
红外·紫外天文观测 Pillar in NGC 2174 Hubble Space Telescope Visible■WFPC2■2001 Infrared■WFC3/IR■2014 孔旭 中国科学技术大学天文学系
红外 - 紫外 天文观测 孔旭 中国科学技术大学 天文学系
课程内容 Radin Infrared visible ltraviolet (1 amma () 基本知识 waves radiation light 红外天文 紫外天文 课程总结 望远镜台址 研究对象 观测终端 望远镜结构
!"#$ u !"#$ u %&'( u )&'( u *+,- . / 0 1 !"#$% ()*+ !"#&
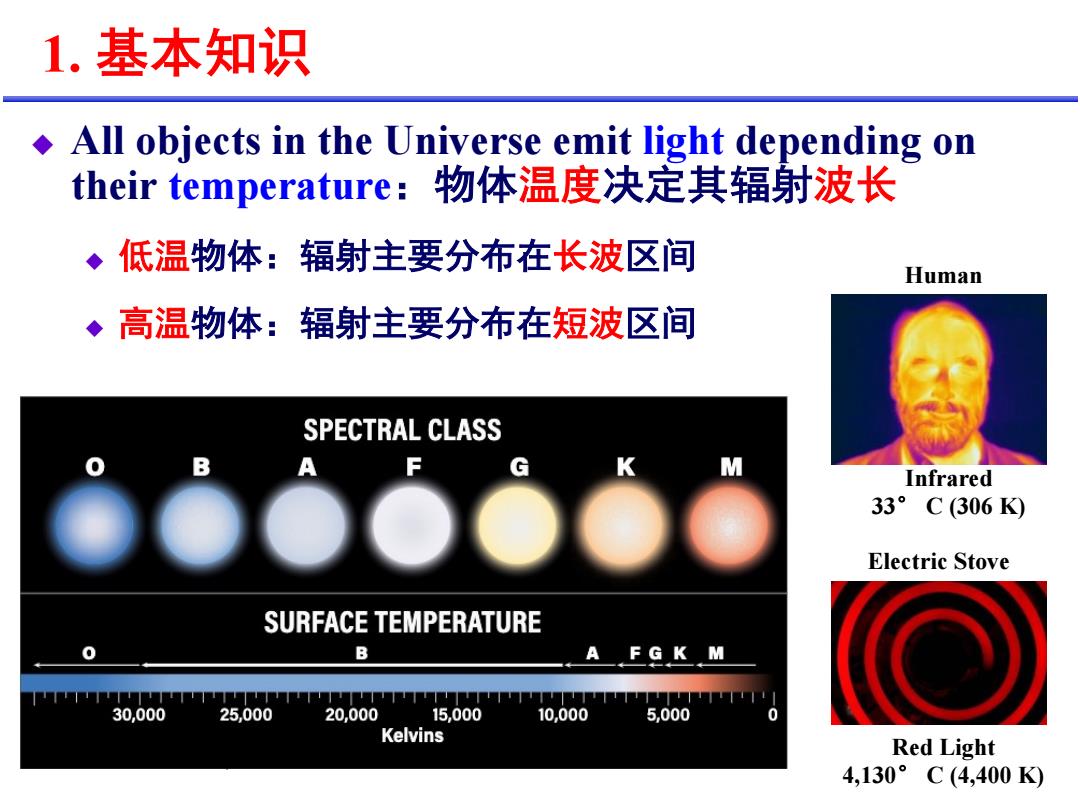
1.基本知识 .All objects in the Universe emit light depending on their temperature:物体温度决定其辐射波长 ◆低温物体:辐射主要分布在长波区间 Human ◆高温物体:辐射主要分布在短波区间 SPECTRAL CLASS Infrared 33°C(306K) Electric Stove SURFACE TEMPERATURE 0 B AFGK M 30,000 25,000 20,000 15,000 10,000 5,000 Kelvins Red Light 4,130°C(4,400K
Infrared 33° C (306 K) Red Light 4,130° C (4,400 K) Electric Stove Human 1. %&'( u All objects in the Universe emit light depending on their temperature,-./01234567 u 23456789:;<=>?@A u B3456789:;<=C?@A
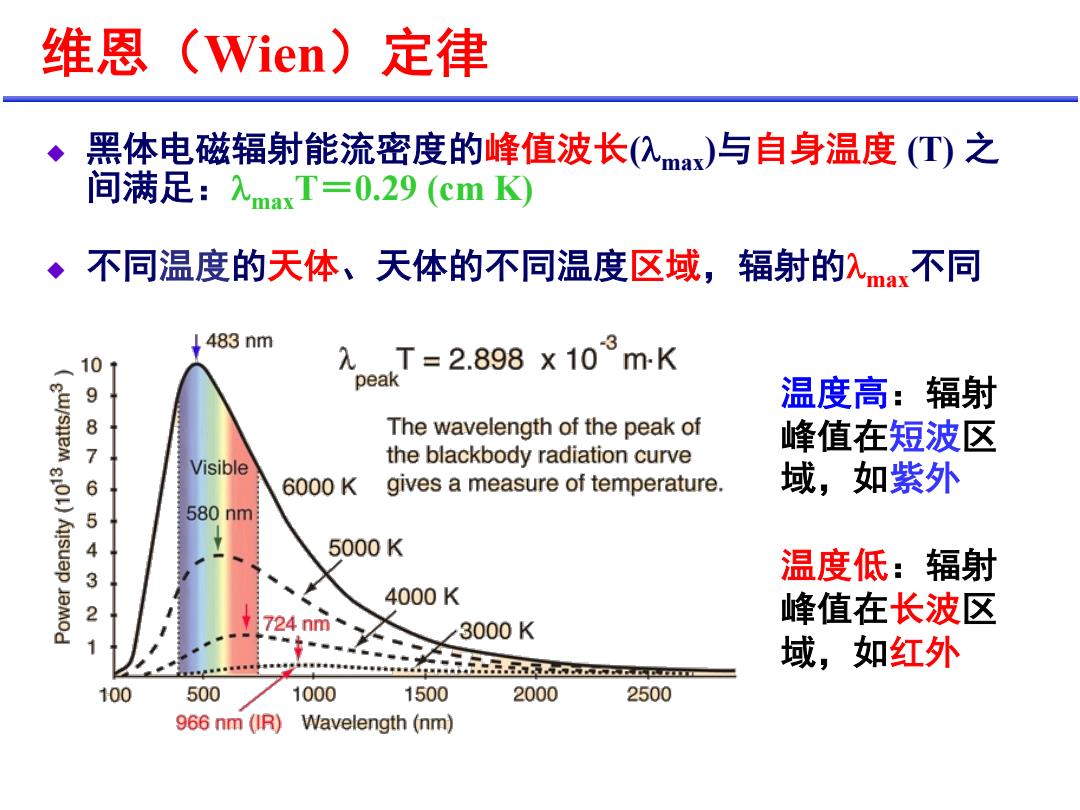
