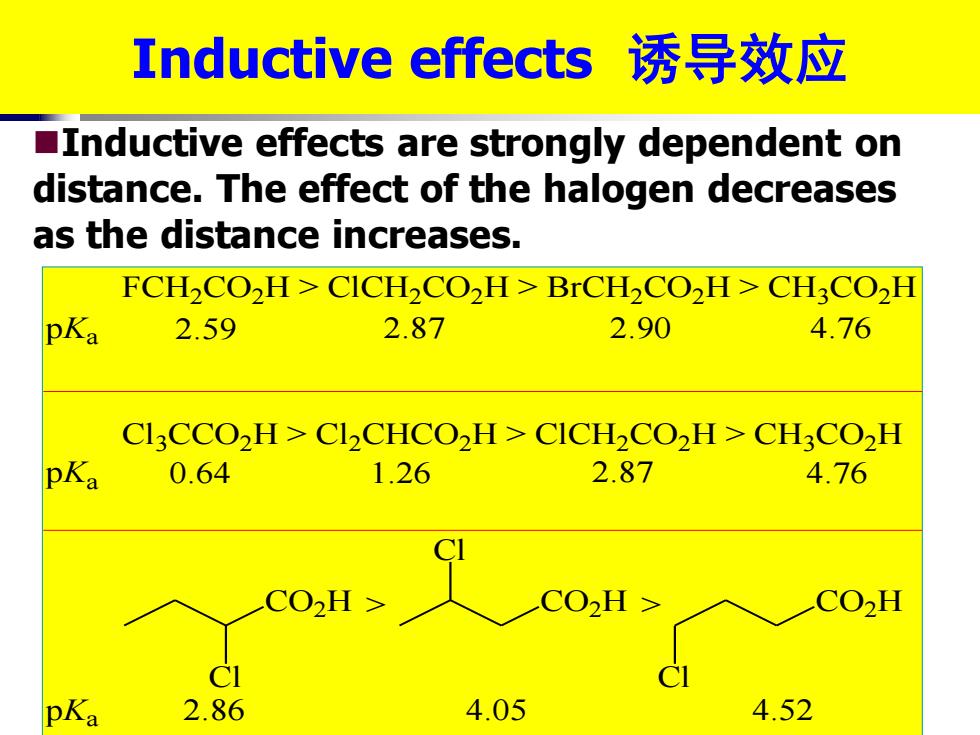
Inductive effects诱导效应 Inductive effects are strongly dependent on distance.The effect of the halogen decreases as the distance increases. FCH2CO2H>CICH2CO2H>BrCH2CO2H>CH3CO2H pKa 2.59 2.87 2.90 4.76 CICCO,H>CICHCO2H>CICH2CO,H>CH3CO2H pKa 0.64 1.26 2.87 4.76 c02H> CO2H> CO2H pKa 2.8 4.05 4.52
FCH2CO2H > ClCH2CO2H > BrCH2CO2H > CH3CO2H Cl3CCO2H > Cl2CHCO2H > ClCH2CO2H > CH3CO2H CO2H Cl CO2H Cl CO2H Cl > > pKa pKa pKa 2.59 2.87 2.90 4.76 0.64 1.26 2.87 4.76 2.86 4.05 4.52 Inductive effects 诱导效应 ◼Inductive effects are strongly dependent on distance. The effect of the halogen decreases as the distance increases
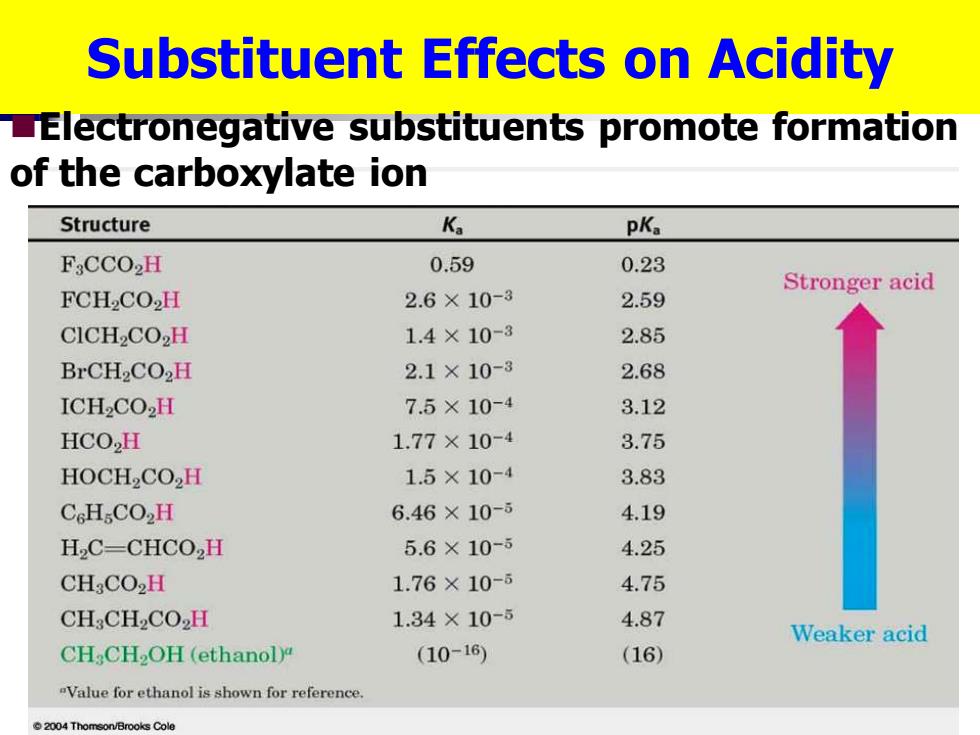
