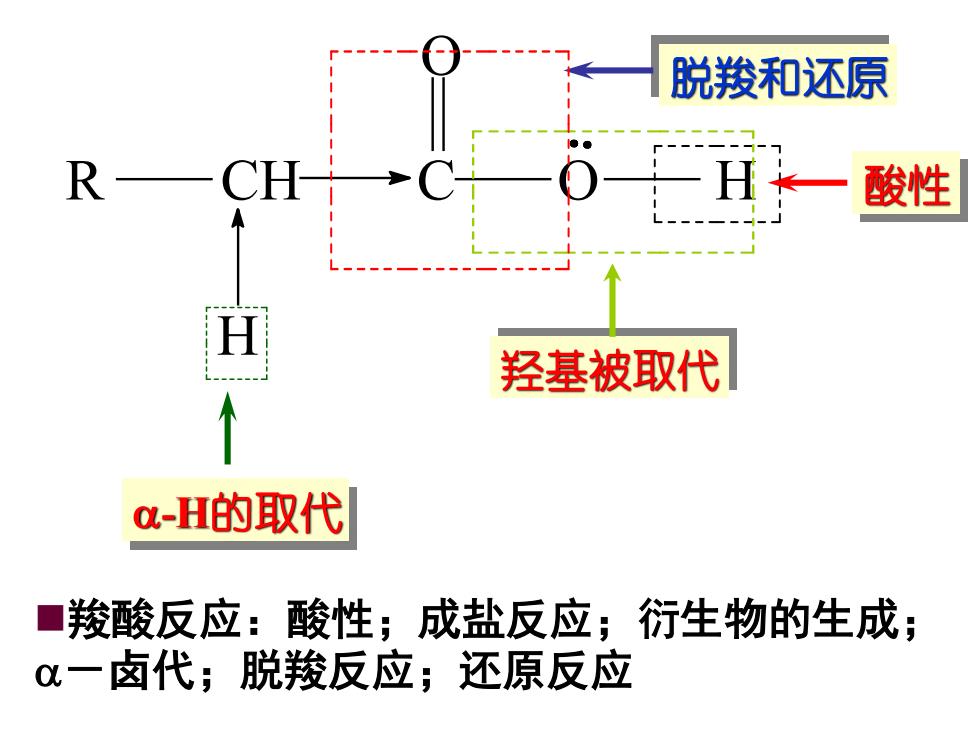
脱羧和还原 R 酸性 羟基被取代 a-H的取代 ■羧酸反应:酸性;成盐反应;衍生物的生成; α一卤代;脱羧反应;还原反应
◼羧酸反应:酸性;成盐反应;衍生物的生成; -卤代;脱羧反应;还原反应 酸性 羟基被取代 脱羧和还原 -H的取代 R CH C O H H O

Acid Derivatives The group bonded to the acyl carbon determines the class of compound: ●-OH,carboxylic acid ●-Cl,acid chloride ●-OR',ester ●-NH2 amide Rex Re08R R8OR R R一C=N RCOX (RCO)2O RCOOR RCONH2 RCN
Acid Derivatives ◼The group bonded to the acyl carbon determines the class of compound: ⚫—OH, carboxylic acid ⚫—Cl, acid chloride ⚫—OR’, ester ⚫—NH2 , amide R C O X R C O O C O R' R C O O R R C O NH2 R C N RCOX (RCO)2O RCOOR RCONH2 RCN
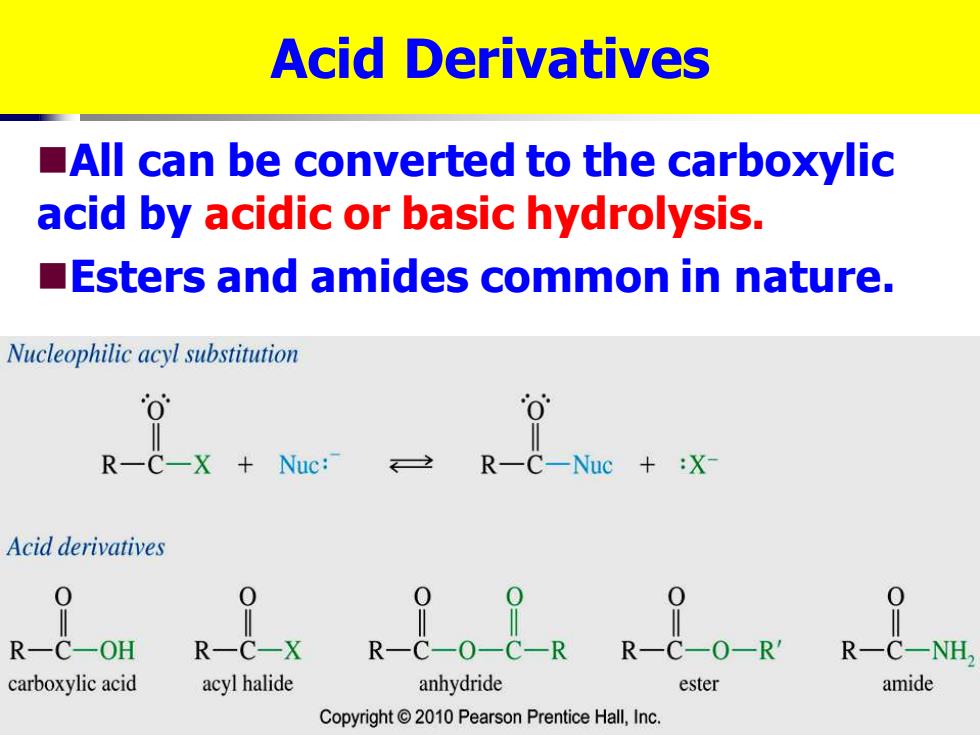
