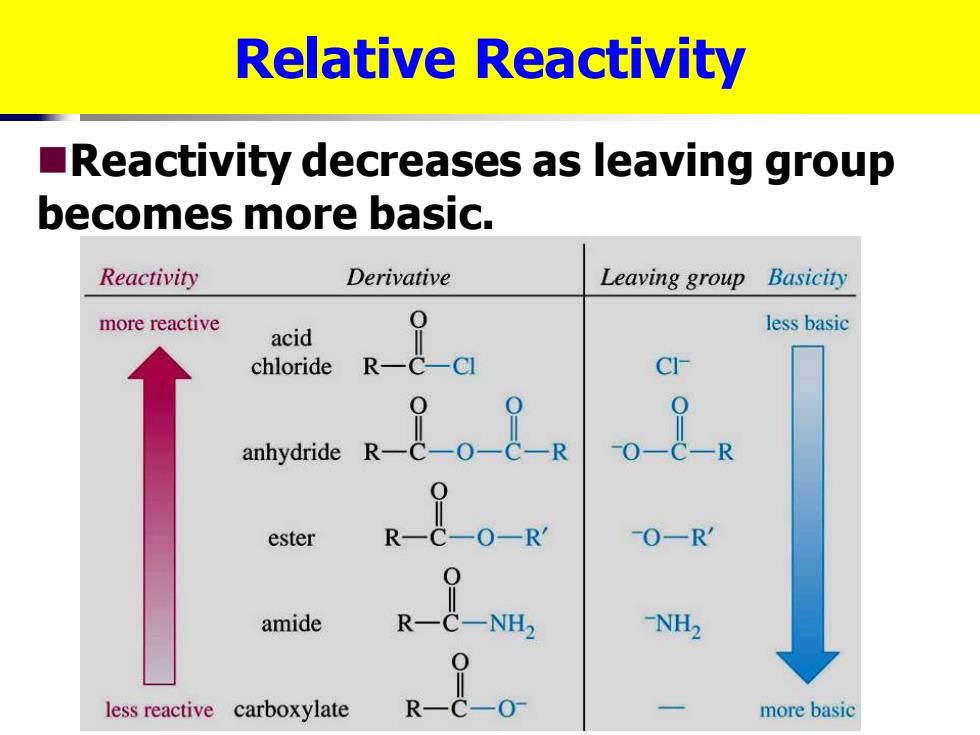
Relative Reactivity Reactivity decreases as leaving group becomes more basic. Reactivity Derivative Leaving group Basicity more reactive less basic acid chloride R anhydride 。8 ester -0-R amide C-NH2 -NH2 less reactive carboxylate R二&0 more basic
Relative Reactivity ◼Reactivity decreases as leaving group becomes more basic
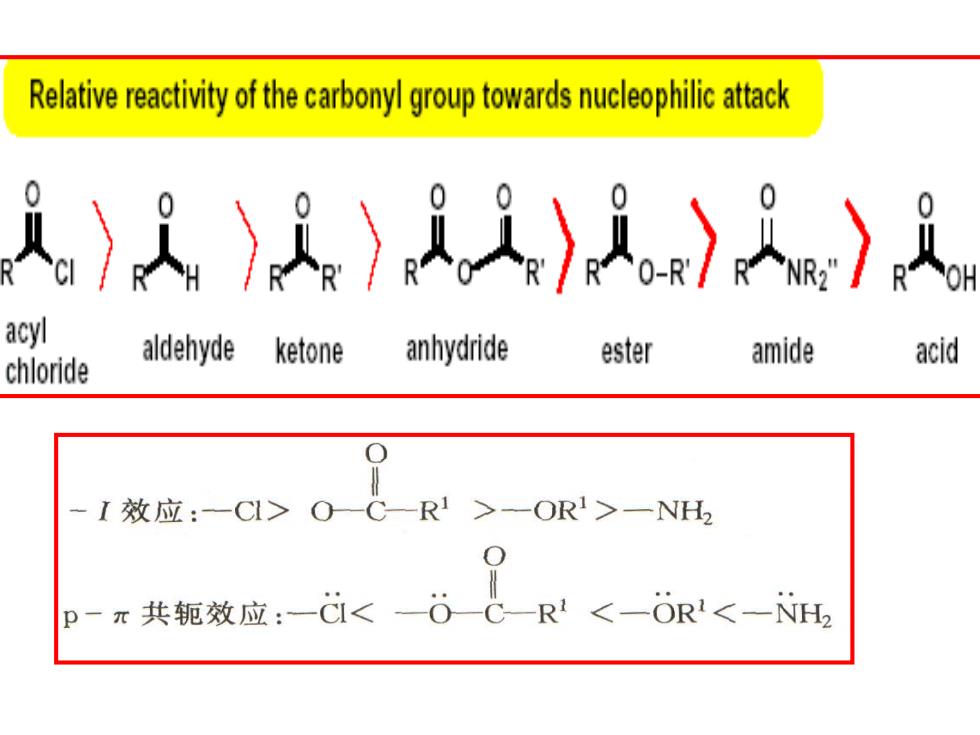
Relative reactivity of the carbonyl group towardsuphilic attack )人A〉)〉) acyl aldehyde ketone anhydride ester amide acid chloride -I效应:-C>OC-R1>-OR>一NH2 p-元共轭效应:-<0CR<一-OR<-NH
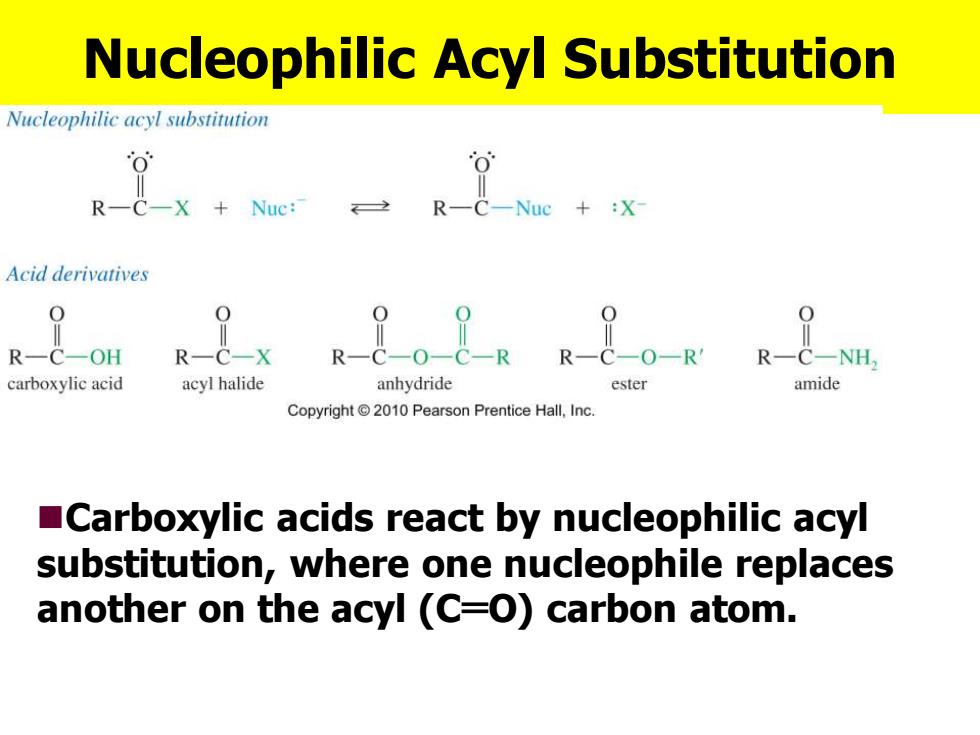
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution Nucleophilic acyl substitution R 一R--Ne+X Acid derivatives R-C-OH R- C-NH, carboxylic acid acyl halide anhydride ester amide Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. Carboxylic acids react by nucleophilic acyl substitution,where one nucleophile replaces another on the acyl (C=O)carbon atom