Substituent Effects on Acidity LElectronegative substituents promote formation of the carboxylate ion Structure Ka pKa FsCCO2H 0.59 0.23 Stronger acid FCH2CO2H 2.6×10-3 2.59 CICH2CO2H 1.4×10-3 2.85 BrCH2CO2H 2.1×10-8 2.68 ICH2CO2H 7.5×10-4 3.12 HCO2H 1.77×10-4 3.75 HOCH2CO,H 1.5×10-4 3.83 CcHCO2H 6.46×10-5 4.19 H2C-CHCO,H 5.6×10-5 4.25 CH:CO2H 1.76×10- 4.75 CH:CH2CO2H 1.34×10-5 4.87 Weaker acid CH:CH2OH(ethanoly (10-16) (16) "Value for ethanol is shown for reference 2004 Thomson/Brooks Cole
Substituent Effects on Acidity ◼Electronegative substituents promote formation of the carboxylate ion
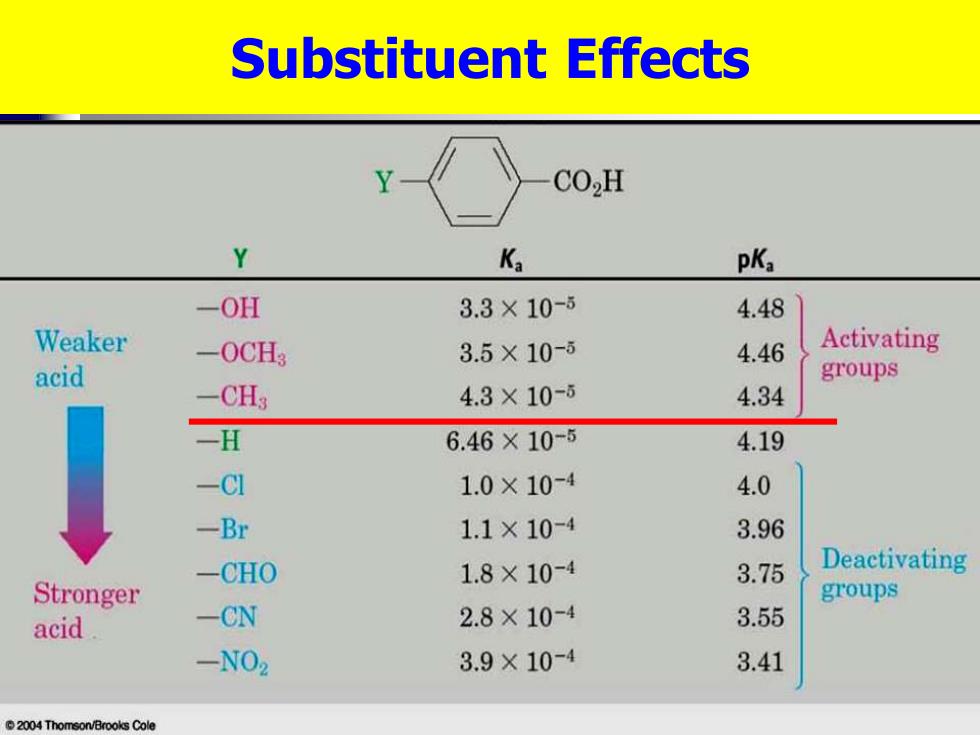
