
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 11 10.2 Ion activities the chemical potential of a solute in a real solution is related to its activity a by μ += lnaRT o μ 1) The definition of activity o = γ / bba If the activity is related to the molality, b, then the standard state is a hypothetical solution with molality =1 mol kg-1 in which the ions are behaving ideally. ob
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 11 10.2 Ion activities the chemical potential of a solute in a real solution is related to its activity a by μ += lnaRT o μ 1) The definition of activity o = γ / bba If the activity is related to the molality, b, then the standard state is a hypothetical solution with molality =1 mol kg-1 in which the ions are behaving ideally. ob

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 12 where the activity coefficient, γ, depends on the composition, molality, and T of the solution. As the solution approaches ideality at low molalities, the activity coefficient tends towards 1: → → bbba →0 as / and 1 o γ 10.2 Ion activities 1) The definition of activity o = γ / bba
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 12 where the activity coefficient, γ, depends on the composition, molality, and T of the solution. As the solution approaches ideality at low molalities, the activity coefficient tends towards 1: → → bbba →0 as / and 1 o γ 10.2 Ion activities 1) The definition of activity o = γ / bba

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 13 Because all deviations from ideality are carried in the activity coefficient, the chemical potential can be written μ μ ++= RTbRT lnln γ o where μideal is the chemical potential of the ideal-dilute solution of the same molality. ln γ ideal μ += RT 10.2 Ion activities
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 13 Because all deviations from ideality are carried in the activity coefficient, the chemical potential can be written μ μ ++= RTbRT lnln γ o where μideal is the chemical potential of the ideal-dilute solution of the same molality. ln γ ideal μ += RT 10.2 Ion activities

版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 14 If the chemical potential of a univalent cation M+ is denoted μ+ and that of a univalent anion X- is denoted μ- , the total Gibbs energy of the ions in the electrically neutral solution is the sum of these partial molar quantities. The molar Gibbs energy of an ideal solution is 2) Mean activity coefficients ideal ideal ideal Gm + += μμ − 10.2 Ion activities
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 14 If the chemical potential of a univalent cation M+ is denoted μ+ and that of a univalent anion X- is denoted μ- , the total Gibbs energy of the ions in the electrically neutral solution is the sum of these partial molar quantities. The molar Gibbs energy of an ideal solution is 2) Mean activity coefficients ideal ideal ideal Gm + += μμ − 10.2 Ion activities
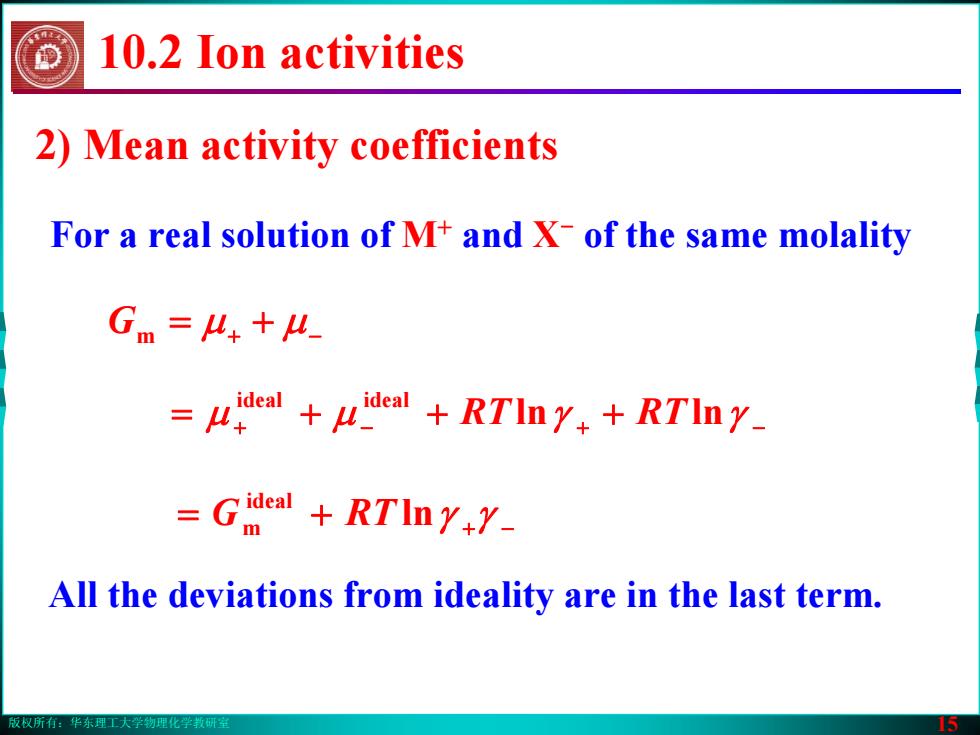
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 15 All the deviations from ideality are in the last term. 2) Mean activity coefficients Gm += μμ −+ + − ++= + + − μμ lnγ lnγ ideal ideal RT RT += −+ ln γγ ideal m RTG For a real solution of M+ and X- of the same molality 10.2 Ion activities
版权所有:华东理工大学物理化学教研室 15 All the deviations from ideality are in the last term. 2) Mean activity coefficients Gm += μμ −+ + − ++= + + − μμ lnγ lnγ ideal ideal RT RT += −+ ln γγ ideal m RTG For a real solution of M+ and X- of the same molality 10.2 Ion activities