Nucleophilic Acyl Substitution ◼Carboxylic acids react by nucleophilic acyl substitution, where one nucleophile replaces another on the acyl (C═O) carbon atom
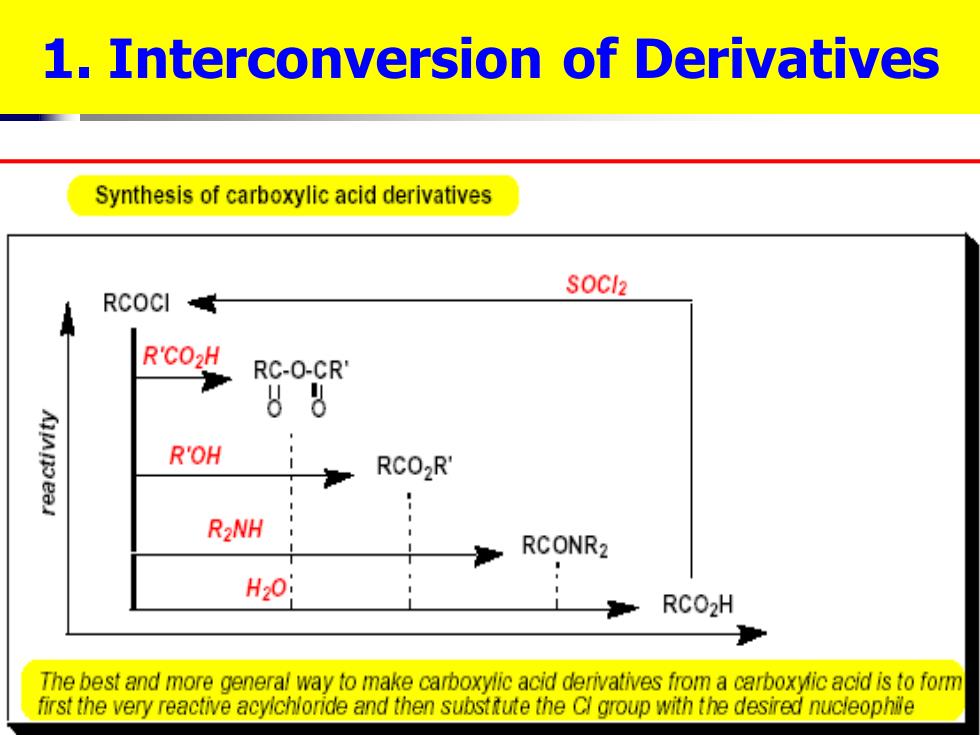
1.Interconversion of Derivatives Synthesis of carboxylic acid derivatives SOCl2 RCOCI R'℃02H RC-O-CR 88 R'OH RCO2R' R2NH RCONR2 H20: RCO2H The best and more general way to make carboxylic acid derivatives from a carboxyic acid is to form first the very reactive acyichloride and then substtute the C group with the desired nucleophile
1. Interconversion of Derivatives

1.Interconversion of Derivatives acid chloride R-C-CI More reactive C-O-CR derivatives can be anhydride converted to less reactive SOCI R-C-OR derivatives. ester amide R-C-NH2 carboxylate RCO
1. Interconversion of Derivatives More reactive derivatives can be converted to less reactive derivatives