
® 嵌入式操作系统 李曦 llxx@ustc.edu.cn
嵌入式操作系统 李曦 llxx@ustc.edu.cn

内容提要 恩 ·嵌入式操作系统概述 -嵌入式操作系统体系结构 一典型的嵌入式操作系统 ·RTOS基本概念 一编程模型 ·RTOS内核功能 ·RTOS的性能指标 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 2/94
内容提要 • 嵌入式操作系统概述 – 嵌入式操作系统体系结构 – 典型的嵌入式操作系统 • RTOS基本概念 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 2/94 – 编程模型 • RTOS内核功能 • RTOS的性能指标

Requirements for Embedded Software Development Increasingly large and complex programs o Rapid technological progress and shortened development periods Demand for reduced development cost In Home In Mobile In Offices and Appliances: Devicas: Factorles: Portsble videogame Parsoral compucers Diottal appliances w家 nSutrlal mecea DVD recordersiplayers Stereo syslams Q日laC排i球表 PPCa Ae conditioners Mobile phon的 Toleghone sets Voice rucoedan Fax machn线s PDAs Home vidsogam machines atc Printers Selar powir systams In Automobiles Car navigat0n雪yst0m3 In-veeicle mistimadin in Infrastructure: 5与:5toms Eeclronic toll cotlclion Wn时poer,amm m楼 Tramsportation mellcent trinspo国 ystoms
Requirements for Embedded Software Development • Increasingly large and complex programs • Rapid technological progress and shortened development periods • Demand for reduced development cost

嵌入式操作系统 ·在本质上与通用的操作系统没有大的区别 一用于手机、PDA等电子类消费产品、机顶盒、路由器等 ·对嵌入式系统的硬件有较高的要求 ·OS体系结构向微内核方向发展 -可伸缩、可移植、可剪裁、可配置 ·许多嵌入式操作系统不划分“系统空间”和“用户 空间”(?!) 操作系统的“内核”与外围应用程序之间不再有物理的 边界,采用静态连接; -系统中所谓“进程”实际上全都是内核线程 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 4/94
嵌入式操作系统 • 在本质上与通用的操作系统没有大的区别 – 用于手机、PDA等电子类消费产品、机顶盒、路由器等 • 对嵌入式系统的硬件有较高的要求 • OS体系结构向微内核方向发展 –可伸缩、可移植、可剪裁、可配置 llxx@ustc.edu.cn 4/94 –可伸缩、可移植、可剪裁、可配置 • 许多嵌入式操作系统不划分“系统空间”和“用户 空间”(?!) –操作系统的“内核”与外围应用程序之间不再有物理的 边界,采用静态连接; –系统中所谓“进程”实际上全都是内核线程
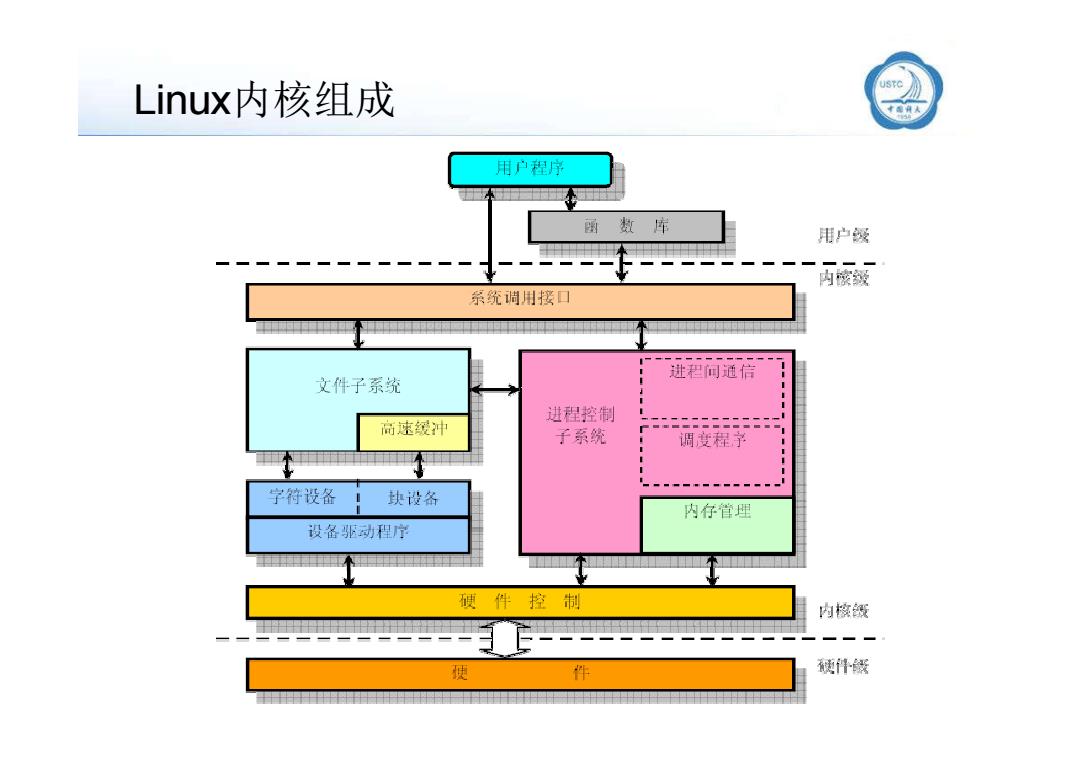
Linux内核组成 用户程序 函 数库 用户餒 丙酸致 系统诮用接口 进君问通信 文件子系统 进程控制 高速缓冲 子系统 ◆N 调度程予 字符设备 块设备 内存管理 设备驱动程 硬件 控制 内核蹑 一2- 瘦 件 便件锈
Linux内核组成