
Telescopes-our eyes on the Universe Nearly all we know of our universe is through observations of electromagnetic radiation,which can be described with four Stokes parameters(i.e.,I,Q,U and V)as the functions of the frequency (v),time (t)and two sky-plane coordinates (a,5) The purpose of an astronomical telescope is to determine the characteristics of this emission,including Angular distribution as a function of I(a,5) Frequency distribution as a function of I(v) Temporal characteristics as a function of I(t) Polarization characteristics:I,Q,U,V Telescopes are sophisticated,but imperfect devices,and proper use requires an understanding of their capabilities and limitations 28
Telescopes – our eyes on the Universe Nearly all we know of our universe is through observations of electromagnetic radiation, which can be described with four Stokes parameters (i.e., I, Q, U and V) as the functions of the frequency (ν), time (t) and two sky-plane coordinates (α,δ) The purpose of an astronomical telescope is to determine the characteristics of this emission, including • Angular distribution as a function of I(α,δ) • Frequency distribution as a function of I(ν) • Temporal characteristics as a function of I(t) • Polarization characteristics: I, Q, U, V Telescopes are sophisticated, but imperfect devices, and proper use requires an understanding of their capabilities and limitations. 28

射电望远镜天线系统组成 >轨道 >座架:方位座架 俯仰机构(俯仰齿轮) 副反射体 >反射体:主反射体 馈源仓 副反射体与其支撑调整机构 与馈源 >馈源仓 俯仰机构 >馈源网络 >伺服控制:天线控制 主反射体 副面控制 方位座架 天线控制 频段切换控制 机房 轨道 29
轨道 座架:方位座架 俯仰机构(俯仰齿轮) 反射体:主反射体 副反射体与其支撑调整机构 馈源仓 馈源网络 伺服控制:天线控制 副面控制 频段切换控制 轨道 方位座架 俯仰机构 主反射体 副反射体 馈源仓 与馈源 天线控制 机房 29 射电望远镜天线系统组成

2012年10月 26日,上海 65米射电望 远镜首次试 观测获得成 功。 10月28日, 落成! 2012/10/25 30
2012年10月 26日,上海 65米射电望 远镜首次试 观测获得成 功。 10月28日, 落成! 30

射电望远镜Radio Telescope/Antenna) ·“the antenna interfaces eon conductors and y in space” 射电波的波长比光学大约5个量级 加工精度比较低,可以制造大口径 天线形状与工作波长及口径有关 米波可用偶极子天线(dipole)或喇叭天线(horn) 厘米波及更短波段通长通常采用抛物面天线(paraboloid 特大的望远镜采用球形(球差)Arecibo 典型的设计是修正的Cassegrain系统 主反射面也偏离真实的抛物面以补偿由于付镜的形状 引入的路径差。 31
射电望远镜 (Radio Telescope/Antenna) “the antenna interfaces e - on conductors and γ in space” 射电波的波长比光学大约5个量级 加工精度比较低,可以制造大口径 天线形状与工作波长及口径有关 米波可用偶极子天线(dipole)或喇叭天线(horn) 厘米波及更短波段通长通常采用抛物面天线(paraboloid) 特大的望远镜采用球形(球差 )Arecibo 典型的设计是修正的Cassegrain 系统 主反射面也偏离真实的抛物面以补偿由于付镜的形状 引入的路径差。 31
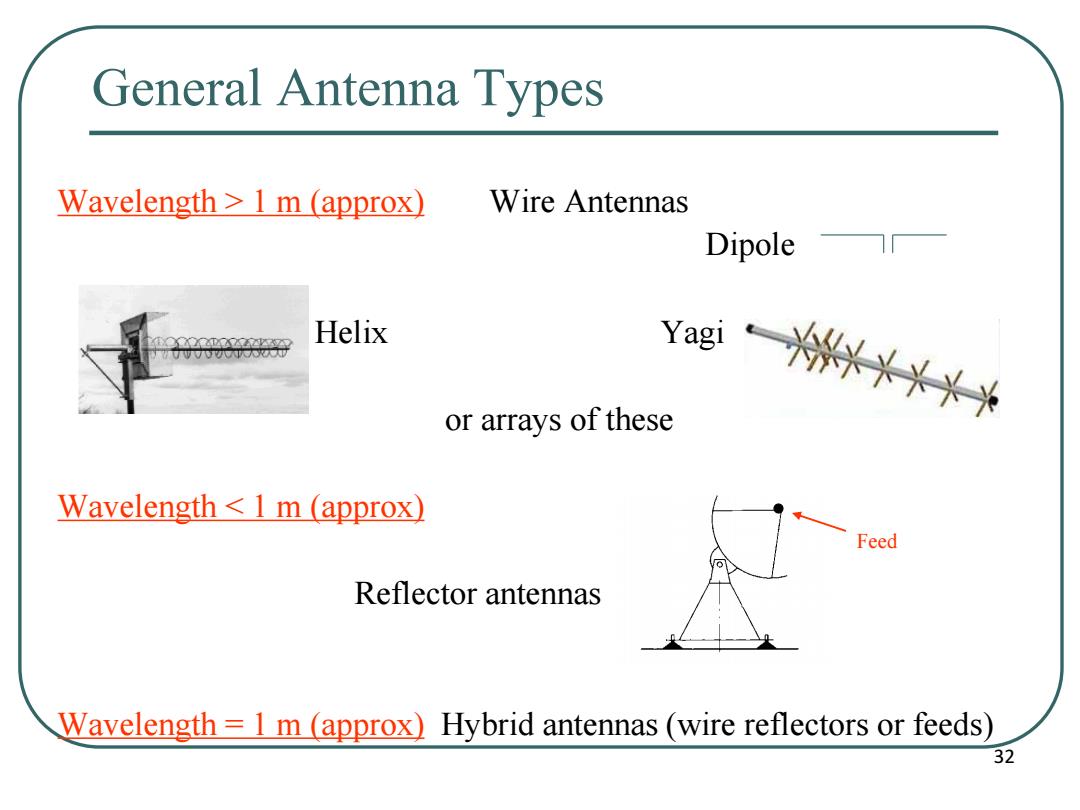
General Antenna Types Wavelength 1 m (approx) Wire Antennas Dipole☐ Helix yag头头X头 or arrays of these Wavelength 1 m (approx) Feed Reflector antennas Wavelength =1 m (approx)Hybrid antennas(wire reflectors or feeds) 32
Wavelength > 1 m (approx) Wire Antennas Dipole Helix Yagi or arrays of these Wavelength < 1 m (approx) Reflector antennas Wavelength = 1 m (approx) Hybrid antennas (wire reflectors or feeds) Feed General Antenna Types 32