Substituent Effects CO2H Y Ka pK -OH 3.3×10-5 4.48 Weaker -0CH3 3.5×10-6 4.46 Activating acid groups -CH3 4.3×10-6 4.34 -H 6.46×10-5 4.19 -C1 1.0×10-4 4.0 -Br 1.1×10-4 3.96 -CHO 1.8×10-4 3.75 Deactivating Stronger groups acid -CN 2.8×10-4 3.55 -N02 3.9×10-4 3.41 2004 Thomson/Brooks Cole
Substituent Effects
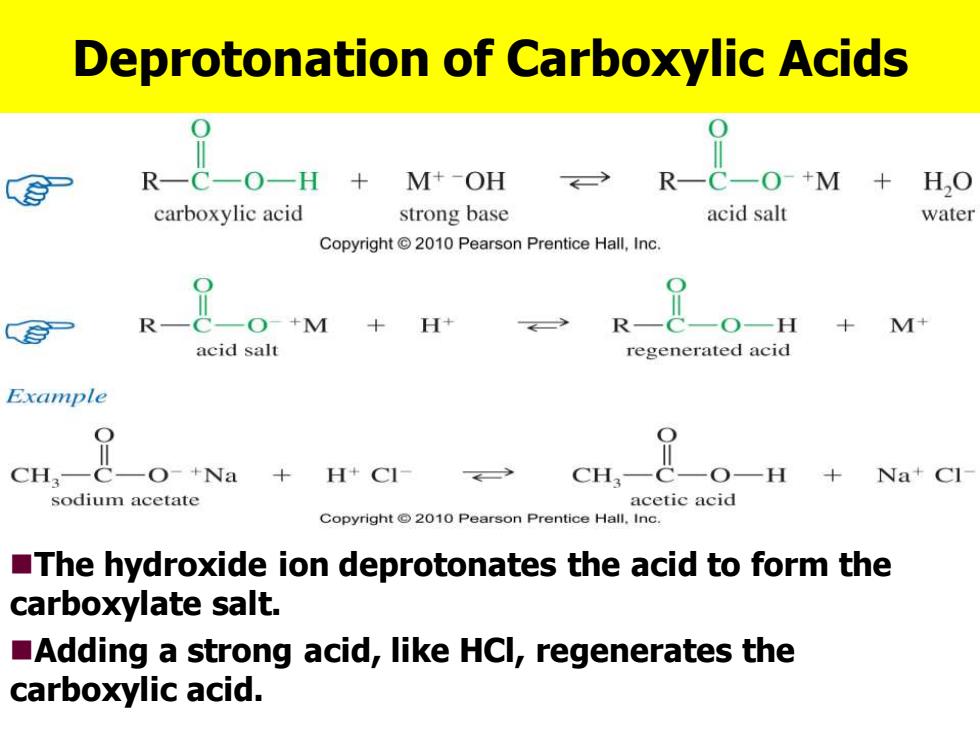
Deprotonation of Carboxylic Acids R-C-O-H M+-OH R-C一O+M HO carboxylic acid strong base acid salt water Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. R-C一O+M+H R-C-O-H +M+ acid salt regenerated acid Example CH.-c-o-+Na +H+CI- cH,-&-0-H +Na+Cl sodium acetate acetic acid Copyright2010 Pearson Prentice Hall.Inc. The hydroxide ion deprotonates the acid to form the carboxylate salt. Adding a strong acid,like HCl,regenerates the carboxylic acid