Acid Derivatives All can be converted to the carboxylic acid by acidic or basic hydrolysis. Esters and amides common in nature. Nucleophilic acyl substitution R-C-X Nuc: R-C-Nuc X- Acid derivatives 0 R一C-OH carboxylic acid acyl halide anhydride ester Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc
Acid Derivatives ◼All can be converted to the carboxylic acid by acidic or basic hydrolysis. ◼Esters and amides common in nature
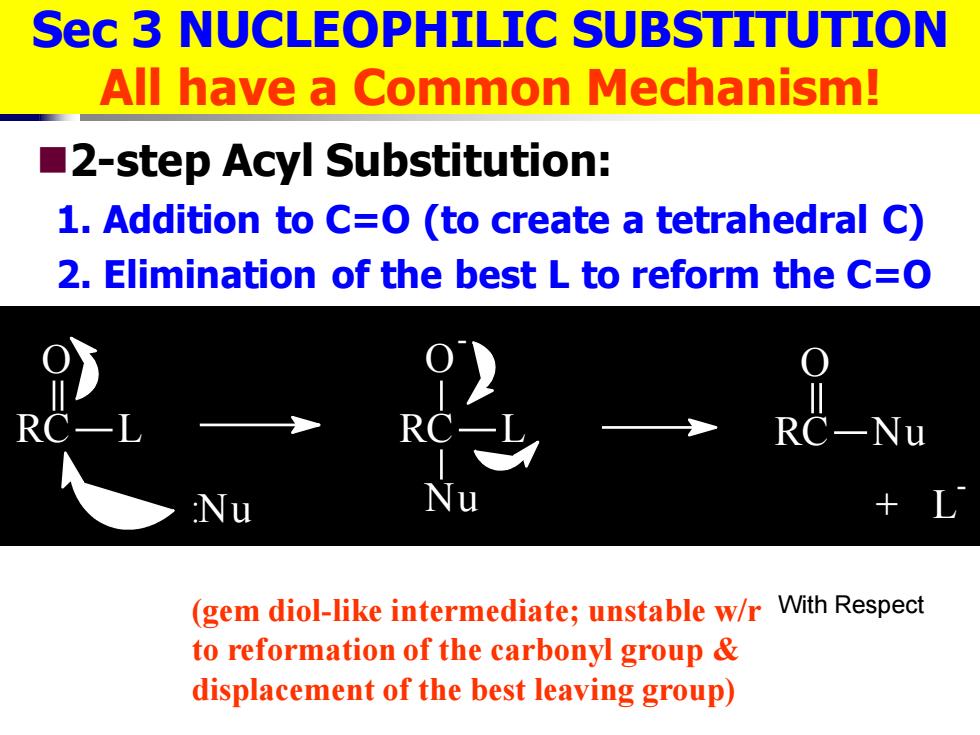
Sec 3 NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION All have a Common Mechanism! 2-step Acyl Substitution: 1.Addition to C=O(to create a tetrahedral C) 2.Elimination of the best L to reform the C=O R Nu (gem diol-like intermediate;unstable w/r With Respect to reformation of the carbonyl group displacement of the best leaving group)