维恩(Wien)定律 黑体电磁辐射能流密度的峰值波长(入ma)与自身温度(T)之 间满足:maxT=0.29(cmK) 不同温度的天体、天体的不同温度区域,辐射的入max不同 483nm 10 λT=2.898x10m-K peak 987 温度高:辐射 The wavelength of the peak of 峰值在短波区 Visible the blackbody radiation curve 6 6000K gives a measure of temperature. 域,如紫外 5 580nm 4 5000K 3 温度低:辐射 4000K 2 724nm 峰值在长波区 3000K 2a 域,如红外 100 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 966nm(0R) Wavelength(nm)
)*+Wien,-. u D5EF78GHIJKLM?>(lmax)NOP3J (T) Q ARS6lmaxTT0.29 (cm K) u UV3JK'5W'5KUV3J@XY78KlmaxUV 3JB678 LM=C?@ XYZ)& 3J2678 LM=>?@ XYZ%&

Visible (VLT] Infrared Combined Protostellar Jet in BHR 71 Dark Cloud Spitzer Space Telescope.IRAC NASA JPL-Caltech T.Bourke [Harvard-Smithsonian CfA) sig07-005 An object can look radically 分子云BHR71:光学波段显示为暗云, different depending on the type of 而红外波段显示暗云内,年轻的恒星 light collected from it 正在形成
!"#BHR71$%&'()*+,#- ./0'()*,#1-23456 789: An object can look radically different depending on the type of light collected from it