Deprotonation of Carboxylic Acids ◼The hydroxide ion deprotonates the acid to form the carboxylate salt. ◼Adding a strong acid, like HCl, regenerates the carboxylic acid
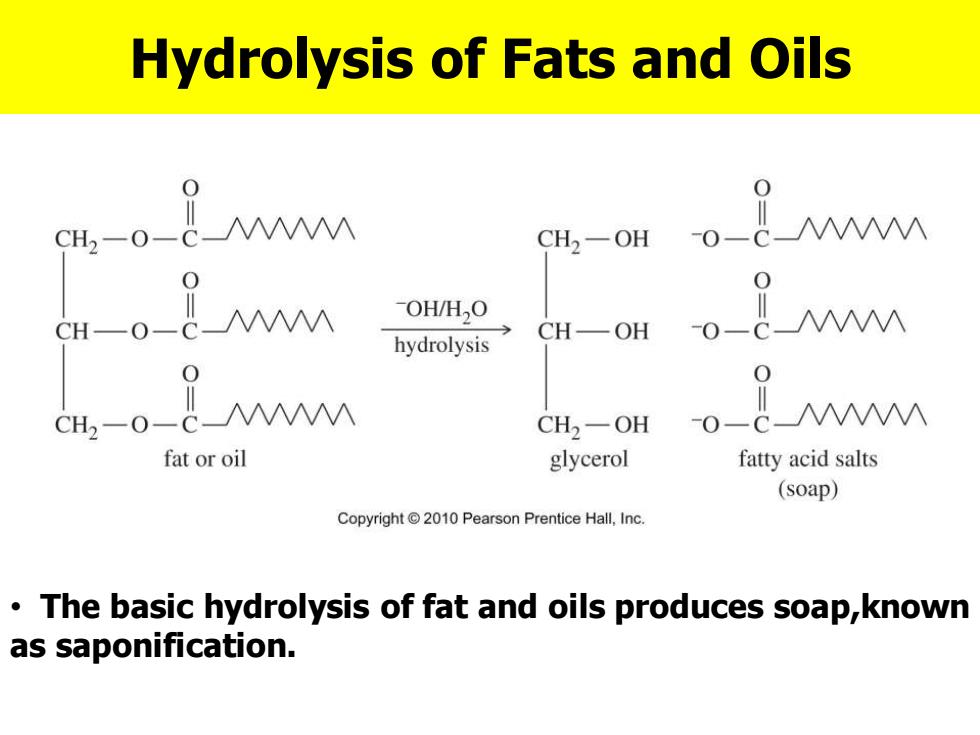
Hydrolysis of Fats and Oils 0 CH2-0-c- CH2-OH -0一 0 CH-0-_M -OH/H,O CH一OH 0 hydrolysis 0 CH2-0-c-M CH2一OH -0-cM fat or oil glycerol fatty acid salts (soap) Copyright 2010 Pearson Prentice Hall,Inc. The basic hydrolysis of fat and oils produces soap,known as saponification
Hydrolysis of Fats and Oils • The basic hydrolysis of fat and oils produces soap,known as saponification