Sec 3 NUCLEOPHILIC SUBSTITUTION All have a Common Mechanism! ◼2-step Acyl Substitution: 1. Addition to C=O (to create a tetrahedral C) 2. Elimination of the best L to reform the C=O RC L O :Nu RC L O - Nu RC Nu O + L- (gem diol-like intermediate; unstable w/r to reformation of the carbonyl group & displacement of the best leaving group) With Respect
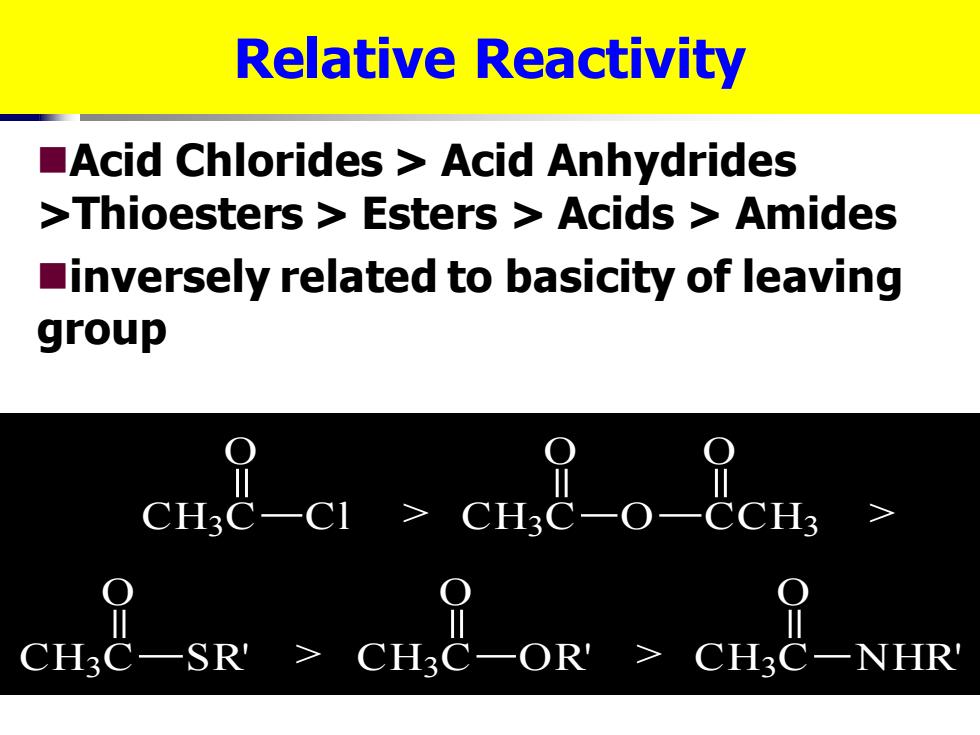
Relative Reactivity Acid Chlorides Acid Anhydrides >Thioesters Esters Acids Amides inversely related to basicity of leaving group cne-cl cue CH3C-SR CHaC-OR'>CH3C-NHR
Relative Reactivity ◼Acid Chlorides > Acid Anhydrides >Thioesters > Esters > Acids > Amides ◼inversely related to basicity of leaving group CH3 C Cl O CH3 C SR' O CH3 C NHR' O CH3 C OR' O CH3 C O O CCH3 O > > > >